The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (993 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
11.94Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
probably have far greater direct influence on the population than the scriptures as such.
The Vedas gave rise to the elaborate ritual instructions and explanations of the texts known as
Br
 hma
hma
 as
as
, and this ritual-based religion is often referred to as brahmanical religion. It gave rise also to reflections on the meanings and implications of the rituals, in the
 ra
ra
 yakas
yakas
and the
Upani
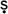 ads
ads
. Based on the consummations of the Veda in
Ved
 nta
nta
, the major forms of philosophical religion were elaborated (see
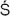 A
A
 KARA
KARA
,
R
 M
M
 NUJA
NUJA
, and
MADHVA
). But philosophical systems had already been established, some of them atheistic or materialist. There are traditionally six ways of orthodox (
 stika
stika
) insight (
dar
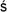 ana
ana
, for list); there is a continuing debate about those which should be considered
n
 stika
stika
(unorthodox: not just, from a Hindu point of view, the obvious aberrations of the Jains and Buddhists, but perhaps also e.g.
S

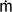 khya
khya
The Vedas gave rise to the elaborate ritual instructions and explanations of the texts known as
Br
 hma
hma as
as, and this ritual-based religion is often referred to as brahmanical religion. It gave rise also to reflections on the meanings and implications of the rituals, in the
 ra
ra yakas
yakasand the
Upani
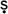 ads
ads. Based on the consummations of the Veda in
Ved
 nta
nta, the major forms of philosophical religion were elaborated (see
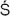 A
A KARA
KARA,
R
 M
M NUJA
NUJA, and
MADHVA
). But philosophical systems had already been established, some of them atheistic or materialist. There are traditionally six ways of orthodox (
 stika
stika) insight (
dar
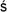 ana
ana, for list); there is a continuing debate about those which should be considered
n
 stika
stika(unorthodox: not just, from a Hindu point of view, the obvious aberrations of the Jains and Buddhists, but perhaps also e.g.
S

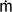 khya
khyaOther books
Mrs. Nixon: A Novelist Imagines a Life by Ann Beattie
The Firefighter Daddy by Margaret Daley
Savage Chains: Captured (#1) by Caris Roane
The Gigantic Shadow by Julian Symons
The Arrangement 21 (The Arrangement #21) by H.M. Ward
A Kind of Grief by A. D. Scott
Rifters 2 - Maelstrom by Peter Watts
The Butchers Funeral: A Medieval Murder by C. M. Harald
Summoning Sebastian by Katriena Knights
Falling For Her Navy Seal…Again by Clarissa Yip
