Pediatric Examination and Board Review (192 page)
Read Pediatric Examination and Board Review Online
Authors: Robert Daum,Jason Canel

12.
(C)
Cigarette burns that are inflicted are usually ovoid and deep, partial-thickness burns that leave a scar. They are about 1 cm in diameter. Round, nonspecific lesions that are hypopigmented are often indeterminate in terms of etiology. In this case, the location of the lesions that are mirror images or kissing lesions on the buttocks raises the question of an infectious etiology (eg, bullous impetigo). The key to making a diagnosis is eliciting a good history from the caretakers as to the presentation, age, and timing of the lesions’ appearance, as well as healing and associated symptoms at the time of presentation.
13.
(B)
When a physician receives a subpoena, he or she must recognize the subpoena is a court order and cannot be ignored. The subpoena may ask for the physician to testify, which is a subpoena ad testificandum, or it may ask for the doctor to appear and bring records or documents. A subpoena that requests documents is called a subpoena duces tecum. The judgment standard required in civil or family court is “preponderance of evidence” (ie, more likely than not). In criminal court, the judgment standard is “beyond reasonable doubt.” An expert witness provides testimony that is either an opinion, an answer to a hypothetical question, or an educational process (eg, lectures on a given subject). The doctor who receives a subpoena as a treating physician will be asked questions with regard to his or her evaluation (eg, historical findings, medical tests, and diagnosis). The judge must be convinced that the expert possesses sufficient knowledge, skill, and experience to qualify.
14.
(E)
Lack of supervision is an identifiable form of neglect. Child neglect is the failure to meet a child’s medical, emotional, environmental, and educational needs. Broadly defined it does not address resources or intent of the parent. Neglect should be viewed within a societal and cultural context. The potential of a lack of supervision must be recognized as potentially fatal. It is important for the pediatrician to be familiar with his or her jurisdiction’s legal definitions and recognize that not all catastrophic outcomes are because of negligence. However, pediatricians have a unique opportunity to help screen preschool-age children who are at risk for neglect and abuse.
15.
(E)
Although prenatal exposure to alcohol and opiates can lead to microcephaly and alcohol is associated with short stature (in addition to other characteristics of fetal alcohol syndrome [FAS]), cocaine and marijuana are not currently accepted explanations for postnatal growth failure. The medical evaluation should be based on family history, medical history, and physical examination.
16.
(B)
Effective management of child neglect must employ a systematic and thorough approach by the clinician. Intervention often requires a long-term investment. Assessment using social services is often a successful strategy to engage the family and develop a care plan. Depending on the circumstances that lead to a neglect concern, child welfare referrals for services without a report are possible in some states. Timely reporting of children who are at risk for harm where the physician either feels he or she cannot assess the level of risk or where the initial assessment is that the family is not invested in a care plan does push the response toward a consideration of formal reporting to child welfare authorities.
17.
(B)
Unfortunately, child welfare systems vary in their expertise with regard to interventional services for FTT, and physicians should not assume that child welfare systems have integrated programs replete with medical expertise to provide a longterm care plan for children with FTT. Children with FTT benefit from early interventional services, another system for monitoring and engagement with the family. Enteral feedings may be necessary for catch-up growth, but the need for this intervention depends on many factors.
18.
(D)
A 10-year-old with sickle cell disease who presents with life-threatening anemia warrants lifesustaining intervention and will require the treating team to take protective custody to treat this child in crisis. The process for this should be known by the physician in advance because it will vary by geographic locale.
 S
S
UGGESTED
R
EADING
Jenny C; Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect. Recognizing and responding to medical neglect.
Pediatrics.
2007;120: 1385-1389.
Child Welfare Information Gateway Website.
http://Childwelfare. gov/
.
Reece RM, Christian CW, eds.
Child Abuse
:
Medical Diagnosis and Management
. 3rd ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics; 2009.
CASE 108: A 2-YEAR-OLD WITH A BURN
A 2-year-old African American girl presents with her aunt for evaluation of a sharply demarcated burn to her right lower leg. The patient is in pain but consoled when sitting in her aunt’s lap. On examination, the child has sustained a burn to the left lower extremity in a stocking distribution (see
Figure 108-1
). The child is alert and appears to be in good health.
SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER
1.
Which of the following descriptions is most consistent with your examination?
(A) 5-10% first-degree scald burn
(B) 3-5% partial-thickness scald burn
(C) 5% partial-thickness flame burn
(D) 9% second-degree contact burn
(E) 5-10% chemical burn
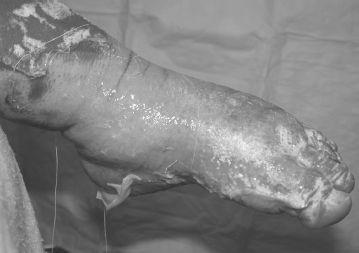
FIGURE 108-1.
Scald burn to the lower extremity of a 2-yearold. See color plates.
2.
Which of the following statements about the depth of a burn is false?
(A) the depth of a burn is an important determinant of severity, management, and potential complications
(B) a first-degree burn or superficial partialthickness burn is painful; such burns are confined to the epidermis and are red because of an inflammatory response in the skin. Healing occurs in 3-5 days without scar formation
(C) a second-degree burn is a partial-thickness burn that involves the epidermis and the dermis; the involvement of the dermis distinguishes between a superficial partial-thickness versus a deep partial-thickness burn where the superficial burn involves less than half of the dermis, has blisters, redness, and swelling; it takes about 2 weeks to heal with minimal scar formation
(D) fourth-degree burns are third-degree burns with secondary infection
(E) full-thickness burns involve destruction of the epidermis and dermis; they are pale, nontender, and cannot heal because they cannot reepithelialize; grafting is required in most of these burns
3.
Appropriate immediate management of this patient would include
(A) debridement, application of silver sulfadiazine cream, and discharge to follow up with a plastic surgeon
(B) debridement, application of 1% silver sulfadiazine cream, admission, and oral hydration
(C) intravenous (IV) hydration, hospitalization, prophylactic oral antibiotics, and pain management
(D) IV hydration and pain control, wound management, and surgical consultation
(E) IV hydration, wound management, IV antibiotics, and consultation with child welfare
4.
Which is a true statement regarding burn injuries and children?
(A) children make up one-half to two-thirds of all burn admissions annually
(B) the most frequent type of burn in children younger than 4 years are electrical burns
(C) nearly 25% of burns in children are life threatening
(D) flame burns related to cooking injuries are responsible for most thermal injuries in children younger than 4 years of age
(E) the risk of thermal injury in children may be reduced by lowering the water heater temperature to 120°F (48.8°C)
5.
The aunt does not know the child’s immunization status; the mother is currently unavailable by phone. Because of the seriousness of this burn you elect to do which of the following?
(A) initiate antibiotic prophylaxis to protect against streptococcal infection
(B) administer tetanus toxoid
(C) administer tetanus immune globulin
(D) administer tetanus toxoid and immune globulin
(E) provide local wound care at this point
6.
Once the child is stabilized, you start to obtain a more extensive history of the injury. According to the aunt, who was the caretaker of this child when the injury occurred, she had just boiled water to use to wash the floor because her hot water heater is broken. She had the hot water in a bucket on the floor in the kitchen. She thought the child was napping and went to get the mop from the closet when she heard the child crying and found her lying on the floor. She examined the child, took her sock off, and found that her foot was red. She ran the child’s foot under cold water. Blisters started to appear and she called 911. No one else was home at the time of the injury, but the aunt did run to the next apartment to ask her neighbor to help as they waited for the ambulance. The next appropriate management steps would include the following
