Build Your Own ASP.NET 3.5 Website Using C# & VB (9 page)
Read Build Your Own ASP.NET 3.5 Website Using C# & VB Online
Authors: Cristian Darie,Zak Ruvalcaba,Wyatt Barnett
Tags: #C♯ (Computer program language), #Active server pages, #Programming Languages, #C#, #Web Page Design, #Computers, #Web site development, #internet programming, #General, #C? (Computer program language), #Internet, #Visual BASIC, #Microsoft Visual BASIC, #Application Development, #Microsoft .NET Framework


Introducing ASP.NET and the .NET Platform
15
After all the notifications are out of the way, you should get a page like that in
Fig-
Figure 1.12. Executing your first ASP.NET web page
You can now close the Internet Explorer window. Visual Web Developer will
automatically detect this action and will cancel debugging mode, allowing you to
start editing the project again. Now let’s do something with that Label control.
Set Your Default Browser to Internet Explorer
When executing the project, the web site is loaded in your system’s default web
browser. For the purposes of developing ASP.NET applications, we recommend
configuring Visual Web Developer to use Internet Explorer, even if this is not your
preferred web browser. We recommend Internet Explorer because it integrates
better with Visual Web Developer’s .NET and JavaScript debugging features. For
example, Visual Web Developer knows to automatically stop debugging the project
when the Internet Explorer window is closed. To change the default browser to
be used by Visual Web Developer, right-click the root node in
Solution Explorer
,
choose
Browse With
, select a browser from the
Browsers
tab, and click
Set as Default
. For our first dynamic web page using ASP.NET, let’s write some code that will
display the current time inside the Label control. That mightn’t sound very exciting,
but it’s only for the purposes of this simple demonstration; don’t worry, we’ll reach
the good stuff before too long. To programmatically manipulate the Label control,
you’ll have to write some C# or VB.NET code, depending on the language you’ve
chosen when creating the project. As suggested earlier in this chapter, ASP.NET
allows
web forms
(
.aspx
pages) to contain C# or VB.NET code, or they can use sepLicensed to [email protected]


16
Build Your Own ASP.NET 3.5 Web Site Using C# & VB
arate files—named
code-behind files
—for storing this code. The
Default.aspx
file that was generated for you when creating the project was created with a code-behind
file, and we want to edit that file now. There are many ways in which you can open
that file. You can click the
View Code
icon at the top of the
Solution Explorer
window, you can right-click the
Default.aspx
file in
Solution Explorer
and choose
View Code
, or you can click the
+
symbol to expand the
Default.aspx
entry. No matter how you open this file, it should look like
Figure 1.13 if you
’re using C#, or like
Figure 1.14
if you’re using VB.NET.
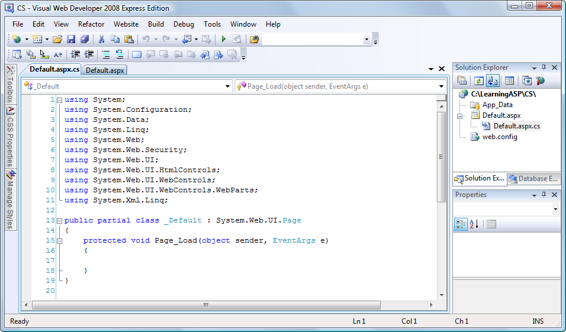
Figure 1.13. Default.aspx.cs in Visual Web Developer
C#, VB.NET, and Visual Web Developer
You may be slightly alarmed, at first, by the fact that the code-behind file template
that Visual Web Developer generates for the
Default.aspx
file in a new project when
you’re using C# is completely different from the one it generates when you’re using
VB.NET. They’re based on the same platform and use the same data types and
features, so C# and VB.NET are fundamentally very similar. However, there are
still large differences between the languages’ syntax. VB.NET is frequently preferred
by beginners because its syntax is perceived to be easier to read and understand
than C#. While the differences can be intimidating initially, after we discuss their
details in
Chapter 3, you
’ll see that it can be relatively easy to understand both. Licensed to [email protected]
Introducing ASP.NET and the .NET Platform
17
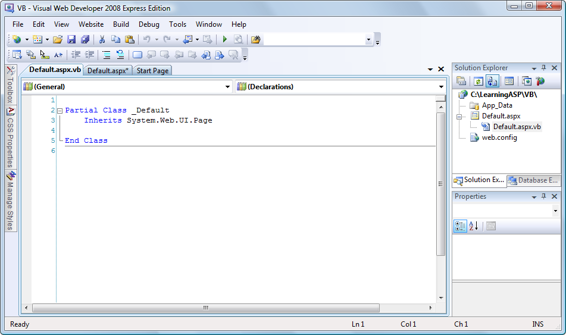
Figure 1.14. Default.aspx.vb in Visual Web Developer
Looking at
Figure 1.13 and
Figure 1.14
you can see that the C# version contains a definition for a method called Page_Load, while the VB.NET version doesn’t. This
is the method that executes automatically when the project is executed, and we
want to use it to write the code that will display the current time inside the Label
control.
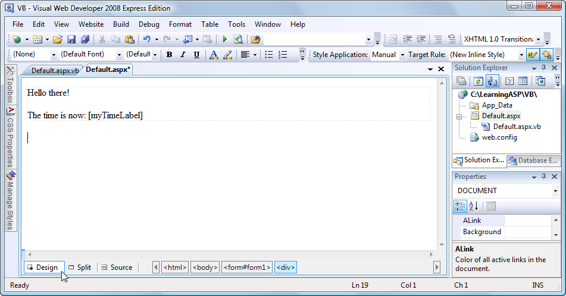
Figure 1.15.
Default.aspx
in Design view in Visual Web Developer
Licensed to [email protected]


18
Build Your Own ASP.NET 3.5 Web Site Using C# & VB
If you’re using VB.NET, you’ll need to generate the Page_Load method first. The
easiest way to have Visual Web Developer generate Page_Load for you is to open
Default.aspx
—
not
its code-behind file—and switch to
Design
view (as shown in
Figure 1.15
). If you double-click on an empty place on the form, an empty Page_Load method will be created in the code-behind file for
Default.aspx
.
Now edit the Page_Load method so that it looks like this, selecting the version that
applies to your chosen language:
Visual Basic
LearningASP\VB\Default.aspx.vb
(excerpt)
Partial Class _Default
Inherits System.Web.UI.Page
Protected Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender As Object,
➥ ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles Me.Load
myTimeLabel.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString()
End Sub
End Class
C#
LearningASP\CS\Default.aspx.cs
(excerpt)
public partial class _Default : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
myTimeLabel.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
C# is Case Sensitive
C#, unlike VB, is case sensitive. If you type the case of a letter incorrectly, the
page won’t load. If these languages look complicated, don’t worry: you’ll learn
If you’ve never done any server-side programming before, the code may look a little
scary. But before we analyze it in detail, let’s load the page and test that it works
