Being a Teen (10 page)
Authors: Jane Fonda

• Sit down. If you can’t sit behind a table or desk, try crossing one leg over the other.
• Hold a book, notebook, or papers in front of you.
• Move behind a piece of furniture.
• Tie a sweater or sweatshirt around your waist.
• Wear long shirts that can hang outside your pants.
Most erections will just go away unless there is stimulation.
Wet Dreams
As you know by now, males often wake up with erections. This happens when the bladder fills with urine during the night. The pressure from the bulging bladder can stimulate nerves at the base of the penis, causing it to become erect. You may find that you’ve ejaculated during the night in your sleep. The scientific name for this type of ejaculation,
nocturnal emission
, means “nighttime release.” It’s not really accurate, because it can occur anytime that you’re asleep. The usual name for it, “wet dream,” isn’t really accurate, either, because you can ejaculate without dreaming.
Either way, you’ll wake up with sticky semen on your body, pajamas, or bedsheets. If it has dried, it may look like a thin yellowish paste.
Although not everyone has wet dreams, after puberty many males do have them.
Taking Care of Yourself
Because your genitals are outside your body, they require extra attention. Wash your genitals with soap and water, cleaning all the skin folds, every day. Dry thoroughly to avoid getting a fungus, which causes an itchy rash. Fungal infections are very common and can usually be cleared up by “jock itch” products sold in drugstores.
Dry cotton underpants that feel soft to your skin and aren’t too tight are a good idea. Cotton is important because it allows your genitals to breathe and, unlike synthetic fabrics, doesn’t trap bacteria in the genital area.
Athletic Supporters
Boys who play sports often wear athletic supporters, which are also called jockstraps. These are special covers for the penis and scrotum.
For sports like running, some athletic supporters fit like snug jockey shorts and either press your genitals against your body or support them in a sling lining or in soft cups. Others are held in place by actual straps. For some sports, like
football, baseball, basketball, and hockey, athletic programs require jockstraps with hard cups.
You can find athletic supporters in the boys’ and men’s clothing sections and sports sections of department stores, in sporting goods stores, and in some drugstores. To buy one, all you need to know is the size of your waist. Just look on the label for the correct size in inches. Some brands have cups in two sizes, youth and adult.
Like your underwear, your jockstrap should fit as comfortably as possible, without chafing, and should always be kept clean. It’s a good idea to have more than one so that you always have a clean one when you need it.
Other External Signs of Puberty
Okay, we talked about the penis and all its parts and behaviors. Now we’ll discuss the other changes boys experience during puberty and adolescence due to the increase in hormone production.
Voice Changes
Your voice may well have changed and deepened already. Your larynx, which produces your deeper voice, may now have begun to stick out from the front of your neck in a bump called an Adam’s apple.
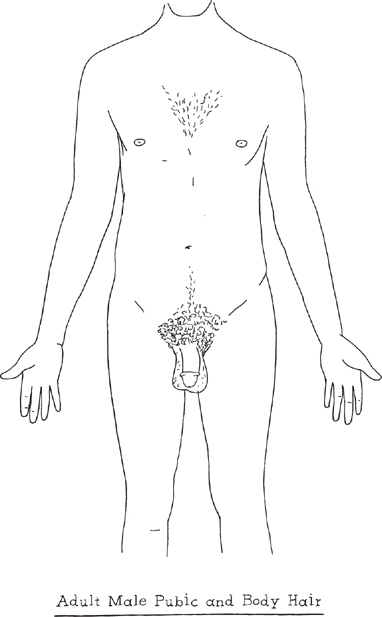
Hair Growth
After your voice changes, your beard may start to grow, usually very slowly for the first few years. Your hair changes, too.
It increases and darkens on your legs, grows under your arms (where you may have more sweat and body odor), and may appear also on your chest, back, abdomen, or shoulders.
The pubic hair around the base of the penis becomes curlier, then turns coarser and darker. As the hair takes on the
color and texture seen in grown men, it starts to form an upside-down triangle.
How much hair a man will have depends on traits inherited from his parents and his ethnic background. Having a lot or almost no hair does not make you more or less masculine.
Facial Hair
Facial hair usually appears on boys at age fourteen or fifteen. Some people might tell you that shaving right away will make your hair come in thicker. That is a myth.
For many boys, starting to shave every day is a big decision. Whether you want to start shaving is entirely up to you. On average, a boy starts shaving sometime between eleven and seventeen years.
If you have curly hair, it might be a good idea to have someone, perhaps a relative or a barber, teach you the best way for you to shave without irritating your face. There are shaving gels made especially for various skin types and ethnicities.
Breasts
As your testosterone levels adjust and settle down, you might develop
gynecomastia.
1
This temporary condition causes your breasts to enlarge and become tender or sore. Your nipples can also enlarge and darken, and you may develop a flat bump that looks like a button under one or both of them. Don’t worry! Gynecomastia occurs in more than half of teenage boys as they go through puberty. It is more common in boys who are overweight or who use a lot of marijuana. Consult your family
doctor if the breast tissue is very firm, painful, has any liquid coming from the nipple, or lasts longer than a few months.
All these changes don’t always happen in exactly the same way, at the same time, for everyone. Depending on what the hormones in your body decide, you may start puberty by developing pubic hair, or underarm hair, or both at the same time.
1
gynecomastia (guy-nuh-co-
mast
-ia)
8.
Changes in Girls’ Bodies That You Can See
Weight Gain
During puberty it is normal not only to grow taller but also to gain weight. This stage lasts about three years, and a girl may gain between thirty-five and fifty-five pounds during this time. Instead of dieting, eat healthily (see
this page
in
Chapter 19
) and stay physically active.
Breasts
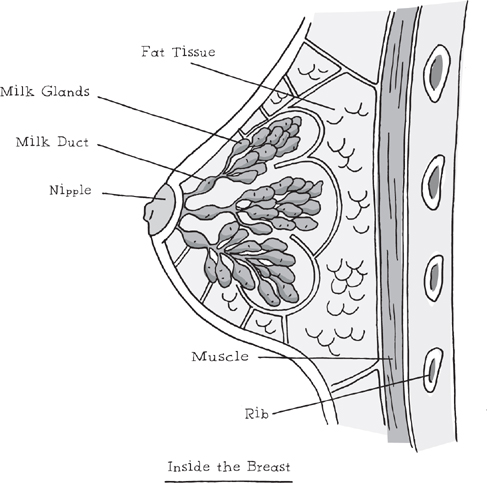
Each breast has a raised nipple, surrounded by a circle of skin of the same color called the
areola.
1
The breasts themselves are made of fat tissue, milk glands, and ducts. After a woman has a baby, the glands will produce milk, which then travels through the ducts to the nipples, each of which has several tiny openings through which the baby can suck the milk.
Sometimes when a nipple is squeezed, a discharge comes out that may look white, clear, or pale yellow-green. Or you may see a little crust around a nipple where fluid came out and dried. Now and then the body makes this fluid to wash out the breast ducts. This is normal.
The nipples and areolae vary in color from light pink to dark brown. Some are quite small and others can be very large, covering almost the entire end of the breast. Nipples are very sensitive and may respond to cold, touch, or sexual feelings by becoming erect. The nipples stiffen and stand up, and the areolae may tighten up and look bumpy. After a while, the nipples return to normal.
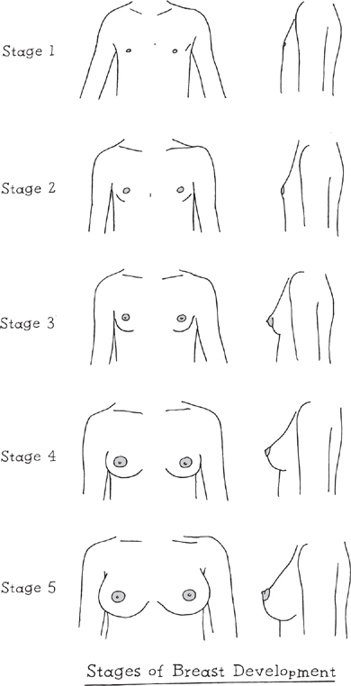
Breast Development
Doctors divide breast growth into five stages.
•
Stage 1: Childhood.
During childhood, breasts are flat. The nipple sticks out from a small areola.
•
Stage 2: Breast Buds.
When puberty begins, breast buds develop. These are raised bumps that start to grow under the nipples. This is normal. Both the nipples and the areolae grow larger and darker. It’s normal sometimes to feel a little tenderness or itchiness in your breasts. This stage can last from several months to over a year.
•
Stage 3: Development.
As the nipples and areolae keep growing and getting darker, breasts, too, grow larger and may look a little pointed. This stage also can last from a few months to a few years.
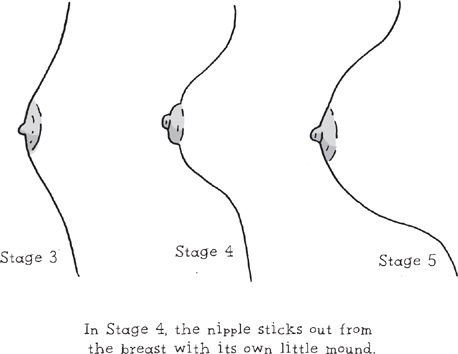
•
Stage 4: Mound.
You may see the nipple and areola blending into a separate mound that sticks out from the breast. It may not happen, or it may happen in the next stage.
•
Stage 5: Adulthood.
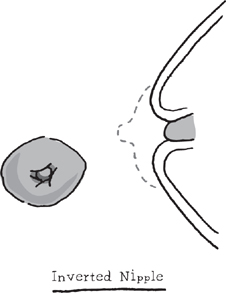
Breasts develop completely, usually with a full, round shape. The areola blends into each breast and may develop a few hairs around its edges. Usually the nipple rises above it, but some women instead have inverted nipples—nipples that go inward.
If inverted nipples develop during puberty, they are normal, and when you have a baby you can breast-feed normally,
so learn how to clean them. You can ask a doctor or medical clinic what to do.
One breast may begin to get larger than the other. Very often, breasts will not grow to be exactly alike—one may be shaped a little differently or hang a little lower. This is normal, just as it’s normal for your hands or eyes or other pairs of body parts each to look a little different.