The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (571 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
6.73Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
’, a period of dissolution (
pralaya
). It was thus possible that the cosmos arose from infinite space and consciousness, a belief expressed through
Aditi
. In truth, Indian religion accepted that the origin of the cosmos could not be known, but that the conditions of ordered life could be extremely well known. Cosmology lays out the terms for achieving that understanding—cosmology, again, as the arena of opportunity—while remaining agnostic about detail.
There was a greater confidence in cosmography. Vertically, the world was understood to be made up of seven continents (
dvipas
), ranged in circles with intervening oceans around the central point of Mount
Meru
. Vertically, if one takes a cross-section of the Brahm


 a, one finds a series of layers. At the top are the
a, one finds a series of layers. At the top are the
lokas
of the gods and high attainers; next are the planets, sky, and earth; then the underworlds, and finally the twenty-eight
narakas
or hells. See also
CARDINAL DIRECTIONS
.
Jainism and Buddhism
The Indian scepticism about the work of the gods or God in creating this cosmos was taken to a further extreme in both Jainism and Buddhism. The Jains inherited the
triloka
(see
LOKA
), and envisaged it as something like an hour-glass, squeezed in at the middle. Above (
Urdhvaloka
) are a series of heavens of increasing brightness, at the top of which is ‘the slightly curved place’ (
I
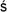 atpragbhara
atpragbhara
) where dwell the liberated and disembodied souls. In the middle is the
Madhyaloka
, which includes the continent inhabited by humans. Below is the
Adholoka
, a series of increasingly terrible hells—from which release is eventually certain, though the intervening time may be unimaginably long.
Buddhism inherited the same basic cosmography, but adapted it greatly. It envisages a series of levels, all of which are open to the process of reappearance: at the summit are the four realms of purely mental rebirth, (
ar
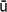 paavacara
paavacara
); below them are the realms of pure form (
r
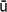 pa-avacara
pa-avacara
), where the gods dwell in sixteen heavens, five of which are known as ‘pure abodes’ (
suddh
 v
v
 sa
sa
), the remaining eleven of which arise out of the jh
 nas (meditational states). Lower still are the sense-desire heavens, including those of the T
nas (meditational states). Lower still are the sense-desire heavens, including those of the T
 vati
vati
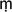 sa gods (the thirty-three Vedic gods, the chief of whom,
sa gods (the thirty-three Vedic gods, the chief of whom,
Indra
, known as Sakka, has become a protector of Buddhism) and of the Tusita gods (where
bodhisattvas
spend their penultimate birth, and in which
Maitreya
now dwells). The world is simply a process, passing through cycles (
kappa
) of immense length.
pralaya
). It was thus possible that the cosmos arose from infinite space and consciousness, a belief expressed through
Aditi
. In truth, Indian religion accepted that the origin of the cosmos could not be known, but that the conditions of ordered life could be extremely well known. Cosmology lays out the terms for achieving that understanding—cosmology, again, as the arena of opportunity—while remaining agnostic about detail.
There was a greater confidence in cosmography. Vertically, the world was understood to be made up of seven continents (
dvipas
), ranged in circles with intervening oceans around the central point of Mount
Meru
. Vertically, if one takes a cross-section of the Brahm


 a, one finds a series of layers. At the top are the
a, one finds a series of layers. At the top are thelokas
of the gods and high attainers; next are the planets, sky, and earth; then the underworlds, and finally the twenty-eight
narakas
or hells. See also
CARDINAL DIRECTIONS
.
Jainism and Buddhism
The Indian scepticism about the work of the gods or God in creating this cosmos was taken to a further extreme in both Jainism and Buddhism. The Jains inherited the
triloka
(see
LOKA
), and envisaged it as something like an hour-glass, squeezed in at the middle. Above (
Urdhvaloka
) are a series of heavens of increasing brightness, at the top of which is ‘the slightly curved place’ (
I
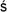 atpragbhara
atpragbhara) where dwell the liberated and disembodied souls. In the middle is the
Madhyaloka
, which includes the continent inhabited by humans. Below is the
Adholoka
, a series of increasingly terrible hells—from which release is eventually certain, though the intervening time may be unimaginably long.
Buddhism inherited the same basic cosmography, but adapted it greatly. It envisages a series of levels, all of which are open to the process of reappearance: at the summit are the four realms of purely mental rebirth, (
ar
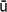 paavacara
paavacara); below them are the realms of pure form (
r
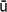 pa-avacara
pa-avacara), where the gods dwell in sixteen heavens, five of which are known as ‘pure abodes’ (
suddh
 v
v sa
sa), the remaining eleven of which arise out of the jh
 nas (meditational states). Lower still are the sense-desire heavens, including those of the T
nas (meditational states). Lower still are the sense-desire heavens, including those of the T vati
vati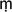 sa gods (the thirty-three Vedic gods, the chief of whom,
sa gods (the thirty-three Vedic gods, the chief of whom,Indra
, known as Sakka, has become a protector of Buddhism) and of the Tusita gods (where
bodhisattvas
spend their penultimate birth, and in which
Maitreya
now dwells). The world is simply a process, passing through cycles (
kappa
) of immense length.
Other books
Age Before Beauty by Smith, Virginia
Claimed by Elizabeth Hendricks
Inherited Magic by Andrew Gordinier
The Young Magician (The Legacy Trilogy) by Foster, Michael
Endless by Tawdra Kandle
Nurse in India by Juliet Armstrong
Chris Powell's Choose More, Lose More for Life by Powell, Chris
The Nine Bright Shiners by Anthea Fraser
Shattered by Natalie Baird
Wall-To-Wall Dead by Jennie Bentley


