Extortion (41 page)
Authors: Peter Schweizer

In July 2009, industry representatives met with key members of Congress and hashed out critical details of the new Obama bill.
3
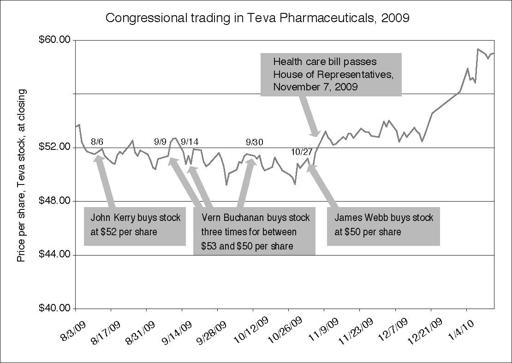
As the bill snaked its way through the House and Senate, where Kerry was actively pushing it, the Kerrys began buying stock in the drug maker Teva Pharmaceuticals as the prospects of its passage improved. In November alone they bought close to $750,000 in the company.
4
When the Kerrys first began buying shares, the stock was trading at around $50. After health care reform passed, it surged to $62. In 2010, after the reform bill was signed, the Kerrys sold some of their shares in Teva, reaping tens of thousands in capital gains. (It’s unclear exactly how much because of the way the transactions are reported. Politicians are required to report ranges only—not exact dollar amounts.) And they held on to more than $1 million worth of Teva shares. All in all, health care stocks proved to be some of the Kerrys’ best investments that year, in terms of return on investment.
To be sure, Senator Kerry wasn’t the only congressional trader in pharmaceuticals. John Tanner of Tennessee, a member of the House Ways and Means Committee, bought up to $90,000 worth back in April 2009, when the House was approving reserve-fund budgeting for health care (part of the annual budget process). Also buying Teva were Senator Jim Webb of Virginia and Congressman Vern Buchanan of Florida. Unlike Kerry and Webb, however, Buchanan voted against the bill. Casting a vote is one thing; betting on the final tally is something else. Most members, most of the time, know full well which bills will pass before they cast their votes. Health care was such an important bill, and the Democrats had such a strong majority (even if Scott Brown’s surprise election in Massachusetts denied them a supermajority of sixty votes in the Senate), that opposing members like Vern Buchanan could still place bets that the bill would eventually get to Obama’s desk.
The very idea that politicians trade stocks while they are considering major bills comes as a shock to many people, but it is standard behavior in Washington. Senator Tom Carper of Delaware sat next to Kerry on the Senate Finance Committee’s Health Subcommittee. Carper, more of a centrist than Kerry, was concerned about the public option. And according to former Senator Tom Daschle, who was a point man in the Obama administration’s push to pass the bill, Carper was intimately involved in hammering together the health care bill throughout the spring, and summer of 2009. By the fall he’d joined a group known as the Gang of Ten, who were trying to bring about a compromise with Republicans.
5
PRIMING THE PUMP
Just a few weeks after three committees had approved health care bills in rapid succession, Carper began buying health care stocks that would benefit from the legislation he was supporting. He bought up to $50,000 in Nationwide Health Properties, a real estate investment trust that specialized in health care—related properties. He also picked up shares in Cardinal Health and CareFusion. (As we will see, Cardinal was a popular investment choice for those involved in the health care debate.)
Congresswoman Melissa Bean of Illinois, a moderate, seemed torn over whether to vote for or against Obamacare. But her indecision didn’t apply to her stock portfolio. Along with her husband, Bean traded shares as she watched the debate unfold in Washington. Indeed, although Bean and her husband are active traders, the
only stock purchases
they made during 2009 were in the health care sector. They bought shares in Cardinal Health, CareFusion, and two drug manufacturers, Mylan and Teva. Bean bought Teva in April at about $46 a share. After Obamacare passed, shares soared to more than $63. She bought Mylan when it traded at $14 a share. After Obamacare became law, it rocketed to $23 a share, up more than 50%.
6
One of the more creative and cynical plays on health care reform came from Congressman Jared Polis of Colorado. Polis is a young politician who had just taken his congressional seat in January 2009. But he was clearly seen as a rising star, with an appointment to the powerful House Rules Committee. He also sits on the House Democratic Steering and Policy Committee and on the Education and Labor Committee’s Subcommittee on Healthy Families and Communities. Polis is wealthy. He grew up amid privilege, and his family became enormously rich after founding and later selling
Bluemountain.com
, the greeting card website.
Throughout 2009, Polis was a tireless advocate for Obamacare, declaring that health care reform “could not come at a better time.” Polis sat on two House committees that were central to the crafting and passage of the health care bill. As a member of the House Education and Labor Committee, he was involved in shepherding through one of the three pieces of legislation that would become the final bill. And as a member of the powerful Rules Committee, he helped shape the parameters and procedures to secure passage of the bill in the House.
None of this gave him pause when it came to investing in health care companies as he helped determine the fate of Obamacare. While Polis was praising the benefits of health care overhaul, he was buying millions of dollars’ worth of a private company called BridgeHealth International.
7
BridgeHealth describes itself as a “leading health care strategic consultancy.” It works with companies to help them cut health care costs. One of the things that BridgeHealth offers is medical tourism: providing less expensive medical procedures in countries such as China, Mexico, India, Thailand, Costa Rica, and Taiwan. In other words, Polis was betting that there would be more, not less, medical tourism after the passage of health care reform. Companies in the medical tourism industry generally agreed, and favored Obamacare. They did not believe the bill would actually contain costs, and if anything, they expected overseas medical procedures to become more attractive.
Medical Tourism
magazine featured an article after the passage of the bill entitled, “Medical Tourism Expands as Alternative to Obamacare.” As the article put it, “Interest in medical tourism has expanded rapidly as Americans react to the new federal law.”
8
After the reform bill became law, BridgeHealth boasted that it was uniquely positioned to help companies cut medical costs. “What we can offer to the employer and insurer is health care reform today because we’ve addressed quality and cost,” Vic Lazzaro, BridgeHealth’s CEO, said in July 2010 after the bill was passed. “This is an opportunity to convert that Cadillac plan to a Buick because you can reduce that cost.”
9
In all, Polis put between $7 million and $35 million into the company as the health care bill wended its way through Capitol Hill. When investment timing was crucial, Polis’s purchases often coincided with the work of his committees. As the Education and Labor Committee considered health care reform in June and July, he made two large purchases of company stock, worth between $1 million and $5 million, on June 16 and 17. His committee passed the health care bill in mid-July. By October 2009, it was Polis’s powerful Rules Committee that was determining which amendments would be considered and what the parameters of the debate would be as the House worked to pass the same legislation that was moving forward in the Senate. On October 13 and 23, Polis made two more purchases of shares worth between $1 million and $5 million. Polis’s office, not surprisingly, insists that his investments had no influence on his vote. (It was all a coincidence!) But people do not make multimillion-dollar investments in a vacuum. And Polis was well positioned to know the details of the massive bill as well as what amendments would or wouldn’t be considered.
Then there is the matter of his biotech investments. The health care reform bill that emerged from Polis’s committees was also enormously beneficial for biotech companies. Embedded in the complex bill were two clauses that were vital for the profitability of these companies. The first was the Therapeutic Discovery Project Credit, which provided a 50% credit for investments in biotech pharmaceutical research. Far more important was the Approval Pathway for Biosimilar Biological Products. The Food and Drug Administration gives traditional branded prescription drugs five years of exclusivity before a generic version of the same medication can be produced. But in this provision, biotech drugs were given a twelve-year exclusivity.
Many observers, like Dr. Jerry Avorn and Dr. Aaron Kesselheim of Harvard University, believed that the twelve-year period was unjustified and that five years was plenty of time. That was the position of the FDA itself.
10
The longer window would, of course, be a boon to biotech investors. As biotech analyst Richard Gayle put it after the law passed, “Biotechnology companies now have a known period of market exclusivity post-approval, one that is independent of patent time frames. This will provide investors with the predictability they crave when they project product sales far into the future for biotech drugs in development.” In the health care bill, he said, the biotech industry “got exactly what it wanted.”
11
Congressman Polis favored the discovery credit and longer-exclusivity provisions. And he made three large purchases of an exchange-traded fund when his committees pushed through the bill. He bought between $750,000 and $1.5 million in the PowerShares Dynamic Biotech and Genome ETF just weeks after the committee proposed to extend the exclusivity period. He bought the fund at about $16 per share. After Obamacare passed, the price jumped to $20, a 25% increase in six months.
How much money did Polis make? We will probably never know. Curiously, having made these aggressive transactions throughout 2009, in January 2010 he suddenly converted his assets to a “qualified blind trust.” As we will see later, these blind trusts are not really blind, and they don’t prevent a politician from providing political intelligence to those who manage the accounts. In Polis’s case, the person handling his trust was a longtime friend and large campaign contributor named Solomon Halpern. By creating the blind trust, Polis no longer had to disclose his stock transactions or profits.
Meanwhile, John and Teresa Heinz Kerry continued to trade. Along with Teva, during 2009 the Kerrys also picked up shares in ResMed—at least $200,000 worth. ResMed makes medical devices such as airway aids for sufferers of sleep apnea. The Kerrys managed to snatch up shares in the $20-to-$25 range. After health care reform passed, shares in the company surged to $34, as much as 71% higher than what the Kerrys paid for them. (Two years later, in the spring of 2011, ResMed’s stock price had fallen back below $30.) ResMed was a winner in the health care reform legislation—as Reuters declared—thanks in part to John Kerry’s efforts. In early versions of the health care bill, device makers like ResMed were to be taxed, starting in 2010, through an “industry fee.” In the final bill, fees for medical device makers were delayed until 2013, and the industry tax was replaced by a smaller sales tax (2.3%). Kerry was a strong opponent of higher taxes on medical device makers.
The Kerrys also bought between $250,000 and $500,000 in Thermo Fisher Scientific, which provides products and services to hospitals and medical centers. The firm had a lot at stake with health care reform. The Kerrys bought the stake at around $35 a share. After the reform bill became law, the stock was selling at more than $50 a share—a jump of more than 40%.
While the Kerrys were buying Obamacare winners, they were dumping losers. In the final bill, pharma was a winner, the health insurance industry was a big loser. Not coincidentally, the Kerrys had been selling all their stock in health insurance companies. One such company, United Health, offers Medicare insurance. The legislation dictated lower reimbursements for Medicare procedures. Lifetime coverage limits and protection against preexisting medical conditions were removed—extremely popular aspects of the bill, to be sure, but they squeezed United Health’s bottom line. By the end of June 2009, the Kerrys had sold all of their shares in United Health. They also dropped their investment in Wellpoint, another health benefits company. Six weeks later, Kerry introduced an amendment to tax generous health care plans, which would clearly hurt companies like those whose stock he had just sold.
12
Kerry’s profitable history of congressional trading does not begin and end with the debate over President Obama’s bill in 2009. Indeed, some of his most dramatic and amazingly well-timed trades occurred earlier, during other health-care-related high-stakes legislative battles. Some of his biggest scores were tied to his knowledge of obscure matters that had huge ramifications for certain companies.
In May 2007, a government agency called the Federal Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services was looking at two drugs that were used to treat anemia in cancer patients. The agency had to decide: Did Johnson & Johnson’s Procrit and Amgen’s Aranesp warrant reimbursement under Medicare? Johnson & Johnson was a large, diversified company with lots of products, so rejection of its drug would not be critical. But for Amgen, losing Medicare reimbursement for Aranesp would be a disaster. The drug was commonly given to elderly cancer patients, many of whom could afford it only under Medicare.
