The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (668 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
10.93Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Din Torah
(Heb., ‘ruling of the law’). A Jewish legal judgement.
Dionysiac
(religion)
:
(religion)
:
Dionysius
the pseudo-Areopagite (
c.
500). The name given to the author of a corpus of theological writings; until the end of the 19th cent., their authorship was generally ascribed to the Dionysius whom Paul had converted (Acts 17. 34).
Four of his works (
The Celestial Hierarchy
,
The Ecclesiastical Hierarchy
,
The Divine Names
, and
The Mystical Theology
) and ten letters are extant. The central characteristic of these works is the synthesis of Christian and
Neoplatonic
thought. The leading theme is that of the intimate union (
hen
 sis
sis
) of God and the soul, and the progressive deification of the human
(thei
 sis
sis
), by a process of unknowing in an ascent to God through the three ways of the spiritual life:
purgative
,
illuminative
, and
unitive
.
Dionysius exerted a profound influence on Christianity. See also
NEOPLATONISM
.
c.
500). The name given to the author of a corpus of theological writings; until the end of the 19th cent., their authorship was generally ascribed to the Dionysius whom Paul had converted (Acts 17. 34).
Four of his works (
The Celestial Hierarchy
,
The Ecclesiastical Hierarchy
,
The Divine Names
, and
The Mystical Theology
) and ten letters are extant. The central characteristic of these works is the synthesis of Christian and
Neoplatonic
thought. The leading theme is that of the intimate union (
hen
 sis
sis) of God and the soul, and the progressive deification of the human
(thei
 sis
sis), by a process of unknowing in an ascent to God through the three ways of the spiritual life:
purgative
,
illuminative
, and
unitive
.
Dionysius exerted a profound influence on Christianity. See also
NEOPLATONISM
.
D
 pa
pa
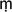 kara
kara
 pa
pa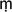 kara
kara(Skt., P
 li, D
li, D
 pankara). ‘Kindler of lights’, best-known and first of the twenty-four
pankara). ‘Kindler of lights’, best-known and first of the twenty-four
Buddhas
who preceded Buddha
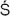
 kyamuni. With him and
kyamuni. With him and
Maitreya
, D
 pa
pa
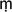 kara is one of the Buddhas of the three ages, past, present, and future. See also
kara is one of the Buddhas of the three ages, past, present, and future. See also
FORMER BUDDHAS
.
 li, D
li, D pankara). ‘Kindler of lights’, best-known and first of the twenty-four
pankara). ‘Kindler of lights’, best-known and first of the twenty-fourBuddhas
who preceded Buddha
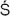
 kyamuni. With him and
kyamuni. With him andMaitreya
, D
 pa
pa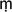 kara is one of the Buddhas of the three ages, past, present, and future. See also
kara is one of the Buddhas of the three ages, past, present, and future. See alsoFORMER BUDDHAS
.
Other books
Death of an Artist by Kate Wilhelm
Beautiful Bedlam by Ali Harper
Neuropath by R. Scott Bakker
The Other Half of My Heart by Sundee T. Frazier
More to Give by Terri Osburn
The Trouble With Tony by Easton, Eli
Love on the Run by Zuri Day
Who I Became (Who I Was Book 2) by Blake, Kasidy
Moon Shell Beach: A Novel by Nancy Thayer
Demonic Designs (To Absolve the Fallen) by Babbitt, Aaron


