Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (611 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
11.66Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
D = decreased; I = increased; N = normal.
TABLE 13–3. Illustrative Serum Electrolyte Values in Various Conditions
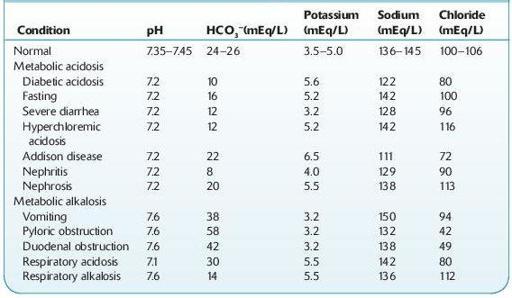
TABLE 13–4. Summary of Pure and Mixed Acid–Base Disorders
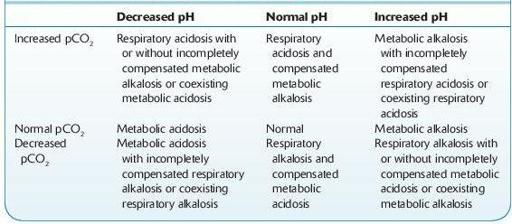
Data from Friedman HH.
Problem-Oriented Medical Diagnosis
, 3rd ed. Boston, MA: Little, Brown; 1983.
TABLE 13–5. Immediate and Delayed Compensatory Response to Acid–Base Disturbances
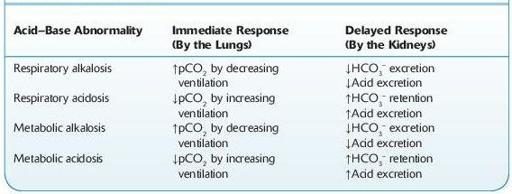
↑, increases; ↓, decreases.
TABLE 13–6. Primary Change, and Compensatory Mechanisms in Delayed Response to, and Chloride Level in AcidBase Disturbances
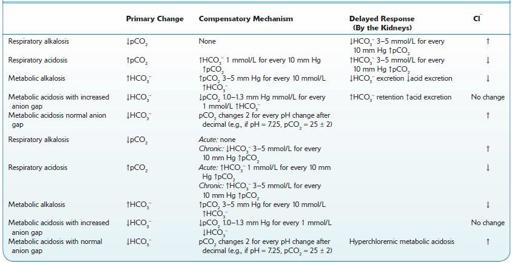
↑, increased;↓, decreased.
RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
Respiratory alkalosis is defined as a decreased pCO
2
of <38 mm Hg.
Caused by Hyperventilation
CNS disorders (e.g., infection, tumor, trauma, CVA, anxiety–hyperventilation)
Hypoxia (e.g., high altitudes, ventilation–perfusion imbalance, PE)
Cardiovascular (e.g., CHF, hypotension)
Pulmonary disease (e.g., pneumonia, pulmonary emboli, asthma, pneumothorax)
Drugs (e.g., salicylate intoxication, methylxanthines, β-adrenergic agonists)
Metabolic (e.g., acidosis [diabetic, renal, lactic], Cirrhosis, liver failure)
Others (e.g., fever, pregnancy, gram-negative sepsis, pain)
Other books
Tinder Stricken by Heidi C. Vlach
Dragonoak: The Complete History of Kastelir by Sam Farren
The Bones Of Odin (Matt Drake 1) by Leadbeater, David
Honor Bound: Bound and Tied, Book 1 by Myla Jackson
The Marriage of Heaven and Hell by Peter Dally
Whispered Confessions (Touched By You) by Trent, Emily Jane
The Gatekeeper's Son by C.R. Fladmark
Parker (Rich & Single #2) by Lexy Timms
SNAP: The World Unfolds by Drier, Michele
Opening Atlantis by Harry Turtledove
