The South Beach Diet (9 page)

FAST FOOD
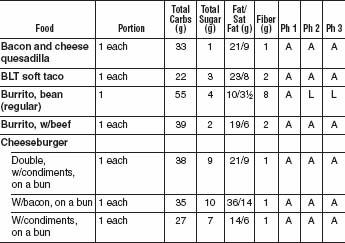
Most fast foods fall into the “avoid” category. They are dripping with saturated fats, trans fats, sugars, and empty calories. But there are ways to eat wisely, even at a fast-food restaurant: Choose broiled or grilled food over deep-fried foods, and choose burgers without all the toppings and special sauces. Look for the salad bar. When you go out for pizza, choose thin-crust vegetarian pizzas. The tomato sauce may play a role in preventing prostate cancer due to lycopene, an antioxidant found in tomato products.
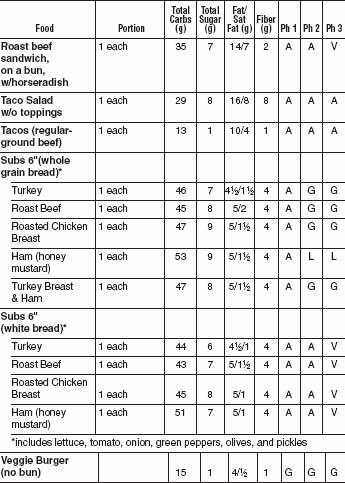
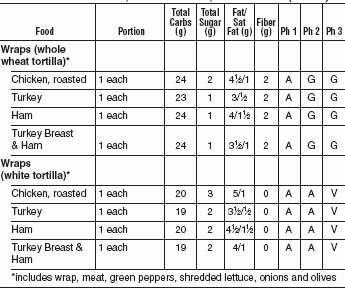
FAST FOOD BURGERS, SANDWICHES, AND WRAPS
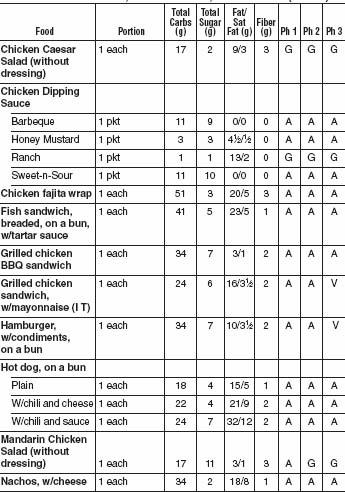
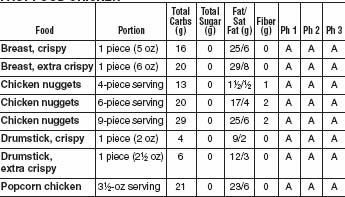
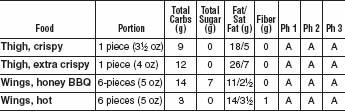
FAST FOOD CHICKEN
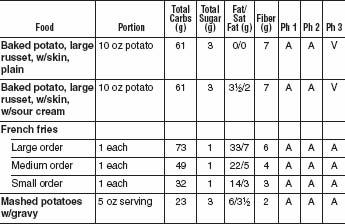
FAST FOOD POTATO ITEMS
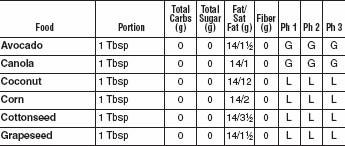
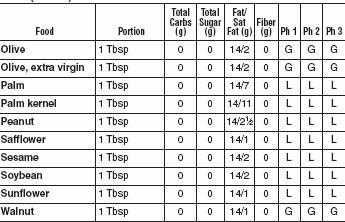
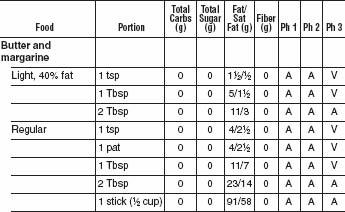
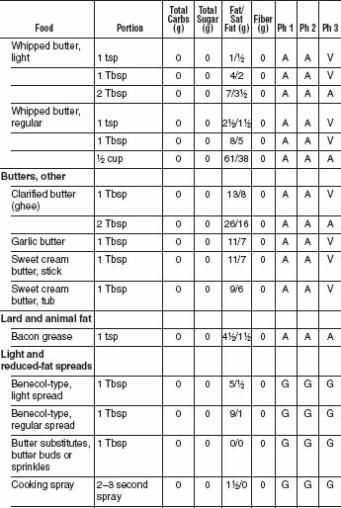
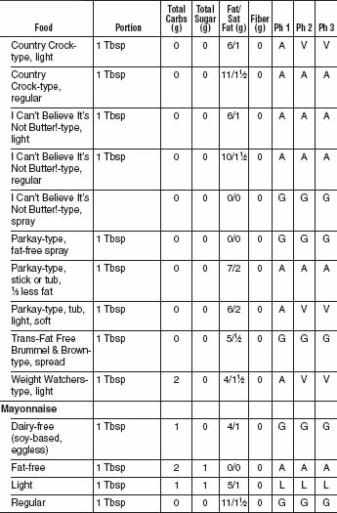
FATS AND OILS
With all the bad press fat has gotten over the last couple of decades, most Americans have concluded that just limiting fats makes a diet healthy. This was a major mistake. While limiting saturated fat (meat-and dairy-derived) and avoiding trans fats (manmade hydrogenated and partially hydrogenated oils) as completely as possible is important, the Mediterranean oils, including olive oil and omega-3 fish oils, appear to be good for both our blood vessels and our waistlines. We’ve given a “good” recommendation for Omega 3 oils and a “limited” recommendation for Omega 6 oils because the optimal ratio of Omega 6 to Omega 3 oils in our diet is 5 to 1. Generally the ratio in the American diet is much higher. Omega 6 oils include corn, safflower, and soybean. There is no advantage to low-fat diet dressings that substitute sugars and starches for healthful oils. Along with a healthy oil, the vinegar in vinaigrette and oil-and-vinegar dressings is acidic and helps slow digestion. This lowers the glycemic index of the whole meal. Remember that nuts are also excellent sources of good fats and have been shown to help prevent heart attacks and strokes.
FATS
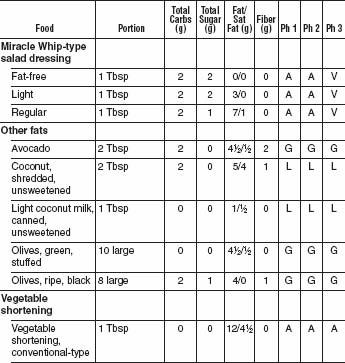
OILS