Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (529 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
8.71Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Immune complex–mediated diseases (typically show hypocomplementemia): for example, IgA nephropathy, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), acute postinfectious GN, membranoproliferative GN
Cell Mediated
Examples include Wegener granulomatosis, polyarteritis.
Infectious
Acute poststreptococcal (group A beta-hemolytic GN)
Non-poststreptococcal: bacterial (e.g., infective endocarditis, bacteremia), viral (e.g., HBV, HCV, CMV infections), parasitic (e.g., trichinosis, toxoplasmosis, malaria), or fungal
Noninfectious
Multisystem (e.g., SLE, Henoch-Schönlein purpura, Goodpasture syndrome, Alport syndrome)
Primary glomerular disease (e.g., IgA nephropathy, membranoproliferative GN)
Hypocomplementemic
Intrinsic renal diseases (especially poststreptococcal, membranoproliferative GN)
Systemic (e.g., SLE, cryoglobulinemia)
Normocomplementemic
Intrinsic renal diseases (e.g., IgA nephropathy, idiopathic rapidly progressive GN)
Systemic (e.g., polyarteritis nodosa, Wegener granulomatosis)
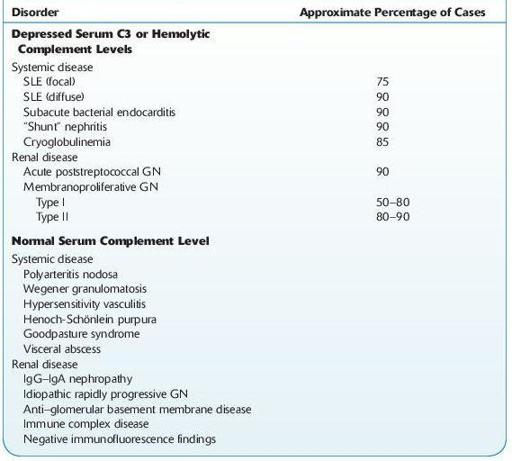
See Table
12-4
.
TABLE 12–4. Serum Complement in Acute Nephritis
Various Clinical Courses of GN
Other books
The Bisbee Massacre by J. Roberts
Totally Joe by James Howe
Waiting for Something by Whitney Tyrrell
Forbidden (Addicted to You Book 2) by Flatman, NJ
Junkyard Dog by Bijou Hunter
Secrets (Swept Saga) by Nyx, Becca Lee
Hiding Out (Hawks MC: Caroline Springs Charter, #2) by Lila Rose
Cabin Fever by Sanders, Janet
John Shirley - Wetbones by Unknown
The Curse of Snake Island by Brian James
