The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (290 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
2.08Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
A
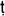
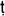 ha-loka-dhamma
ha-loka-dhamma
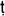
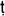 ha-loka-dhamma
ha-loka-dhamma(P
 li, ‘eight worldly concerns’). Buddhism teaches that there are eight matters which are common human preoccupations. They are ‘gain and loss, fame and obscurity, praise and blame, happiness (
li, ‘eight worldly concerns’). Buddhism teaches that there are eight matters which are common human preoccupations. They are ‘gain and loss, fame and obscurity, praise and blame, happiness (
sukha
) and suffering (
dukkha
)’. Looking at the world in these terms, however, is regarded as inherently unsatisfying, and perfect happiness (
paramasukha
) is not possible until they are abandoned.
 li, ‘eight worldly concerns’). Buddhism teaches that there are eight matters which are common human preoccupations. They are ‘gain and loss, fame and obscurity, praise and blame, happiness (
li, ‘eight worldly concerns’). Buddhism teaches that there are eight matters which are common human preoccupations. They are ‘gain and loss, fame and obscurity, praise and blame, happiness (sukha
) and suffering (
dukkha
)’. Looking at the world in these terms, however, is regarded as inherently unsatisfying, and perfect happiness (
paramasukha
) is not possible until they are abandoned.
Auden, Wystan Hugh
(1907–73).
A poet increasingly involved in the exploration and expression of Christian themes. After the death of his mother (a committed Anglo-Catholic) in 1941, he became increasingly concerned with religion. This is particularly evident in a Christmas oratorio (written for Benjamin Britten),
For the Time Being
(1944) and a reflection on Good Friday,
Horae Canonicae
(1955). Acknowledgement of guilt becomes the ground of freedom: to live in the tangle of human history makes one, inevitably, an accomplice, but to acknowledge complicity is the beginning of
grace
.
A poet increasingly involved in the exploration and expression of Christian themes. After the death of his mother (a committed Anglo-Catholic) in 1941, he became increasingly concerned with religion. This is particularly evident in a Christmas oratorio (written for Benjamin Britten),
For the Time Being
(1944) and a reflection on Good Friday,
Horae Canonicae
(1955). Acknowledgement of guilt becomes the ground of freedom: to live in the tangle of human history makes one, inevitably, an accomplice, but to acknowledge complicity is the beginning of
grace
.
Augsburg Confession
.
.
A summary of the Christian faith drawn up during the
Reformation
for the Diet of Augsburg, and presented to the emperor Charles V. It was written by
Luther
,
Melanchthon
, and two others. A final authorized text was issued, to create the document which remains of foundational importance in Lutheranism. The first twenty-one articles deal with similarities and dissimilarities between Lutherans and Roman Catholics, the last seven with abuses in the existing church.
Reformation
for the Diet of Augsburg, and presented to the emperor Charles V. It was written by
Luther
,
Melanchthon
, and two others. A final authorized text was issued, to create the document which remains of foundational importance in Lutheranism. The first twenty-one articles deal with similarities and dissimilarities between Lutherans and Roman Catholics, the last seven with abuses in the existing church.
Augustine of Canterbury, St
(d. 604 or 605).
Missionary to England and first
archbishop
of
Canterbury
. He was sent by Pope
Gregory
in 596 to re-establish the church in England. A few months after his landing in 597, Christianity was formally adopted by King Ethelbert of Kent. About 603 he attempted but failed to reach an agreement with the Celtic Church on matters of discipline and practice. At Canterbury, he helped to establish the monastery of Sts Peter and Paul, where the first ten archbishops were buried.
Missionary to England and first
archbishop
of
Canterbury
. He was sent by Pope
Gregory
in 596 to re-establish the church in England. A few months after his landing in 597, Christianity was formally adopted by King Ethelbert of Kent. About 603 he attempted but failed to reach an agreement with the Celtic Church on matters of discipline and practice. At Canterbury, he helped to establish the monastery of Sts Peter and Paul, where the first ten archbishops were buried.
Augustine of Hippo, St
(354–430).
Christian
father
and
doctor of the Church
. He was a native of Tagaste in N. Africa. His mother
Monica
was a Christian, but as a young man he gradually abandoned what Christian belief he had. For nine years he was associated with the
Manichaeans
, but had left this religion also by the time he came to Rome as a teacher of rhetoric. Becoming a professor of rhetoric at Milan, he became a Neoplatonist and, under the influence of
Ambrose
, was converted to Christianity in 386, after responding to a command, ‘Tolle, lege’, and opening the New Testament at Romans 13. 13 f. He returned to N. Africa, was ordained priest in 391 and became
bishop
of Hippo (modern B
 ne in Algeria)
ne in Algeria)
c.
396. His own life and conversion were the subject of his deeply moving
Confessions.
Augustine's influence on Christian thought and theology, especially down to the 13th cent., has been immense. His own theology was formulated in controversy with three opponents in particular. First, against Manichaeism, he defended the essential goodness of all that God, as sole creator, has created. Thus evil could only be
privatio boni
, the absence of the good which ought to be. Second, the
Donatist
controversy caused him to formulate systematic doctrines of the church and
sacraments
. Augustine's last battle was with the
Pelagians
, clarifying his teaching on the
fall
,
original sin
, and
predestination
. He held that man's original endowment from God was lost by the fall of
Adam
, so that now all suffer from an inherited defect and liability from Adam's sin; and from this the whole human race is justly
massa damnata
, to be saved only by the grace of God. Since God knows what he intends to do, Augustine is inevitably predestinarian to some extent, and this influenced especially
Calvin
and other Reformers. Apart from his polemical works, the
Confessions
and
The
City of God
are most important.
Christian
father
and
doctor of the Church
. He was a native of Tagaste in N. Africa. His mother
Monica
was a Christian, but as a young man he gradually abandoned what Christian belief he had. For nine years he was associated with the
Manichaeans
, but had left this religion also by the time he came to Rome as a teacher of rhetoric. Becoming a professor of rhetoric at Milan, he became a Neoplatonist and, under the influence of
Ambrose
, was converted to Christianity in 386, after responding to a command, ‘Tolle, lege’, and opening the New Testament at Romans 13. 13 f. He returned to N. Africa, was ordained priest in 391 and became
bishop
of Hippo (modern B
 ne in Algeria)
ne in Algeria)c.
396. His own life and conversion were the subject of his deeply moving
Confessions.
Augustine's influence on Christian thought and theology, especially down to the 13th cent., has been immense. His own theology was formulated in controversy with three opponents in particular. First, against Manichaeism, he defended the essential goodness of all that God, as sole creator, has created. Thus evil could only be
privatio boni
, the absence of the good which ought to be. Second, the
Donatist
controversy caused him to formulate systematic doctrines of the church and
sacraments
. Augustine's last battle was with the
Pelagians
, clarifying his teaching on the
fall
,
original sin
, and
predestination
. He held that man's original endowment from God was lost by the fall of
Adam
, so that now all suffer from an inherited defect and liability from Adam's sin; and from this the whole human race is justly
massa damnata
, to be saved only by the grace of God. Since God knows what he intends to do, Augustine is inevitably predestinarian to some extent, and this influenced especially
Calvin
and other Reformers. Apart from his polemical works, the
Confessions
and
The
City of God
are most important.
Other books
Magical Masquerade: A Regency Masquerade by Gilman, Hilary
A Desperate Wager by Em Taylor
Assignment - Karachi by Edward S. Aarons
Rescate en el tiempo by Michael Crichton
The City Below by James Carroll
Cloud Cuckoo Land by Anthony Doerr
Joss Whedon: The Genius Behind Buffy by Havens, Candace
Controversy Creates Cash by Eric Bischoff
Secret Santa by Mina Carter
Deadly Wands by Brent Reilly


