The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (1531 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
2.61Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Men-shen
(Chin., ‘gods of the doorway’). Deities in Chinese folk religion who protect the doorways of public or private buildings. They appear to have been promoted
euhemeristically
from two generals of the T’ang dynasty, Ch’in Shu-pao and Hu Ching-te. Their fearsome figures are painted on doorposts.
euhemeristically
from two generals of the T’ang dynasty, Ch’in Shu-pao and Hu Ching-te. Their fearsome figures are painted on doorposts.
Menstruation
.
.
The periodic loss of blood from the womb: as such, it has evoked in all religions responses of caution, since blood, connected as it is with life and death, is regarded as potentially threatening, and therefore polluting.
Even in a religion, Christianity, which is supposed to have transcended the detail of the law, the tenacity of this fear has persisted, especially in those parts of the Church dominated by male celibates (e.g. the
Roman Catholic
refusal until very recently, 1992, to allow girl servers into the sanctuary). The dissonance now set up, in law- or custom-based religions, between modern knowledge and religious requirement is an increasing point of stress.
Even in a religion, Christianity, which is supposed to have transcended the detail of the law, the tenacity of this fear has persisted, especially in those parts of the Church dominated by male celibates (e.g. the
Roman Catholic
refusal until very recently, 1992, to allow girl servers into the sanctuary). The dissonance now set up, in law- or custom-based religions, between modern knowledge and religious requirement is an increasing point of stress.
Me’or ha-Golah
:
:
Mercersburg theology
.
.
Movement in American theology in the 19th cent. Its principal figures were John W. Nevin (1803–86) and Philip Schaff (1819–93), colleagues at the German Reformed seminary in Mercersburg, Pennsylvania, from 1844 to 1851. Opposing what Nevin called ‘Puritanic’ in American Protestantism, the movement decried
revivalism
, accorded Christian
tradition
an importance complementary to that of
scripture
, affirmed the
Church
as an article of faith, asserted a
Calvinist
sacramental view of the
eucharist
, and championed
liturgical
worship.
revivalism
, accorded Christian
tradition
an importance complementary to that of
scripture
, affirmed the
Church
as an article of faith, asserted a
Calvinist
sacramental view of the
eucharist
, and championed
liturgical
worship.
Merit
.
.
In Christian thought, the recognition by God that certain works are worthy of reward. In Catholic teaching—deriving ultimately from statements about reward in the New Testament (e.g. Matthew 5. 46; Romans 2. 6; 1 Corinthians 3. 8)—merit has a central place, although it is emphasized that merit
de condigno
(‘of worthiness’) must be acquired in a state of
grace
and with the assistance of actual grace. Protestant theology denies or limits merit as efficacious in salvation: created beings can never establish any claim upon God or earn any reward from him; otherwise salvation is a matter of works and not God's grace. Merit
de congruo
is merit based on equity.
In Buddhism, merit and its transfer form one of the most important parts of the dynamic of society. The acquiring of merit and its transfer to others is an important way in which monks and laypeople interact. For details, see
D
 NA
NA
;
PU
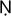 YA
YA
(P
 li, puñña);
li, puñña);
KU
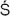 ALA (kusala)
ALA (kusala)
.
Among Jains, there are seven types of activity which are conducive to progress in rebirth (
pu
 yak
yak
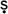 etra
etra
): donating an image, or a building to house an image, paying for the copying of holy texts, giving alms to monks, or to nuns, assisting laymen, or laywomen, in their religious activities or other needs.
de condigno
(‘of worthiness’) must be acquired in a state of
grace
and with the assistance of actual grace. Protestant theology denies or limits merit as efficacious in salvation: created beings can never establish any claim upon God or earn any reward from him; otherwise salvation is a matter of works and not God's grace. Merit
de congruo
is merit based on equity.
In Buddhism, merit and its transfer form one of the most important parts of the dynamic of society. The acquiring of merit and its transfer to others is an important way in which monks and laypeople interact. For details, see
D
 NA
NA;
PU
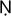 YA
YA(P
 li, puñña);
li, puñña);KU
 ALA (kusala)
ALA (kusala).
Among Jains, there are seven types of activity which are conducive to progress in rebirth (
pu
 yak
yak etra
etra): donating an image, or a building to house an image, paying for the copying of holy texts, giving alms to monks, or to nuns, assisting laymen, or laywomen, in their religious activities or other needs.
Other books
The Other Countess by Eve Edwards
Harvesting Ashwood Minnesota 2037 by Kraack, Cynthia
Return to Mystic Lake by Carla Cassidy
Short Stories 1927-1956 by Walter de la Mare
Forster, Suzanne by Blush
Doom Helix by James Axler
Barbarian Bride by Scott, Eva
The Cowboy's E-Mail Order Bride by Seton, Cora
Hellbent by Priest, Cherie


