Essential Facts on the Go: Internal Medicine (40 page)
Read Essential Facts on the Go: Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Lauren Stern,Vijay Lapsia
Tags: #Medical, #Family & General Practice, #Internal Medicine

ONCOLOGY-HEMATOLOGY
X_1_a
Oncologic Emergencies
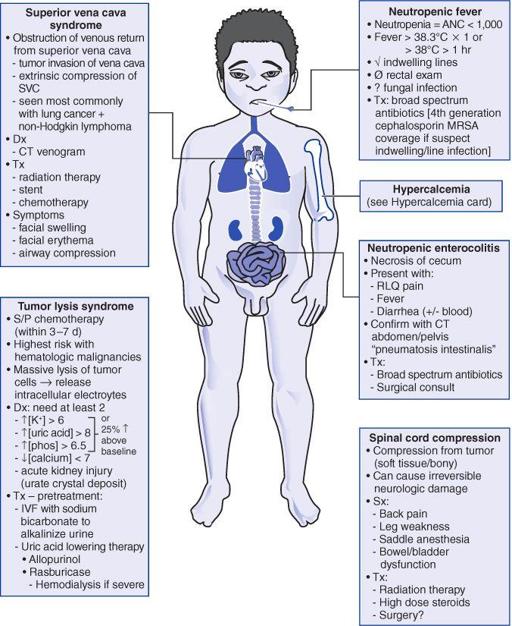
X_1_b
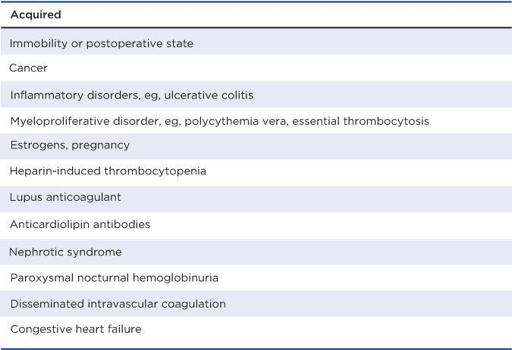
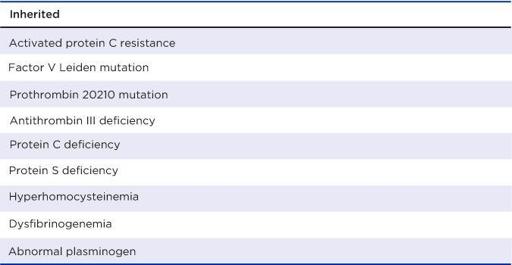
Risk Factors for Hypercoagulable State
Etiology
MEDICATIONS
XI_1_a
Corticosteroids: Potency and Monitoring
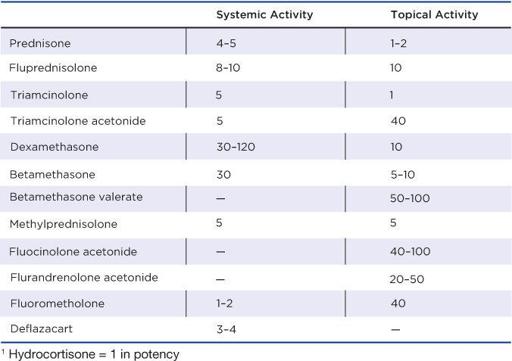
Monitoring Recommendations
• Screen for tuberculosis with a purified protein derivative (PPD) test or chest radiograph before commencing long-term corticosteroid therapy.
• Screen for diabetes mellitus before treatment and at each clinician visit.
Have patient test urine weekly for glucose.
Teach patient about the symptoms of hyperglycemia.
• Screen for hypertension before treatment and at each clinician visit.
• Screen for glaucoma and cataracts before treatment, 3 months after treatment inception, and then at least yearly.
• Monitor plasma potassium for hypokalemia and treat as indicated.
• Obtain bone densitometry before treatment and then periodically. Treat osteoporosis.
• Weigh daily. Use dietary measures to avoid obesity and optimize nutrition.
• Measure height frequently to document the degree of axial spine demineralization and compression.
• Watch for fungal or yeast infections of skin, nails, mouth, vagina, and rectum, and treat appropriately.
• With dosage reduction, watch for signs of adrenal insufficiency or corticosteroid withdrawal syndrome.
XI_1_b
Opiate Conversions
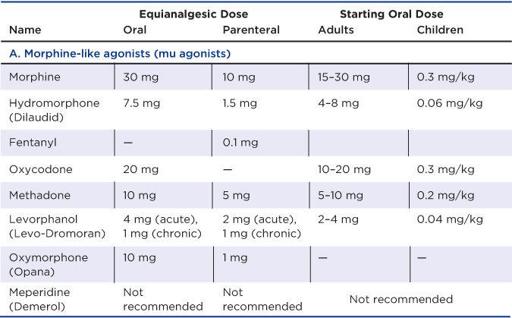
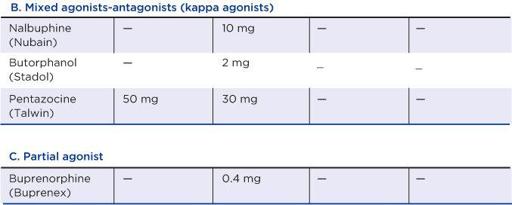
Starting dose should be lower for older adults. These are standard parenteral doses for acute pain in adults and can also be used to convert doses for IV infusions and repeated small IV boluses. For single IV boluses, use half the IM dose. IV doses for children > 6 months = parenteral equianalgesic dose times weight (kg)/100. Irritating to tissues with repeated IM injections.
Modified from American Pain Society,
Principles of Analgesic Use in the Treatment of Acute Pain and Cancer Pain
, 6th ed. American Pain Society, 2008.
OPHTHALMOLOGY
XII_1_a
Selected Retinopathies on Funduscopy

Background diabetic retinopathy: hard exudates, dot hemorrhages, blot hemorrhages, flame hemorrhages, and microaneurysms
1

Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
2

Background diabetic retinopathy: diabetic maculopathy
3

