Wayward Son (64 page)
Authors: Tom Pollack
Tags: #covenant, #novel, #christian, #biblical, #egypt, #archeology, #Adventure, #ark

READERPEDIA®
King Nebuchadnezzar
was a well-known king of the Babylonian empire, who ruled from 605-562 BC. He is the ruler responsible for leading the development of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the seven wonders of the world. He is most famously tied to the book of Daniel in the Old Testament.
[back]

READERPEDIA®
The Huaqing Hot Springs
are located at the foot of Mount Li and have been home to the palaces of several Chinese emperors. They were built in 723 by Emperor Xuanzong of the Tang dynasty as an addition to the palace there.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
As part of the Qinling mount range,
Mount Li
(“Black Steed Mountain”) is northwest of Xi’an in China and provides one of the more scenic vistas in the Shaanxi Province.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
The Wei River
is the largest tributary of the Yellow River at nearly 500 miles and flows through China’s Gansu and Shaanxi provinces.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
The Qinling Mountains
serve as a boundary between the north and south of China in the southern region of the Shaanxi province.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Quicksilver
is an ancient name for mercury, which is literally translated from Old English into “living silver” due to its movement-like properties.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Shaqiu
is located in the Hebei Province in the northeast section of China.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Zhifu Island,
also known as the North Island, is located in China’s Shandong Province and is home to archeological exhibitions that have unearthed more than 200 artifacts that show the area was settled during the Neolithic period. It is also home to the legend about the Mountain of Immortality.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Also known as the Phurba,
the Golden Passport
was a golden dagger with three blades that was supposedly the key to Shambhala as recorded by Marco Polo.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Hipparchus
was a Greek mathematician, astrologer, geographer and astronomer who is considered the father of trigonometry.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Ostia
was a harbor city located at the mouth of the Tiber River in ancient Rome.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
The Tiber River,
which is the third longest river in Italy, has served as the watercourse of Rome. Rome was founded on the eastern banks of the Tiber River.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Located halfway between Tel Aviv and Haifa in Israel,
Caesarea
was built by Herod in 13 BC as a port city. Its inhabitants were exempt from Jewish law since it was comprised of mostly non-Jewish residents.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
The Great Fire of Rome
gutted Rome in 64 AD, sparing just four of the city’s 14 districts. For six days the fire raged as it destroyed much of the town. However, Nero, in an effort to suppress the Christians blamed the fire on the Christians, claimed it was an act of arson. He arrested many Christians for crimes punishable by death, going so far as wrapping them in thorn baskets and burning them on a stake. These human torches were used to light the streets of Rome as a reminder of their conviction for setting the Great Fire.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Campus Martius
, which means “Field of Mars” in Latin, was a low-lying plain near the web bend of the Tiber River where most of the Romans lived in the Middle Ages. Initially, it primarily was used as a pasture for horses and sheep as well as army training immediately after the city was founded. However, it later became a central region for people to dwell.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Paulinus
was the Roman general who helped squash Boudica’s uprising and restore order. He was eventually appointed the governor of Britain in 59 AD.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
As king of the Celtic tribe known as the Iceni,
King Prasutagus
was the husband of Boudica. His will was not honored and the Romans took over the region he ruled, which is now known as Norfolk.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
The Iceni
were the tribe who refused to be ruled by the Romans when King Prasutagus’ will was ignored in first century AD. Led by Boudica, they revolted and nearly forced the Roman troops to leave before being subdued by Paulinus and the Romans.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
Catus Decianus
was the procurator of Roman Britain in AD 60 or 61 and was responsible for provoking the rebellion of Boudica.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
The Dead Sea Scrolls
are documents found near the Dead Sea that are significant both religiously and historically. Dating back to 150 BC and 70 AD, the manuscripts demonstrate the accuracy of biblical texts pertaining to the time frame in which they were originally written. A total of 972 texts were discovered between 1947 and 1956.
Dig a little deeper at:
http://dss.collections.imj.org.il/
NOTE:
If you elect to utilize this or any other hyperlink within this e-book you will have to navigate back to the application/carousal that contains your books. Simply re-open
Wayward Son
and you will return to the page where you left off.
READERPEDIA®
Named after Appius Claudius Caecus,
the Appian way
was the longest and most important Roman road in the ancient Roman empire. It connected Rome with the southeast coast of Italy, providing for easy transportation of merchandise as well as quick military mobilization.
[back]

READERPEDIA®
The Neronian Baths
were first built by Nero in 65 AD and served as public bath houses with heated waters. Patrons often had to wear special shoes to avoid blistering on their feet. They were immensely popular with the citizens and were more like a visit to an exercise facility and spa than simply a place to bathe.
[back]

READERPEDIA®
Sicinnus
served as a slave for Themistocles and played a pivotal role in the second Persian inversaion of Greece. At the behest of Themistocles, Sicinnus managed to persuade Xerxes that the Greeks were panicking and a Persian fleet could serve as a blockade to prohibit the Greeks from escaping. However, it was a trap and the Greeks warded off the Persians, resulting in great reward for Sicinnus.
[back]
READERPEDIA®
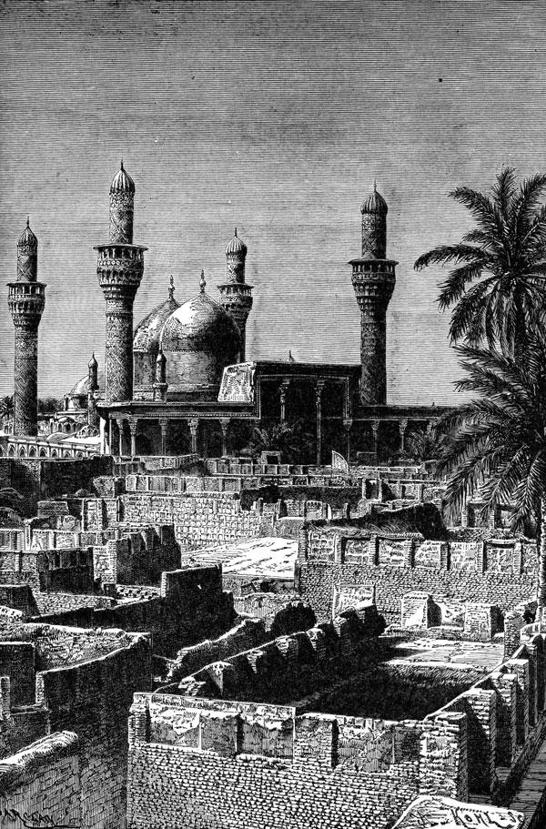
The Babylonians were notorious for building
towers
, also known as ziggurats, most notably, the Tower of Babel, which was made infamous in a story found in Genesis 11. It is the location where God confused the languages of the people in order to thwart an attempt to build a tower that reached to the heavens. Notice the tower rising in the background in the image below.
[back]

READERPEDIA®
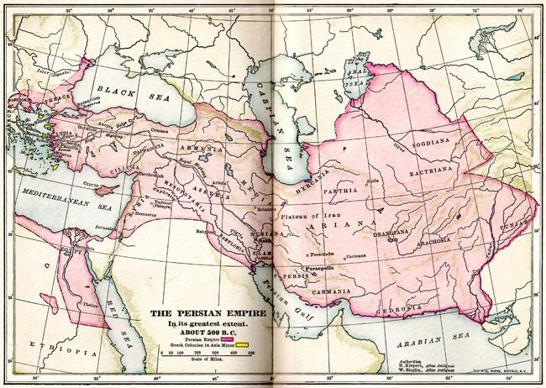
The Persian Empire
(550 BC - 330 BC) was the largest empire in the history of the world during its day, stretching from the Indus Valley in the west to Greece in the east. It spanned three continents and contained more than 50 million people, comprising approximately 44 percent of the world's population at the time.
[back]