Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era (95 page)
Read Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era Online
Authors: James M. McPherson
Tags: #General, #History, #United States, #Civil War Period (1850-1877), #United States - History - Civil War; 1861-1865, #United States - History - Civil War; 1861-1865 - Campaigns

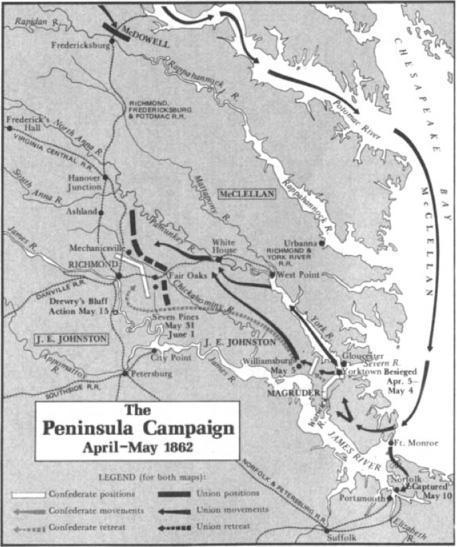
With 1,200 picked men he rode north from Richmond on June 12 and swung east across the headwaters of the Chickahominy, brushing aside the small enemy patrols he encountered. Stuart's progress was helped by the fragmented organization of Union cavalry, which was sprinkled by companies and regiments throughout the army instead of consolidated into a separate division as the southern cavalry was. Stuart's troopers discovered the location of Fitz-John Porter's 5th Corps, which McClellan had kept north of the Chickahominy while transferring the rest of the army to the other side. Stuart had accomplished his mission. But he knew that by now the enemy was swarming in his rear. To return the way he had come would invite trouble. To continue on, to make a complete circuit around McClellan's army, might foil the pursuit. Besides, it would be a glorious achievement. In his mind Stuart could already see the headlines. He pushed on, winning skirmishes, capturing 170 enemy soldiers and nearly twice as many horses and mules, destroying wagonloads of Union supplies, traveling day and night over byways guided by troopers who had grown up in these parts, and crossed the swollen Chickahominy on an improvised bridge which the rebels burned behind themselves minutes before pursuing Union cavalry reined up impotently on the north bank. Stuart's horsemen evaded further clashes and completed the circuit to Richmond by June 16, four days and a hundred miles after setting out. This exploit won Stuart all the acclaim he could have desired. He also gained great personal satisfaction from the enterprise, for one of the opposing cavalry commanders was his father-in-law, Philip St. George Cooke, a Virginian whose decision to remain loyal to the Union had vexed Stuart. "He will regret it but once," Jeb had vowed, "and that will be continuously."
8
Lee had the information he needed. And he knew whom he wanted to lead the attack: Jackson. He would bring Jackson's army secretly from the Valley to hit Porter's corps on the flank while three divisions of the Richmond army crossed the Chickahominy and simultaneously attacked its front. The danger in this, of course, was that while Lee concentrated 60,000 men against Porter's 30,000 north of the Chickahominy, the 75,000 bluecoats south of the river might smash through the 27,000 Confederates on their front and walk into Richmond. But Lee had already taken McClellan's measure. The Union commander, as usual, believed himself outnumbered south as well as north of the Chickahominy.
All this time McClellan was sending a steady stream of telegrams to Washington explaining why he was not quite ready to launch his own offensive: the roads were too wet; his artillery was not all up; it took time to reorganize the divisions crippled in the Seven Pines/Fair Oaks fighting, and to incorporate the one division of reinforcements finally received from McDowell; and when, asked McClellan, was the rest of McDowell's corps going to join him? By June 24, McClellan had penetrated the rebel smokescreen to learn of Jackson's approach; on June 25 he wired Stanton: "The rebel force is stated at 200,000, including Jackson [it was actually less than 90,000] . . . I shall have to contend against vastly superior odds. . . . If [the army] is destroyed by overwhelming numbers . . . the responsibility cannot be thrown on my shoulders; it must rest where it belongs."
9
Lee attacked next day, June 26, the second day of what became known as the Seven Days' battles.
10
The fighting began inauspiciously for the rebels. Lee's plan called for Jackson to hit Porter's flank early in the morning. The sun passed the meridian while the silence continued and Lee fretted in frustration. Where was Jackson? Unable to wait longer, the impulsive A. P. Hill sent his division forward in a late-afternoon assault against an equal number of Federals (16,000) entrenched behind
8
. Foote,
Civi1 War
, I, 472.
9
.
O.R
., Ser. I, Vol. 11, pt. 1, p. 51.
10
. On June 25, Union forces reconnoitering near Seven Pines had clashed with Confederates in a large skirmish that produced about 500 casualties on each side. This action at Oak Grove was subsequently recorded as the first day of the Seven Days' battles.
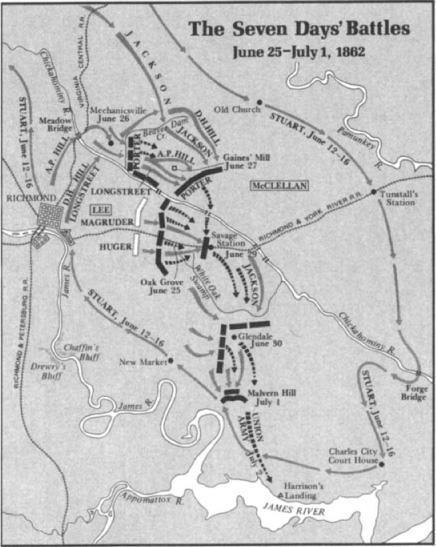
Beaver Dam Creek near Mechanicsville, about six miles northeast of Richmond. The result was a slaughter: nearly 1,500 rebels killed and wounded by Yankees who suffered only 360 casualties. All this time Jackson's three divisions were only a few miles to the north, but their commander made no effort to hasten to Hill's aid.
No single explanation for Jackson's lethargy is satisfactory. Union cavalry had harassed his advance. Northern axemen had felled trees across the road and burned bridges across creeks. But Jackson's foot cavalry had brushed this sort of thing aside in the Valley; why did it slow them now? The best answer seems to be exhaustion: the weariness of men who had endured the bone-jarring start-and-stop travel on southern railroads followed by marching in unaccustomed lowland heat before they had recovered from the exertions of their Valley campaign; and more significantly the weariness of Jackson, a man who seemed to need more than an average amount of sleep but had enjoyed only a few hours of rest during the past several days after six weeks of strain in the Valley. Jackson was probably suffering from what today would be called stress fatigue. Intolerant of weakness in others, he refused to recognize it in himself or to do anything about it—except to collapse into unscheduled naps at crucial times during the Seven Days' fighting.
11
Despite having won what he described as a "complete victory" at Mechanicsville, McClellan had no thought of going over to the offensive. Aware of Jackson's arrival near his right flank, he instructed Porter on the night of June 26–27 to fall back four miles to an even stronger position on the high ground behind Boatswain's Swamp, near Gaines' Mill. Believing that his rail supply line north of the Chickahominy was threatened by the Confederate drive against his right, McClellan also decided to shift his base and all of his supplies to the James River on the south side of the Peninsula. This meant giving up his original plan of capturing Richmond by a siege and artillery bombardment, for his siege guns could travel overland only by rail and there was no railroad from the James. McClellan thenceforth fought only to protect his retreat, euphemistically called a "change of base." Thus while the battle of Mechanicsville had been a tactical defeat for the South, it turned out to be a strategic victory. It accomplished Lee's first goal of dislodging
11
. For good discussions of this matter see Douglas Southall Freeman,
R. E. Lee: A Biography
, 4 vols. (New York, 1934–35), II, 578–82; Douglas Southall Freeman,
Lee's Lieutenants:
A
Study in Command
(New York, 1942–44), I, 656–59; Dowdey,
The Seven Days
, 193–202; Tanner,
Stonewall in the Valley
, 358–60.
McClellan's siege operations. It gave the Confederate commander a psychological edge over his adversary—which Lee never yielded. Even though Jackson had failed to attack on June 26, his appearance near the battlefield and his reputation from the Valley gave him the drop on the Yankees once again.
Before Lee could reap the harvest of this advantage, however, he must drive Porter's corps from its rifle pits behind Boatswain's Swamp. This proved costly. The rebel attack on June 27 again suffered from poor coordination between Lee and his division commanders. Lee's plan called for A. P. Hill to attack Porter's center while Longstreet made a feint against the left and Jackson with four divisions assaulted the Union right. If Porter shifted troops to meet Jackson's threat, Longstreet was to convert his feint into an attack and all 55,000 rebels would go forward together against Porter's 35,000. But once more Jackson was slow getting into position and lethargic in attacking. Once again A. P. Hill's division fought almost alone for several hours on a hot afternoon, attacking across a deep ravine and through entangling woods against well-placed Union defenders who punished Hill's brigades.
12
Disjointed assaults by Longstreet and by portions of Jackson's command relieved some of the pressure on Hill. Finally, near sundown, Lee got all his divisions to go forward in concert. In the middle of the line a brigade of Texans commanded by a tall, tawny-bearded, gladiatorial brigadier named John Bell Hood achieved a breakthrough. Pierced in the center, Porter's line collapsed. Fresh Union brigades from across the Chickahominy formed a rear guard and prevented a rout, enabling Porter to get most of his men and guns across the river during the night. Nevertheless, 2,800 bluecoats were captured and 4,000 were killed or wounded. But the Confederate triumph cost Lee close to 9,000 casualties—nearly as many, in six hours of fighting, as the South had lost in two days at Shiloh.
McClellan had sent Porter 6,000 men from the south side of the Chickahominy. The remaining 69,000 Federals on that side had remained quiet during the two days of bloody conflict north of the river. Their officers were transfixed by a repeat performance of Prince John Magruder's theatrics. Left by Lee in charge of 27,000 men holding the line east of Richmond, Magruder had ordered his troops to bristle with aggressive intent. These gray-costumed thespians responded enthusiastically.
12
. In all of the Seven Days', Hill's large division, containing about 15 percent of Lee's army, suffered 21 percent of the southern casualties while Jackson's three divisions, constituting 21 percent of the army, suffered 14 percent of the casualties.
Artillery fired salvos; infantry lined up in attack formations and probed Union defenses; officers with stentorian voices called out orders to imaginary regiments in the woods. Several Union generals took the bait and informed McClellan that the rebels were strong and threatening on their front. The Federals thus missed an opportunity to counterattack with their overwhelming superiority south of the Chickahominy on June 27. Indeed, at 8:00 p.m. McClellan telegraphed Stanton that he had been "attacked by greatly superior numbers" on
both
sides of the Chickahominy!
13
In reality the Army of the Potomac was still in good shape despite the defeat at Gaines' Mill. But McClellan was a whipped man mentally. After midnight he again wired Stanton: "I have lost this battle because my force was too small. . . . The Government has not sustained this army. . . . If I save this army now, I tell you plainly that I owe no thanks to you or to any other persons in Washington. You have done your best to sacrifice this army." That McClellan escaped removal from command after sending such a dispatch was owing to an astonished colonel in the telegraph office, who excised the last two sentences before sending the message to Stanton.
14
As McClellan pulled his army back toward the James River, Lee hoped to hit them in the flank while they were on the move. He improvised a new plan that called for nine Confederate divisions to converge by six different roads against the retreating bluecoats. But poor staff work, faulty maps, geographical obstacles, timid division commanders (especially Magruder and Benjamin Huger), stout Yankee resistance, and—yet again—Jackson's slowness frustrated Lee's efforts. The first failure occurred on June 29 at Savage's Station just three miles south of the Chickahominy. Three Union divisions formed a rear guard there to protect a field hospital and the southward passage of a huge wagon train. Lee ordered Magruder to attack this position from the west while Jackson came down on its right from the north. But Jackson dawdled all day rebuilding a bridge instead of fording the river. Magruder finally went forward alone with less than half of his division. The Yankees repulsed this feeble attack, then withdrew during the night leaving behind 2,500 sick and wounded men (from earlier fighting) and several surgeons who volunteered to share their captivity.
