Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (503 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

The risk of progression to AIDS is related to the baseline HIV-1 viral load after seroconversion. Plasma viral load >100,000 copies/mL at 6 months after seroconversion are associated with a 10-fold greater risk of progression to AIDS within 5 years, compared to patients with lower baseline levels.
Although the results of HIV-1 viral load assays are correlated, there may be proportional differences in the results from laboratories performing testing using different platforms. It is recommended that viral load testing to monitor patients be performed in the same laboratory using the same platform. If the testing platform is changed, unexpected changes in viral load must be interpreted with caution. It may be important to “rebaseline” the patient with sequential testing on the new platform.
Patients with HIV infection are at high risk for coexisting infections. Patients should be carefully evaluated to rule out the following infections: hepatitis B, hepatitis C, CMV,
Toxoplasma gondii
, syphilis, and TB.
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS (HPV) INFECTION
Definition
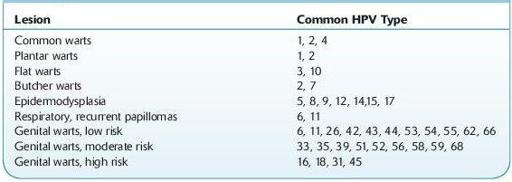
Papillomaviruses are nonenveloped DNA viruses that cause a spectrum of diseases of epithelial tissues, ranging in severity from benign plantar warts to genital tract cancers. The papillomaviruses are widespread in vertebrate hosts, but individual viruses are narrowly species specific. HPVs have a supercoiled, nonsegmented circular double-stranded DNA genome. They are classified by genotype, with different genotypes associated with different clinical diseases (Table
11-1
).
TABLE 11–1. Disease Associations of Specific Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Genotypes
Who Should Be Suspected?
Three types of warts are most common: common warts, plantar warts, and flat warts.
Common warts often occur in groups and are round, hyperkeratotic papules that usually occur on the dorsum of the hand or on the fingers. Common warts are painless.
Plantar warts are usually solitary and occur on the weight-bearing locations of the foot. Plantar warts are circular and commonly show a keratotic ring surrounding a roughened, dark-speckled center. They are deep-set and usually painful.
Flat warts usually occur as multiple, painless smooth papules on the face or hands. Immunocompromised patients are at increased risk for the occurrence and severity of cutaneous warts. In immunocompetent patients, cutaneous warts typically resolve spontaneously.
Papillomavirus infections of squamous epithelial tissues of the anogenital tract are responsible for genital warts and carcinomas. These infections are primarily sexually transmitted, and the risk of infection is most strongly related to the patient’s lifetime number of sexual partners and history of other STIs. Most infections are acquired in the teens and early 20s.
Condylomata acuminata are multiple hyperkeratotic papules that commonly develop irregular surfaces. Groups of venereal warts may coalesce to form cobblestone patches. Warts may occur at any genital site, including the distal urethra. In males, lesions usually appear on the shaft of the penis. In women, most warts occur at the posterior introitus. Warts may also occur in anal and perianal surfaces. Genital warts are usually asymptomatic, but patients may complain of itch or burning pain.
Anogenital papillomavirus infections are associated with malignant transformation. Globally, HPV-16 and HPV-18 are the genotypes most strongly associated with invasive cervical carcinoma, but there is variability in the genotypes less frequently associated with cervical cancer in different geographic regions.
