The Giza Power Plant (7 page)

F
IGURE
7.
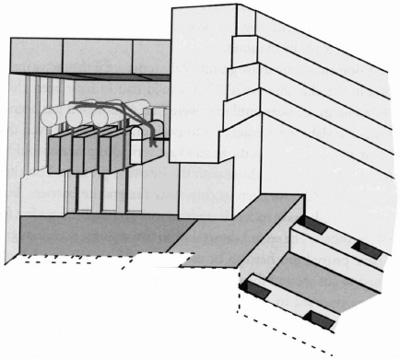
Borchardt's Theory on the Antechamber
Even if a reasonable explanation for the less-than-perfect work in the Antechamber is accepted, the characteristics of the chamber still initiate a great deal of thought. Egyptologist Ludwig Borchardt theorized that this small chamber contained a mechanism that closed off the access to the King's Chamber after the funeral procession made its exit. This was supposedly accomplished by lowering granite slabs, suspended by ropes down the slots located in the east and west walls of the chamber
(see Figure 7).
10
In explaining the "disappearance" of these slabs, Egyptologists claim they were removed by grave robbers. Once again, the poor old grave robber gets the blame! Of course, after digging the tortuous Well Shaft with such remarkable precision, and luckily finding himself in the Grand Gallery, nothing would be impossible for this ingenious thief. Still, what would a grave
robber want with chunks of masonry? What possible value would granite chips have to someone with easy access to an abundance of masonry available on the outside of the pyramid?
In addition, how were those granite slabs removed if they were installed in the slots in the chamber walls? They would had to have been chipped away or lifted up in the slots until they were free. Although it has been conjectured that the slabs were lowered into position by ropes, or even the release of sand, it is unlikely that the means to reverse this process would have been left readily available to those with the intent to plunder. The alternative, therefore, would have been to chip away the granite barriers. But yet again, the remarkable grave robber is credited with accomplishing a feat found impossible by others. The record shows that on two separate occasions granite barriers have proved too hard to be cut away with simple hand tools. Al Mamun had to cut around the granite plugs in the Ascending Passage, and Howard-Vyse resorted to detonating gunpowder charges, for even in his modern time (as compared to the time of Al Mamun), an effective cutting tool for this granite was not available.
It is possible that, if the granite slabs were thin enough, they could have been broken by sheer pressure, but if the slots inside the Antechamber are any indication of the slabs' thickness, they would have been 21.6 inches thick, which is quite a hefty piece of stone. A conveniently located cleavage plane on each of the granite slabs might have enabled the grave robbers to break through, if they were able to apply the necessary pressure to the granite. Nevertheless, the very idea that granite slabs were once in place in the Antechamber is pure speculation. Howeverâdiscounting the previous argument regarding the possibility of grave robbers breaking through to the King's Chamberâwe can still respect the argument laid down by Piazzi Smyth:
These three grand, flat, vertical grooves, then, on either side of the narrow ante-chamber, have been pronounced long since by Egyptologists to be part of a vertical sliding portcullis system for the defense of the door of the King's Chamber. There are no blocks now to slide up and down these grooves, nor have such things ever been seen there: but the gentlemen point triumphantly to a fourth groove, of different order, existing to the north of all the others, indeed near the
north-beginning of the ante-chamber; and with its portcullis block, they say, still suspended, and ready for work.
That alleged block, however, contains many peculiarities which modern Egyptologists have never explained; and as it was first carefully described by Professor Greaves under the appellation of the "granite leaf" (from the so-called "leaf" or "slat" or sliding door over the water-way of a lock-gate in an English navigation canal), we had better keep to that name.
Its groove, instead of being 21.6 inches broad, like the others is only 17.1 broad; and in place of being like them cut down to, and even several inches into, the floor, terminates 43.7 inches above that basal plane; so that the leaf's block, or rather blocksâfor it is in two pieces, one above the otherâstand on solid stone of the walls on either side, and could not be immediately lowered to act as a portcullis, though an Emperor should desire it. Nor would they make a good portcullis if they were to be forcibly pushed, or chiseled down in their vertical plane, seeing that there are 21 inches free end space between the leaf and the north entering wall and doorway, where a man may worm himself in, in front of that face of it ; and 57 inches above the leaf's utmost top, where several men might clamber over; and where I myself sat on a ladder, day after day, with lamps and measuring rods, but in respectful silence and generally in absolute solitude, thinking over what it might
mean.
11
Smyth's meditation on the Antechamber, its granite leaf, and the slots in the east and west walls left him resigned to a conclusion that does not seem to have been improved upon after the passing of a complete century. Writing in 1880, Smyth sagely concluded that "the granite leaf is, therefore, even by the few data already given, a something which needs a vast deal more than a simple portcullis notion to explain it. And so do likewise the three broader empty pairs of grooves to the south of it, remarkable with their semi-cylindrical hollows on the west side of the
chamber."
12
How correct, then, are those theories that explain the existence of the Antechamber? Not very, for none adequately explains the indisputable amount of work that went into making it more than just a simple room with
four walls, floor, ceiling, and two passageways. There must have been a reason for the additional effort expended in cutting the four slots in the chamber walls and installing a granite slab in an immovable position. As we will soon discover, one explanation that does explain the Antechamber is that it had a mechanical function. The evidence is plainly clear if one knows how to read it.
For example, the presence of half-round hollows in the top surface of the granite wainscot definitely suggests that cylindrical objects were at one time suspended across the width of the Antechamber and that these may have been receptacles for bearings, or were the bearing surfaces themselves. Again, Piazzi Smyth took careful notes:
. . . Little indeed is the ante-chamber, when it measures only 65.2 inches in utmost breadth from east to west, 116.3 long from north to south, and 149.4 high; but it has a sort of granite wainscot on either side of it, full of detail; and was to me so complicated and troublesome a matter as to occupy three entire days in measuring.
On the east side, this wainscot is only 103.1 inches high, and is flat and level on the top; but on the west side it is 111.8 inches high, and has three semi-cylindrical cross hollows of nine inch radius, cut down into it, and also back through its whole thickness of 8.5 to 11.7 inches to the wall. Each of those semi-cylindrical hollows stands over a broad, shallow, vertical, flat groove 21.6 inches wide, 3.2 inches deep, running from top to bottom of the wainscot, leaving a pilaster like separation between them. The greater part of the said pilasters has indeed long since been hammered away, but their fractured places are easily traced; and with this allowance to researchers in the present day, the groove and pilaster part of the arrangement is precisely repeated on the east side, within its lower compass of
height.
13
Is it conceivable that the pyramid builders went to such a great amount of trouble to cut this granite for a one-time operation? If this chamber was designed to be a closing mechanism, and it was to be activated only one time, it would not have been necessary to include such a complicated design and to cut that design out of such hard and durable material. Still, if we try
our hardest to give this theory its due, we would have to admit that there are cases today where a tool or machine may be "over-designed" to do the work for which it was built. But we must be aware that for the Antechamber to find a parallel in modern industry, we would have to allow for an equivalent situation, such as an expensive die being built from the finest quality tool-steel, even though it would be used to produce only one part. The theory strains under the weight of such an unlikelihood.
Under the Egyptologists' present theories, the Antechamber is, indeed, a perplexing and contradictory inclusion in the design and building of the Great Pyramid. But there is a reasonable answer to this mysterious and puzzling feature of the Great Pyramidâit is a mechanical and technological answer that so far has not attracted any consideration.
Perhaps the clue to answering this question lies inside the King's Chamber, or perhaps above the King's Chamber in the superimposed "construction chambers." A thorough investigation of the King's Chamber by Petrie revealed that the chamber had, at one time, been subject to a violent disturbance, which had shaken it so badly that the entire chamber was caused to expand approximately one inch! The granite beams on the south end of the chamber were wrenched loose and cracked through, indicating a powerful destructive force. Petrie attributed this disturbance to an earthquake, which has been the general assumption since. In Petrie's words, "All these motions are yet but smallâonly a matter of an inch or twoâbut enough to wreck the theoretical strength and stability of these chambers, and to make their downfall a mere question of time and
earthquakes."
14
Here again something does not seem to add up. It has been accepted that an earthquake could be the only disturbing force affecting the King's Chamber, and yet we could bring the same argument into play here that we used to refute the speculation that the ancient guardians noticed subsidence on the outside of the pyramid. If an earthquake had disturbed the King's Chamber to the extent that several giant granite beams were cracked and the entire chamber was expanded a whole inch, wouldn't it be reasonable to find similar disturbances elsewhere in the Great Pyramid? The King's Chamber is located 175 feet above ground level, and yet on the lower levels of construction, no similar disturbances have been noted. On the contrary! These areas show remarkable precisionâa precision that has astounded those
who have researched and measured the Great Pyramid and many who have subsequently studied those findings.
The King's Chamber, it appears, shows a greater amount of discrepancy than the entire thirteen-acre base of the pyramid! Why would an earthquake seek out one lonely chamber in a giant complex of masonry, passages, and chambers? The Queen's Chamber seems to have been unaffected by this catastrophic event. The Descending Passageâas mentioned earlierâis remarkably precise. No unusual disturbances were noted inside the Grand Gallery; even the Antechamber does not show the extent of damage suffered by the King's Chamber. More important, it is the specific characteristics of the disturbance that give rise to serious misgivings about the earthquake theory. Something caused the King's Chamber to expand! This small granite chamber, surrounded by a giant mass of limestone masonry, apparently pushed against that encompassing weight to the extent that the walls were moved outward from their original position. Petrie explained the damage:
The King's Chamber was more completely measured than any other part of the pyramid; the distances of the walls apart, their verticality in each corner, the course heights, and the levels, were completely observed. On every side the joints of the stones have separated, and the whole chamber is shaken larger. By examining the joints all round the second course, the sum of the estimated openings is 3 joints opened on N. side, total =.19; 1joint on E. =.14; 5 joints opened on S. = .41; 2 joints on W = .38. And these quantities must be deducted from the measure, in order to get the true original lengths of the chamber. I also observed, in measuring the top near the W, that the width from N. to S. is lengthened .3 by a crack at the S.
side.
15
It would be interesting to find out what pressure would be needed to move the walls and affect the chamber this way, especially taking into consideration that all the spaces above the King's Chamber also were affected by the disturbance. Petrie continues with his observations:
These openings or cracks are but the milder signs of the great injury that the whole chamber had sustained, probably by an earthquake,
when every roof beam was broken across near the south side; and since which the whole of the granite ceiling (weighing some 400 tons) is upheld solely by sticking and thrusting. Not only has this wreck overtaken the chamber itself, but in everyone of the spaces above it are the massive roof beams either cracked across or torn out of the wall, more or less, at the south side; and the great eastern and western walls of limestone, between and independent of which, the whole of these construction chambers are built, have sunk
bodily.
16
Several facts support the speculation that the guardians of the Great Pyramid were aware of the damage suffered by the King's Chamber. The hole Davison discovered, which in turn led to the discovery of the superimposed chambers above the King's Chamber, can be explained by surmising that the guardians carried out a close inspection of the damage affecting the upper levels of the granite complex. The guardians, after satisfying themselves that no further attention was required, terminated their inspection at that point.
