Chinese Brush Painting (2 page)
Read Chinese Brush Painting Online
Authors: Caroline Self,Susan Self


The Roots
of Chinese
Painting
C
enturies ago in China, the first writers, whoever they were, made lines in the sand with their fingers. Then they added another line and another, until the designs reminded them of objects they had seen. The wind blew, and the images disappeared. Later, they found sticks and made marks in the hard dirt. Again, the lines suggested objects.

Meaningful Scratches
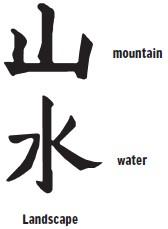
Such drawings were the beginning of written language in China. They are called
pictographs
. Five marks put together in a certain order looked like the sun, so the group of lines was read as “sun.” Other lines put together looked like mountain peaks and were read as “mountain.”
Researchers have discovered pictographs scratched onto turtle shells and the flat shoulder bones of animals. These are sometimes called “oracle bones” because they were used for telling the future. The practice dates back to around 1500 B.C., during the Shang dynasty. About 5,000 different pictographs have been discovered. They represent animals, plants, natural elements, manmade objects, and human beings.
Later, people wrote pictographs in ink with brushes on silk or paper. Over time, the pictographs changed from images of objects to symbolic figures called
characters
. New characters are always being added, so that today the Chinese language has over 50,000 characters. Many of these are not used very often. In China today, people learn how to speak and write about 2,800 characters for everyday use. A highly educated person learns at least 4,000 to 5,000 characters. So kids in China need to spend a lot of time learning to read and write characters.
Calligraphy
Writing a character with a brush is called
calligraphy
. This word means “beautiful writing.” Calligraphy has been very important throughout Chinese history. Learning to write characters correctly, with each brushstroke in the proper order, was considered the sign of an educated person. People who wanted to work in government or business were required to learn calligraphy. A person had to pass a test that awarded the title of “calligrapher.”
In addition to representing a word, brushstrokes could also show the writer’s mood and personality. So calligraphy became more than simply writing to communicate. It was considered the highest form of art. People thought writing characters with a brush was much more impressive than painting pictures. Artists who painted but were not good at calligraphy were not considered good artists.
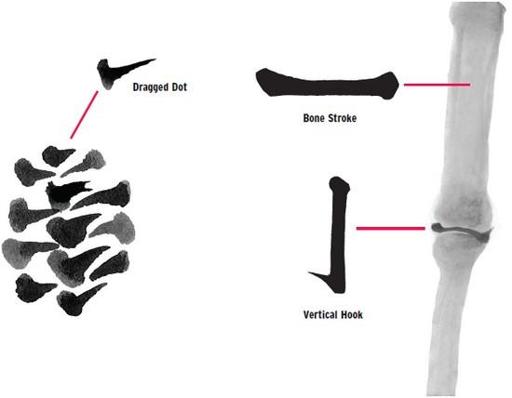
Calligraphers can use different types of scripts to make the characters, just as in Western writing people can use fun or formal alphabets for different purposes. For clear communication, calligraphers use the K’ai-shu script, and you will learn some K’ai-shu characters in this book. The different brushstrokes used to make the characters have names, such as the dragged dot, the bone stroke, and the vertical hook.
Artistic painters learn the K’ai-shu strokes of calligraphy because the same strokes are also used to paint traditional subjects. For example, the dragged dot is used to make the spikes of a pine cone, and variations of the bone stroke and the vertical hook stroke are used in painting bamboo.
This book teaches you the basic strokes of K’ai-shu calligraphy so that you can use the strokes in your paintings and write characters to describe your paintings. Learning the strokes also teaches you how to hold your hand and control the brush and paint.
Can you make these marks with a brush?
Principles of Chinese Characters
A
character
is a picture or “figure” made of brushstrokes. The Chinese language has no letters or alphabet but uses characters instead. Each character represents a word.
Two or more basic parts of characters can be squeezed together to form more complicated words.
One part in a complicated word is called a radical, meaning “root.” The radical is used to look up the word in a dictionary.
Sometimes two characters written one above the other have a special meaning:
The Soft Martial Art
Maybe you or your friends have studied a martial art like karate, aikido, or t’ai chi. You might be surprised, but painting with a brush is like doing a martial art. Why? Because in brush painting, too, you have to focus, especially when painting long strokes:
First, you think about what step you’re at in your painting;
Then, you focus your thoughts on how you are about to move;
You carefully take a breath and hold it;
You make the move;
Toward the end of the stroke, you let out your breath.