Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1106 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
8.68Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Values are slightly lower in supine position.
Difference between arterial blood and venous blood varies considerably, depending on the skin temperature, length of stasis, and muscular activity.
PARTIAL PRESSURE OF OXYGEN (pO
2
),
BLOOD
Definition
The partial pressure of oxygen (pO
2
) is a measure of the tension or pressure of oxygen dissolved in the blood. The pO
2
of arterial blood is primarily related to the ability of the lungs to oxygenate blood from alveolar air.

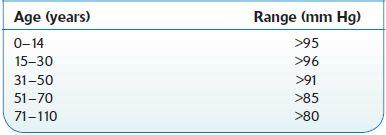
Normal range:
Arterial: >80–95 mm Hg (see Table 16.64)
Venous: 35–40 mm Hg
TABLE 16–64. Arterial pO
2
Use
To evaluate patients with pulmonary or acid–base disturbances
To monitor patients with carbon monoxide poisoning, methemoglobinemia, or hemoglobin variant for O
2
saturation
To manage patients on mechanical respirators
Prior to thoracic or general surgery
Other books
Sweet Contradiction by Peggy Martinez
Complete Book of Wedding Vows by Diane Warner
Her Adoring SEAL (Midnight Delta Book 3) by Caitlyn O'Leary
Tracked by Jenny Martin
Alpha (Wolves Creek Book 1) by Samantha Horne
The Marriage Bargain by Michelle McMaster
The Morgue and Me by John C. Ford
Confessions of an Almost-Girlfriend by Louise Rozett
Wizard: The Life and Times of Nikola Tesla by Seifer, Marc
Crash Landing by Lori Wilde
