Breast Imaging: A Core Review (25 page)
Read Breast Imaging: A Core Review Online
Authors: Biren A. Shah,Sabala Mandava
Tags: #Medical, #Radiology; Radiotherapy & Nuclear Medicine, #Radiology & Nuclear Medicine

A. Surgical excisional biopsy
B. Breast-specific gamma imaging (BSGI)
C. Breast MRI
D. Follow-up diagnostic ultrasound in 6 months
99
Which condition most commonly causes bilateral breast edema?
A. Inflammatory breast cancer
B. Superior vena cava syndrome
C. Mastitis
D. Trauma
E. Coumarin necrosis
100
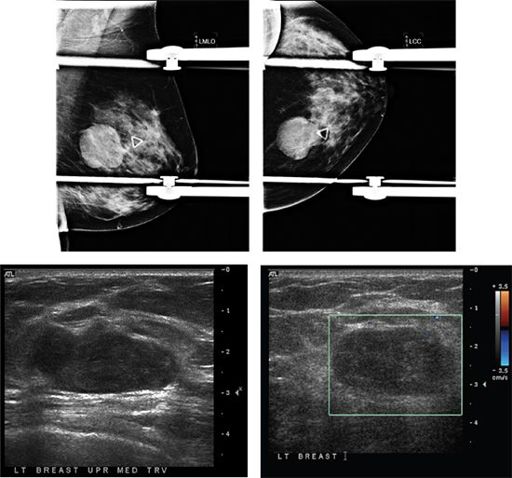
A 28-year-old female presents with a palpable abnormality in the left breast. Based on the images, what is the most appropriate management?
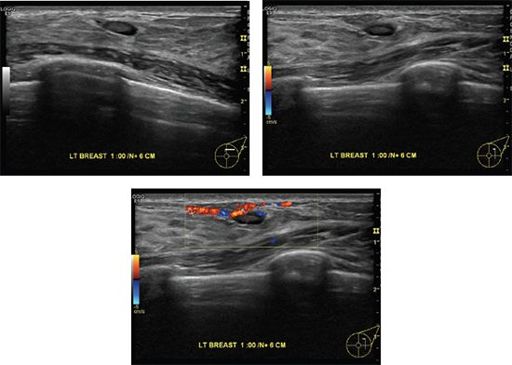
A. No further management
B. Cyst aspiration
C. Core needle biopsy
D. Antibiotic therapy
101
After lumpectomy and radiation therapy the enhancement of the postoperative cavity site begins to subside on postcontrast breast MRI after how many months?
A. 3–5 months
B. 6–7 months
C. 8–9 months
D. 10–18 months
102
The statement “Multiple, bilateral, circumscribed, noncalcified masses” is given a BI-RADS of:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
103
A 78-year-old male presents with a palpable lump in the right breast. Based on the diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
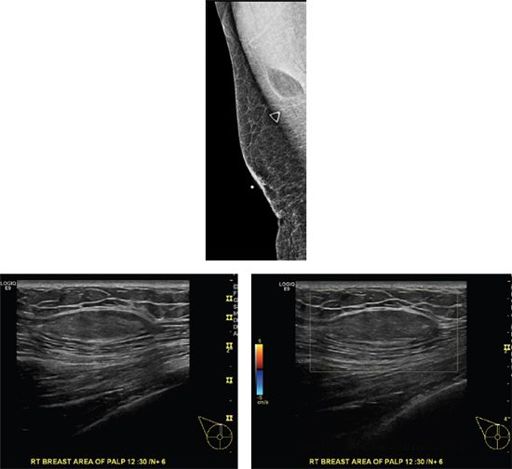
A. Invasive ductal carcinoma
B. Cyst
C. Lipoma
D. Fibroadenoma
E. Gynecomastia
104
A 2.5 cm in greatest dimension malignant mass with metastasis to a level 2 movable ipsilateral level 1 axillary lymph node and with no clinical or radiographic evidence of distant metastasis has a TNM staging classification of
A. T1a, N2, M0
B. T2, N1, M0
C. T3, N3, M0
D. T2, N2a, M1
E. T4, N3, M0
105
The calcifications seen on the mammogram below are dermal in nature. What is the cause?
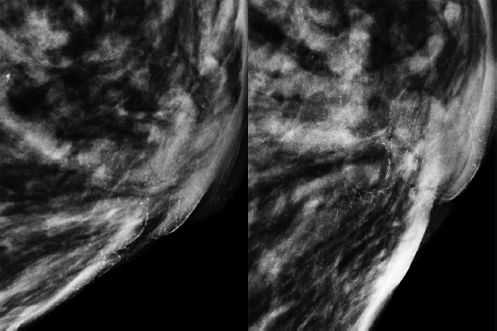
A. Calcium carbonate
B. Methyl salicylate
C. Zinc oxide
D. Glycerol
106
Based on the mammographic and sonographic images below, what is the most likely diagnosis?
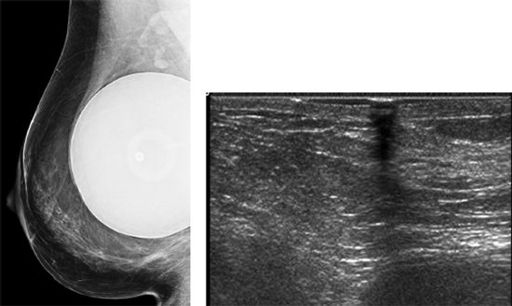
A. Sebaceous cyst
B. Normal breast tissue
C. Scar
D. Invasive lobular carcinoma
107a
The first set of mammographic images is from 3 years ago. After this mammogram, asymmetry in the upper outer quadrant was excised demonstrating pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia (PASH). Patient returns for annual screening mammogram. What is the appropriate BI-RADS category assessment?
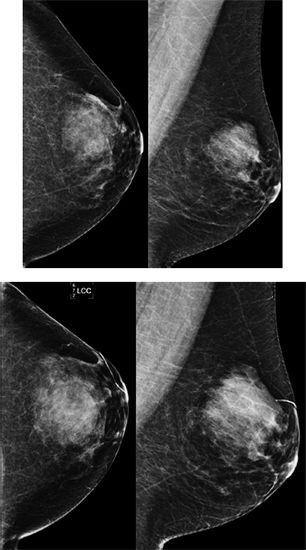
A. 0
B. 1
C. 3
D. 4
107b
Additional views and ultrasound images are given below. What is the next step in management?
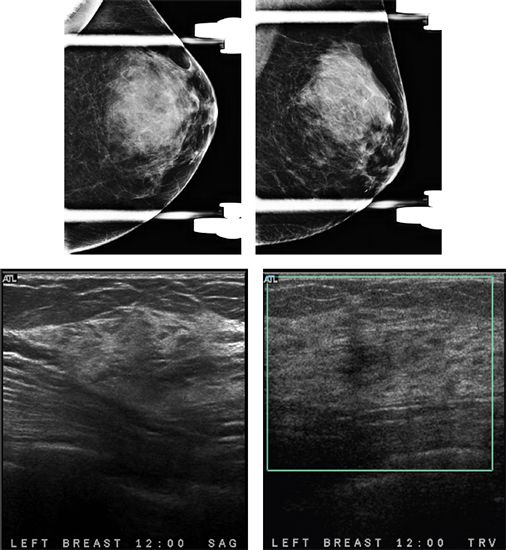
A. Refer to surgeon for excision
B. Needle core biopsy
C. Return to annual screening
D. Short-term follow-up mammogram in 6 months
107c
Needle core biopsy was performed, and pathology is pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia (PASH). You are asked to do radiology–pathology correlation. What is your assessment and recommendation?
A. Concordant benign radiology–pathology results. Return to annual screening mammography.
B. Concordant benign radiology–pathology results. Recommend surgical excision.
C. Concordant benign radiology–pathology results. Recommend short-term follow-up mammogram.
D. Discordant radiology–pathology results. Recommend surgical excision.
108
A 44-year-old woman presents with a palpable finding in the right breast since 2 months. Based on the mammogram and ultrasound images below, what is the most likely diagnosis?
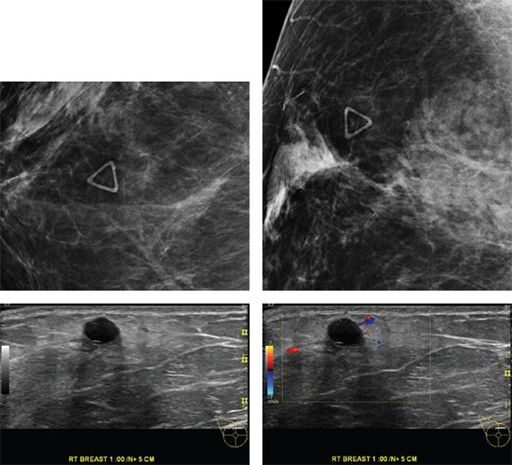
A. Fibroadenoma
B. Complicated cyst
C. Mucinous carcinoma
D. Oil cyst
E. Lipoma
Other books
A Good Food Day: Reboot Your Health with Food That Tastes Great by Marco Canora, Tammy Walker
Requiem Murder [Book 2 of the Katherine Miller Mysteries] by Janet Lane Walters
The Temporary Wife by Jeannie Moon
Our Lady of the Flowers by Jean Genet
Game On by Snow, Wylie
Archives of the Frontier Universe: An Assassin's Assignment by Villanueva, Christopher
Moontide Embrace (Historical Romance) by Constance O'Banyon
Night Whispers: ShadowLands, Book 1 by Alisha Rai
Eclipse of Hope by David Annandale
