Cleopatra: A Life
Authors: Stacy Schiff


Finally, for Max, Millie, and Jo


“Man’s most valuable
trait is a judicious sense of what not to believe.”—EURIPIDES

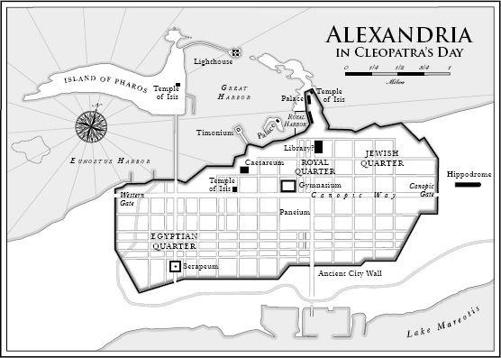
AMONG THE MOST
famous women to have lived, Cleopatra VII ruled Egypt for twenty-two years. She lost a kingdom once, regained it, nearly lost it again, amassed an empire, lost it all. A goddess as a child, a queen at eighteen, a celebrity soon thereafter, she was an object of speculation and veneration, gossip and legend, even in her own time. At the height of her power she controlled virtually the entire eastern Mediterranean coast, the last great kingdom of any Egyptian ruler. For a fleeting moment she held the fate of the Western world in her hands. She had a child with a married man, three more with another. She died at thirty-nine, a generation before the birth of Christ. Catastrophe reliably cements a reputation, and Cleopatra’s end was sudden and sensational. She has lodged herself in our imaginations ever since. Many people have spoken for her, including the greatest playwrights and poets; we have been putting words in her mouth for two thousand years. In one of the busiest afterlives in history she has gone on to become an asteroid, a video game, a cliché, a cigarette, a slot machine, a strip club, a synonym for Elizabeth Taylor. Shakespeare attested to Cleopatra’s infinite variety. He had no idea.
If the name is indelible, the image is blurry. Cleopatra may be one of the most recognizable figures in history but we have little idea of what
she actually looked like. Only her coin portraits—issued in her lifetime, and which she likely approved—can be accepted as authentic. We remember her too for the wrong reasons. A capable, clear-eyed sovereign, she knew how to build a fleet, suppress an insurrection, control a currency, alleviate a famine. An eminent Roman general vouched for her grasp of military affairs. Even at a time when women rulers were no rarity she stood out, the sole female of the ancient world to rule alone and to play a role in Western affairs. She was incomparably richer than anyone else in the Mediterranean. And she enjoyed
greater prestige
than any other woman of her age, as an excitable rival king was reminded when he called, during her stay at his court, for her assassination. (In light of her stature, it could not be done.) Cleopatra descended from a long line of murderers and faithfully upheld the family tradition but was, for her time and place, remarkably well behaved. She nonetheless survives as a wanton temptress, not the last time a genuinely powerful woman has been transmuted into a shamelessly seductive one.
Like all lives that lend themselves to poetry, Cleopatra’s was one of dislocations and disappointments. She grew up amid unsurpassed luxury, to inherit a kingdom in decline. For ten generations her family had styled themselves pharaohs. The Ptolemies were in fact Macedonian Greek, which makes Cleopatra approximately as Egyptian as Elizabeth Taylor. At eighteen Cleopatra and her ten-year-old brother assumed control of a country with a weighty past and a wobbly future. Thirteen hundred years separate Cleopatra from Nefertiti. The pyramids—to which Cleopatra almost certainly introduced Julius Caesar—already sported graffiti. The Sphinx had undergone a major restoration, a thousand years earlier. And the glory of the once great Ptolemaic Empire had dimmed. Cleopatra came of age in a world shadowed by Rome, which in the course of her childhood extended its rule to Egypt’s borders. When Cleopatra was eleven, Caesar reminded his officers that if they did not make war, if they did not obtain riches and rule others, they were not Romans. An Eastern sovereign who waged an epic battle of his own against Rome articulated what would become Cleopatra’s predicament
differently: The Romans had the temperament of wolves. They hated the great kings. Everything they possessed they had plundered. They intended to seize all, and would
“either destroy everything
or perish in the attempt.” The implications for the last remaining wealthy country in Rome’s sphere of influence were clear. Egypt had distinguished itself for its nimble negotiating; for the most part, it retained its autonomy. It had also already embroiled itself in Roman affairs.
For a staggering sum of money, Cleopatra’s father had secured the official designation “friend and ally of the Roman people.” His daughter would discover that it was not sufficient to be a friend to that people and their Senate; it was essential to befriend the most powerful Roman of the day. That made for a bewildering assignment in the late Republic, wracked by civil wars. They flared up regularly throughout Cleopatra’s lifetime, pitting a succession of Roman commanders against one another in what was essentially a hot-tempered contest of personal ambition, twice unexpectedly decided on Egyptian soil. Each convulsion left the Mediterranean world shuddering, scrambling to correct its loyalties and redirect its tributes. Cleopatra’s father had thrown in his lot with Pompey the Great, the brilliant Roman general on whom good fortune seemed eternally to shine. He became the family patron. He also entered into a civil war against Julius Caesar just as, across the Mediterranean, Cleopatra ascended to the throne. In the summer of 48 BC Caesar dealt Pompey a crushing defeat in central Greece; Pompey fled to Egypt, to be stabbed and decapitated on an Egyptian beach. Cleopatra was twenty-one. She had no choice but to ingratiate herself with the new master of the Roman world. She did so differently from most other client kings, whose names, not incidentally, are forgotten today. For the next years she struggled to turn the implacable Roman tide to her advantage, changing patrons again after Caesar’s murder, ultimately to wind up with his protégé, Mark Antony. From a distance her reign amounts to a reprieve. Her story was essentially over before it began, although that is of course not the way she would have seen it. With her death Egypt became a Roman province. It would not recover its autonomy until the twentieth century.
Can anything good be said of a woman who slept with the two most powerful men of her time? Possibly, but not in an age when Rome controlled the narrative. Cleopatra stood at one of the most dangerous intersections in history: that of women and power. Clever women, Euripides had warned hundreds of years earlier, were dangerous.
A Roman historian
was perfectly happy to write off a Judaean queen as a mere figurehead and—six pages later—to condemn her for her reckless ambition, her indecent embrace of authority. A more disarming brand of power made itself felt as well. In a first-century BC
marriage contract
, a bride promised to be faithful and affectionate. She further vowed not to add love potions to her husband’s food or drink. We do not know if Cleopatra loved either Antony or Caesar, but we do know that she got each to do her bidding. From the Roman point of view she “enslaved” them both. Already it was a zero-sum game: a woman’s authority spelled a man’s deception. Asked how she had obtained her influence over Augustus, the first Roman emperor, his wife purportedly replied that she had done so
“by being scrupulously chaste
herself, doing gladly whatever pleased him, not meddling with any of his affairs, and, in particular, by pretending neither to hear of nor to notice the favorites that were the objects of his passion.” There is no reason to accept that formula at face value. On the other hand, Cleopatra was cut from very different cloth. In the course of a leisurely fishing trip, under a languid Alexandrian sun, she had no trouble suggesting that the most celebrated Roman general of the day tend to his responsibilities.
To a Roman, license and lawlessness were Greek preserves. Cleopatra was twice suspect, once for hailing from a culture known for its
“natural talent for deception
,” again for her Alexandrian address. A Roman could not pry apart the exotic and the erotic; Cleopatra was a stand-in for the occult, alchemical East, for her sinuous, sensuous land, as perverse and original as its astonishment of a river. Men who came in contact with her seem to have lost their heads, or at least to have rethought their agendas. She runs away even with Plutarch’s biography of Mark Antony. She works the same effect on a nineteenth-century historian, who describes
her, on meeting Caesar, as
“a loose girl of sixteen.”
(She was rather an intensely focused woman of twenty-one.) The siren call of the East long predated Cleopatra, but no matter; she hailed from the intoxicating land of sex and excess. It is not difficult to understand why Caesar became history, Cleopatra a legend.
Our view is further obscured by the fact that the Romans who told Cleopatra’s story very nearly knew their ancient history too well. Repeatedly it seeps into their accounts. Like Mark Twain in the overwhelming, overstuffed Vatican, we sometimes prefer the copies to the original. So did the classical authors. They conflated accounts, refurbishing old tales. They saddled Cleopatra with the vices of other miscreants. History existed to be retold, with more panache but not necessarily greater accuracy. In the ancient texts the villains always wear a particularly vulgar purple, eat too much roasted peacock, douse themselves in rare unguents, melt down pearls. Whether you were a transgressive, power-hungry Egyptian queen or a ruthless pirate, you were known for the
“odious extravagance”
of your accessories. Iniquity and opulence went hand in hand; your world blazed purple and gold. Nor did it help that history bled into mythology, the human into the divine. Cleopatra’s was a world in which you could visit the relics of Orpheus’s lyre, or view the egg from which Zeus’s mother had hatched. (It was in Sparta.)
