The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (2256 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
3.73Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Sh
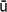 j
j

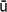 j
j
(Jap., ‘teaching of a school’). The teaching of a Buddhist school or movement, and in particular that of
Zen
.
Zen
.
Shul
(Yid., ‘School’). Yiddish term for
synagogue
, common among
Ashkenazi
Jews in Europe. It was a community meeting-place, in which local politics were as prominent as prayer.
synagogue
, common among
Ashkenazi
Jews in Europe. It was a community meeting-place, in which local politics were as prominent as prayer.
Shul

 n Arukh
n Arukh

 n Arukh
n Arukh(Heb., ‘the prepared table’). Code of Jewish
halakhah
(law) written by Joseph
Caro
. The
Shul

 n Arukh
n Arukh
is a synopsis of
Jacob b. Asher's
Arba‘ah Turim
. Its four parts deal with the daily and
Sabbath
Commandments
, laws governing everyday life (e.g.
dietary laws
,
purity
,
mourning
), laws of
marriage and divorce
and, finally, civil and criminal law. It was first printed in 1565, and after amendments for the
Ashkenazim
had been added by Moses
Isserles
, it became accepted as the most authoritative code of Jewish law.
halakhah
(law) written by Joseph
Caro
. The
Shul

 n Arukh
n Arukhis a synopsis of
Jacob b. Asher's
Arba‘ah Turim
. Its four parts deal with the daily and
Sabbath
Commandments
, laws governing everyday life (e.g.
dietary laws
,
purity
,
mourning
), laws of
marriage and divorce
and, finally, civil and criminal law. It was first printed in 1565, and after amendments for the
Ashkenazim
had been added by Moses
Isserles
, it became accepted as the most authoritative code of Jewish law.
Shushi-gaku
.
.
Japanese term for the orthodox
neo-Confucian
teachings of
Chu Hsi
(1130–1200) and his followers. The major advocates of Shushi-gaku in Japan were Hayashi Razan (1583–1657), who served the sh
 gun and established a school staffed throughout the Tokugawa (1600–1868) period by his descendants, and Yamazaki Ansai (1618–82), who stressed the more religious aspects of neo-Confucianism.
gun and established a school staffed throughout the Tokugawa (1600–1868) period by his descendants, and Yamazaki Ansai (1618–82), who stressed the more religious aspects of neo-Confucianism.
neo-Confucian
teachings of
Chu Hsi
(1130–1200) and his followers. The major advocates of Shushi-gaku in Japan were Hayashi Razan (1583–1657), who served the sh
 gun and established a school staffed throughout the Tokugawa (1600–1868) period by his descendants, and Yamazaki Ansai (1618–82), who stressed the more religious aspects of neo-Confucianism.
gun and established a school staffed throughout the Tokugawa (1600–1868) period by his descendants, and Yamazaki Ansai (1618–82), who stressed the more religious aspects of neo-Confucianism.Other books
A Touch of Mistletoe by Megan Derr, A.F. Henley, Talya Andor, E.E. Ottoman, J.K. Pendragon
The Boy in the Black Suit by Jason Reynolds
Rise of the Dark Sun (The Blood Lust Plague Trilogy Book 1) by Kendall Pearce
Wicked Ties (Steele Security Series) by Justice, A.D.
Happy Endings by Jon Rance
Last Car to Annwn Station by Michael Merriam
Always by Nicola Griffith
TurningWildBlankEditionHTML by Erika Masten
Horse Talk by Bonnie Bryant
[Invitation to Eden 21.0] Falling or Flying by RG Alexander


