Bombshell: Explosive Medical Secrets That Will Redefine Aging (52 page)
Read Bombshell: Explosive Medical Secrets That Will Redefine Aging Online
Authors: Suzanne Somers
Tags: #Health & Fitness, #Healthy Living, #Alternative Therapies, #Diseases, #Cancer

A
GING
F
ACTOR
4:
M
ITOCHONDRIAL
D
YSFUNCTION
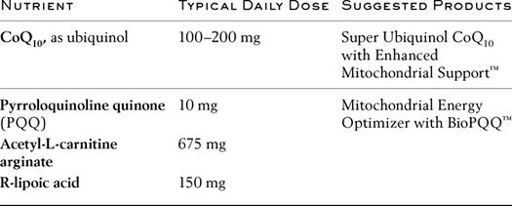
Over 350 studies published in 2010 alone show how mitochondrial
degradation
leads to the onset of virtually every degenerative disease. Mitochondrial dysfunction can result in congestive heart failure, muscle weakness, fatigue, and neurological disease. The good news is that researchers have found that age-related mitochondrial decline may be
reversed
.
S
OLUTION:
M
ITOCHONDRIAL
S
UPPORT
To energize and restore aging mitochondria, the following four nutrients should be taken each day.
A
GING
F
ACTOR
5:
H
ORMONE
I
MBALANCE
S
OLUTION:
B
IOIDENTICAL
H
ORMONE
R
EPLACEMENT WITH
N
UTRIENT
S
UPPORT
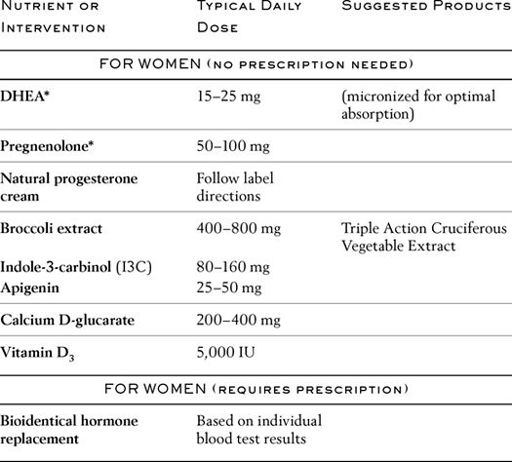
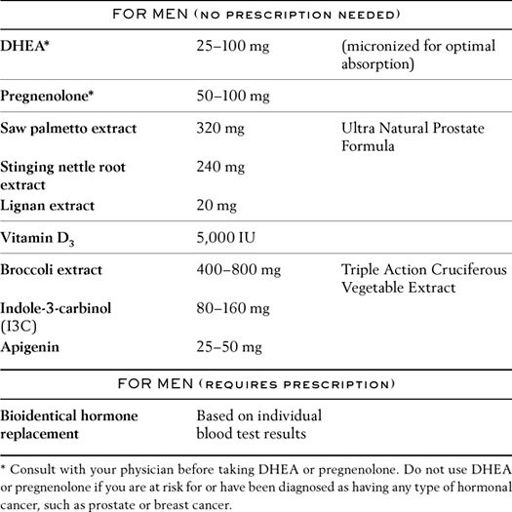
The most effective way to bring your sex hormones into balance is by
restoring
them to youthful levels with bioidentical hormone replacement therapy. There’s no fixed dosage for these hormones. You and your doctor tailor the amount that’s right for you through careful monitoring of your blood test results.
HOW TO SUPPORT HORMONE BALANCE
Those taking bioidentical hormones should consider taking nutrients shown to help aging men and women safely utilize their hormones, protect against hormone-dependent cancers, and eliminate potentially carcinogenic compounds found in our diet and environment.
Estrogen imbalance poses a major threat to both women
and
men. Clinical studies reveal that too much or too little estrogen puts men at greater risk for heart disease, atherosclerosis, stroke, prostate cancer, and osteoporosis. Compounds found in
cruciferous vegetables
help our bodies regulate estrogen metabolites, neutralizing dangerous ones.
The chart in this section describes bioidentical hormones you can obtain right now and the nutrients you should take with them. Fortunately, many of these nutrients are available in special multiformulas, so you don’t have to take a lot of pills.
A
GING
F
ACTOR
6:
E
XCESS
C
ALCIFICATION
Aging
disrupts
calcium transport, resulting in excess calcium infiltration into the soft tissue cells of the brain, heart valves, and middle arterial wall (causing arteriosclerosis). Many age-related disorders are related to excessive calcification, including memory loss, aortic valve stenosis, atherosclerosis, vision problems, even dementia.
Gradual calcium buildup in your coronary arteries can constrict blood flow, causing chest pains and putting you at greater risk for a heart attack.
These deadly age-related processes can be halted and possibly
reversed
using two low-cost nutrients.
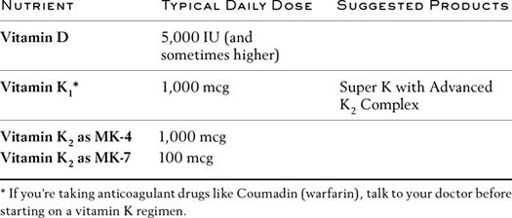
S
OLUTION
:
V
ITAMINS
K
AND
D
Lining our blood vessels is a
protein
that regulates whether or not circulating blood calcium
infiltrates
(calcifies) our arteries. This protein requires
vitamin K
2
to function. When one is deficient in vitamin K
2
, vascular calcification occurs. When sufficient K
2
is present, this protein functions to shield against arterial calcification.
Vitamins D and K work
together
to help remove calcium from circulation in the blood, trigger bone formation, and maintain bone strength. Vitamin D helps your bones absorb calcium. Vitamin K ensures that calcium is deposited in your bones and stays out of your arteries. Together they work to prevent excess calcium from depositing in your brain, arteries, and other soft tissues.
A
GING
F
ACTOR
7:
D
IGESTIVE
E
NZYME
D
EFICIT
Digestive enzymes are essential to the body’s absorption and full utilization of food. They speed the chemical reactions that break down food in the digestive tract. Raw foods also provide enzymes that naturally break down food for proper absorption. The capacity of the living organism to make enzymes diminishes with age. One reason we pack on the fat pounds, feel sluggish, and grow more vulnerable to infectious disease as we grow old may surprise you. It’s a connection I never made until I started talking to antiaging experts.
Our aging bodies no longer produce sufficient amounts of the active chemical compounds we need to extract essential nutrients from the foods we eat.
Meeting the full range of our nutritional requirements can create a high demand for these
digestive enzymes
. Their gradual loss accounts for many health problems that plague aging adults, from impaired immunity to digestive distress and nutritional deficiencies.
S
OLUTION
:
T
AILORED
E
NZYMATIC AND
N
UTRITIONAL
S
UPPORT
Another way to restore digestive enzyme balance is to ensure you have enough beneficial bacteria in your gut. Supplements that supply these living bacteria are called
probiotics
.
You also need to ensure that “good” bacteria are getting enough of the nutrients they need to thrive. Dietary deficiency of these nutrients—known as
prebiotics
—is another reason we don’t have the robust digestive enzyme balance of our younger days.
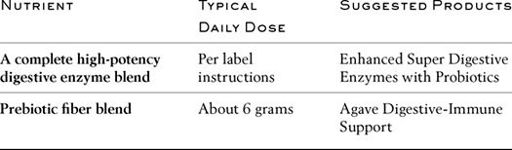
So your digestive support strategy is threefold:
1. Replenish youthful levels of digestive enzymes.
2. Repopulate your gut with beneficial bacteria using probiotics.
3. Nourish beneficial bacteria so they can thrive with prebiotics.
One final word of caution, and something else that might surprise you: High-quality digestive enzyme supplements can cause you to gain weight if you’re not careful.
They work so well in helping your body break down food efficiently that you don’t get that “full” feeling as quickly. So you may wind up eating more than you should,
even though you know you shouldn’t
.
A
GING
F
ACTOR
8:
F
ATTY
A
CID
I
MBALANCE
Aging
distorts
the metabolism of
essential
fatty acids, throwing their delicate proportion and interplay off balance. The resulting
fatty acid imbalance
may manifest as anything from irregular heartbeat and skin disorders to heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
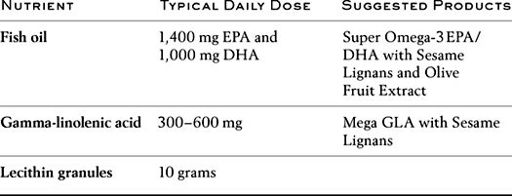
S
OLUTION
:
F
ATTY
A
CID
I
NTERVENTION
A
GING
F
ACTOR
9:
DNA M
UTATION
We are continuously exposed to synthetic
and
natural carcinogens in our food supply, in everyday household products, and in our environment. Cooking any food at high temperatures (above 250 degrees Fahrenheit) also generates toxic cancer-causing agents. These environmental and dietary compounds
mutate
cellular DNA.