The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (1897 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
4.73Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
P
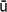 r
r
 a-yoga
a-yoga
.
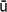 r
r a-yoga
a-yoga.
Purohita
.
.
Early functionary in Aryan India, who counselled the ruler, especially through ritual techniques. The best-known purohita in post-Vedic times was Kau
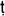 ilya, to whom
ilya, to whom
Artha
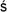 astra
astra
is attributed. See also
VASI
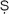 THA
THA
. In the Vedic period, the purohita was also an advisor at all levels of sacrifice, and could be the officiant.
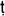 ilya, to whom
ilya, to whomArtha
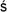 astra
astrais attributed. See also
VASI
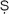 THA
THA. In the Vedic period, the purohita was also an advisor at all levels of sacrifice, and could be the officiant.
Puru
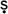 a
a
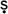 a
a(Skt., ‘man’, ‘person’). A spiritual concept variously understood in Hindu religion and philosophy. The famous
Puru
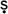 a-s
a-s
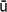 kta
kta
(
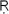 g Veda
g Veda
10. 90) celebrates puru
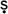 a as a cosmic demiurge, the material and efficient cause of the universe, whose sacrifice and division gave rise to the
a as a cosmic demiurge, the material and efficient cause of the universe, whose sacrifice and division gave rise to the
Veda
and all of creation. The early
Upani
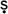 ads
ads
and the
Bhagavad-g
 t
t
 use the term to mean an individual's spirit, psychic essence, or immortal Self. In
use the term to mean an individual's spirit, psychic essence, or immortal Self. In
S

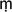 khya
khya
philosophy, puru
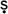 a is the first principle (
a is the first principle (
tattva
), pure contentless consciousness, passive, unchanging, and witness to the unconscious dynamism of
Prak
 ti
ti
, primordial materiality.
Puru
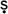 a-s
a-s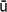 kta
kta(
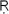 g Veda
g Veda10. 90) celebrates puru
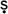 a as a cosmic demiurge, the material and efficient cause of the universe, whose sacrifice and division gave rise to the
a as a cosmic demiurge, the material and efficient cause of the universe, whose sacrifice and division gave rise to theVeda
and all of creation. The early
Upani
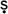 ads
adsand the
Bhagavad-g
 t
t use the term to mean an individual's spirit, psychic essence, or immortal Self. In
use the term to mean an individual's spirit, psychic essence, or immortal Self. InS

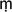 khya
khyaphilosophy, puru
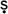 a is the first principle (
a is the first principle (tattva
), pure contentless consciousness, passive, unchanging, and witness to the unconscious dynamism of
Prak
 ti
ti, primordial materiality.
Other books
Encyclopedia Brown Gets His Man by Donald J. Sobol
Night Plague: A Post Apocalyptic Thriller by Rook, Rowan
10 - The Ghost Next Door by R.L. Stine - (ebook by Undead)
AddingHeat by Anson, Cris
Clarity's Doom (Ancient Origins Book 1) by C.L. Scholey
Someone Like You by Susan Mallery
Witness Protection (Defenders of Love Book 1) by LaRoche, Carolyn
Duty Bound (1995) by Scott, Leonard B
Reawakened by the Surgeon's Touch by Jennifer Taylor


 ri
ri