Delphi Complete Works of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (Illustrated) (1343 page)
Read Delphi Complete Works of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (Illustrated) Online
Authors: SIR ARTHUR CONAN DOYLE

Allusion has been made to the check caused by the strong point called “The Pump” and the trenches called the Kleemanstellung just east of it. Some detail should be added in this matter, for it retarded the attack of the flanks of two divisions, and the delay caused by it had the effect that the Canadians on the left and the Ninth upon the right were further forward in the late afternoon than part of the Fifty-first and the Thirty-fourth, which might have caused a dangerous situation. The Thirty-fourth Division had advanced upon a three-brigade front, which consisted from the south of the 101st, the 102nd, and the 103rd. On the north of the 103rd was the 152nd Brigade of the Fifty-first Division with the Seaforths as the flank battalion. This pestilent strong point, armed with well-served and well-concealed machine-guns, lay between the two brigades and held up the flanks of both, inflicting considerable losses not only on the Seaforths, but on the 25tb Northumberland Fusiliers, who were on Chapter the left of the Thirty-fourth Division. For a considerable time the advance was held. The 27th reserve battalion of the Northumberland Fusiliers were sent up, and one of its companies, led with a fine mixture of valour and cunning, carried the place by storm. The whole line then got forward, but the losses had been heavy, including Colonel Hermon of the 24th Northumberland Fusiliers. In the evening it was found that the final objective had not yet been fully attained at this quarter of the field, for it had been marked at a farm called Maison de la Côte, from which the front line was still a thousand yards distant. A brilliant little attack, however, by the 103rd Brigade, in the early morning of April 10, captured the whole position. Besides the check at The Pump, there had been another on the Fifty-first divisional front at a post called the “Deutsches Haus.” The consequence of this was a loss of the barrage and a delay which led to the isolated left of the Fifty-first losing direction entirely and wandering round in a half-circle. The circumstances were so complex that it was not until next morning that they could be cleared up. Had the Germans had the spirit for a counter-attack, they would certainly have found a considerable gap in the line.
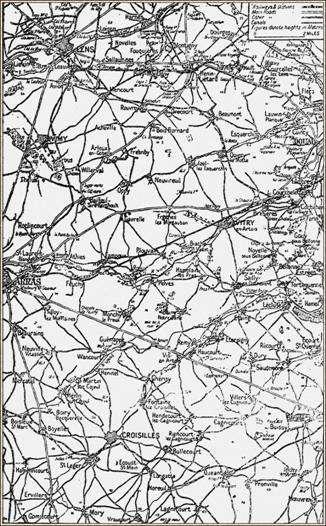
The Arras Front
These events were in the northern area of the Seventeenth Corps. In the southern portion, at about eleven o’clock, the reserve division came forward, and, passing through the weary ranks of the Ninth, pushed on along the northern bank of the river. The advance had already been a splendid one, the Ninth Division having 2000 prisoners to its credit, but this movement of the Fourth Division against an enemy who was already badly shaken was a very fruitful one. The 12th Brigade was nearest the Scarpe, with the 11th upon the left, while the 10th moved forward in close support. Two obstacles faced the division, the straggling village of Fampoux upon the bank of the river, and the Hyderabad Redoubt, a considerable fort to the north of the village. The 12th Brigade moved swiftly forward in the nearest approach to open warfare that had been seen for years. The 1st Royal Lancasters were on the right of the swift flexible line, the 2nd Lancashire Fusiliers in the centre, and the 2nd Essex upon the left. The brigade fought its way in the teeth of a very hot fire to the outskirts of Fampoux, where the reserve battalion, the 2nd West Ridings, passed through the King’s Own and carried the village in splendid style late in the evening at the point of the bayonet. It is a remarkable fact that the wire in front of the village had not been cut by the artillery, and the infantry passed in single file through the gaps in it, after disposing of the only German machine-gunner who offered resistance. At the same time the 11th Brigade kept pace upon their left flank — the Hampshires to the left and Somersets to the right, while the 1st Rifle Brigade, passing through them, rushed the strong position of the Hyderabad Redoubt, and the East Lancashires formed a defensive flank. Communication was at once opened across the Scarpe with Haldane’s Corps upon the south side. By this fine advance of the Fourth Division the right of the Seventeenth Corps had got considerably further forward than the centre, so that a defensive line had to be formed sloping back from this advanced point. This was the position upon the evening of the first day of battle, and it was destined to remain so in the south for many a day to come, for the formidable Chemical Works lay immediately to the east on either side of the Arras-Douai railway track, and these were to prove a very grave obstacle to a further advance on this line. Meanwhile, 3500 prisoners with 50 captured guns testified to the success of the Seventeenth Corps.
Following upon this brief sketch of the work done by the Seventh, Sixth, and the Seventeenth Corps upon the first day of the Battle of Arras, we must now turn to the splendid achievement of the Canadian Corps upon the left. The reputation of the Canadians as brilliant soldiers, as dashing in attack as they were steady in defence, had already been solidly established by a long series of military feats beginning with the ever-memorable second battle of Ypres and continuing on to the capture of Courcelette and the fine fighting of the Somme. Hitherto, they had acted in comparatively small bodies, but now the whole might of Canada was drawn together in the four fine divisions which lay facing the historic Vimy Ridge — a long gradual slope which reaches a height of more than
During the night of the 9/1 0th April there was fighting at several points, notably at the north end of the Vimy Ridge. Here the Fourth Canadian Division had some difficulty in holding its ground against several strong counter-attacks of the Germans. It is probable that no body of troops in the whole battle had a harder task, or stuck to it more tenaciously, than this Fourth Canadian Division. Hill 145, which was an outlier of the Ridge, was very strongly held and desperately defended, so that it would have turned any but first-class troops. The final clearing of this point was effected upon April 10, and led to further operations in conjunction with British troops to the north, which will be afterwards described.
The second day of the Battle of Arras, April 10, was spent partly in the consolidation of the ground gained and partly in increasing the area now occupied. The troops were in high heart, for although the full extent of the victory had not yet been realised, it was already known that at least 10,000 prisoners and 100 guns had fallen into their hands, figures which showed that the battle had been the most serious military disaster which had yet befallen the enemy. A fuller enumeration taken some days later gave 13,000 men, 3 howitzers, 28 heavy guns, 130 field-guns, 84 trench-mortars, and 250 machine-guns as the total capture. It may be mentioned that over 1000 prisoners were taken from each of the six different German divisions already enumerated, which disposes of their mendacious assertion that only two divisions occupied their front. It was certainly the greatest blow delivered by the British Army up to that date; and the only other day’s fighting at all comparable in its results was the French attack upon the Champagne front on September 25, 1915, where the number of prisoners was greater but the capture of guns was
The Battle of Arras may be considered as having been in truth a one-day battle in the same sense as the succeeding Battle of Messines, for in each case the attack was delivered in order to gain a definite objective, which was the ridge from which observation could be obtained. The extreme limit of advance had not, however, been reached either in the south or in the north, and so in both these areas hard fighting continued, due partly to the efforts of the British to enlarge their gains and partly to the rally of the Germans and their attempts at counter-attack. There was no concentration of troops or guns, however, upon the side of the British, and no attempt at any considerable advance. We shall first follow these operations in the south where they centred chiefly round the village of Monchy and Wancourt in the areas of the Sixth and Seventh Corps. These we shall weave into a connected narrative, after which we shall return to the Vimy region and trace the movements which led to hard fighting in that quarter.
In the Seventh Corps to the south the Fifty-sixth Division of London Territorials had, as already described, enlarged the area which it had taken the day before in the Neuville Vitasse sector. The general curve of the line was such that it was not possible for the units of the Seventh Corps to get forward until the Sixth Corps to the north had won some ground, but upon the afternoon of the 12th a very fine advance was made, by which the 169th Brigade stormed Heninel. The Cojeul River was crossed by the Fourteenth Light Division, and the heights upon the eastern bank were occupied. The 41st Brigade of this unit had now come into the line. The first attempt upon the heights failed with heavy losses Next morning it was found that Hill 90 had been evacuated, and they were able to advance and seize Wancourt. This brought the left flank of the Seventh Corps up to the right flank of the Sixth Corps, and ensured close co-operation in those operations to the north which will presently be more fully described. This storming of the German position in this section was the more important as the troops were faced by the new Hindenburg Line. It was well known that an alternative line from Drocourt to Quéant existed some miles to the eastward, but none the less the fall of the front section at a period when much of its wire was still intact proved to the Germans how impossible it was to hold off British troops by mere passive obstacles. The tanks were of great assistance to the assailants in this difficult operation. Upon April 13 and 14 the Twenty-first Division, with the aid of the 19th Brigade from the Thirty-third Division, carried forward the line to the high ground about
The immediate task which lay before the Sixth Corps upon April 10 was to get the Third and Twelfth Divisions forward to the same line which the Fifteenth Division had reached. It will be remembered that the 46th Brigade of the latter division, together with the 63rd Brigade from the supporting Thirty-seventh Division, had pushed on as far as Orange Hill, half a mile farther eastward than the Feuchy Line which formed the front of the two southern Divisions. Six brigades of field artillery had been hurried up, and with the help of these guns, aided by trench-mortars, the wire which held up the advance was partly blown away. The Third and Twelfth Divisions were then able to move forward and to make one line with the Fifteenth — an operation which was completed by mid-day, the 8th Brigade doing some brilliant work. The strongly fortified-village of Monchy, elevated above the plain, lay immediately in front of the Sixth Corps, and its capture was their next task. With this object in view, the 63rd Brigade was swung found from the north and worked its way south and east, getting into touch with the other brigades of the Thirty-seventh Division, which passed through the newly captured third objective and occupied the ground upon the west of the village. A general advance was then made on each side of the village, the 112th Brigade occupying La Bergère upon the Cambrai road due south of Monchy, while the 1/1 1th Brigade, with the 9th and 10th Royal Fusiliers in the lead, in the face of a considerable opposition, pushed onwards until it gained a footing on the outskirts of the village and on the high ground to the north of it, where the 154th Company R.E. dug a temporary line. This was the position on the evening of April 10, while the British line had been strengthened by the presence of the 7th Brigade of Cavalry from the Third Cavalry Division, who were following closely behind the Thirty-seventh Division. In all these operations the weather greatly impeded progress, as it prevented the advance of the guns needed to break down wire and other obstacles.
