The Last Days of Richard III and the Fate of His DNA (24 page)
Read The Last Days of Richard III and the Fate of His DNA Online
Authors: John Ashdown-Hill

As a result, Sir Robert Constable found himself drawn into the movement known as the âPilgrimage of Grace'. This movement was for the defence of the Church in the face of Henry VIII's break with Rome and his attack upon the monasteries. Its supporters demanded âthat the king should suppress no more abbeys, should impose no more taxation, should surrender Cromwell to the people, and get rid of the heretical bishops'.
4
Having been drawn into the âPilgrimage', Constable soon became one of its leaders. Although he accepted Henry VIII's royal pardon under the terms of the agreement reached at Doncaster in early December 1535, Constable was later summoned to London where he was imprisoned in the Tower of London. He was subsequently tried, not for his activities in the main phase of the rebellion, but for offences allegedly committed after his pardon. Condemned to death, Constable was transported to Hull for execution. On 6 July 1537, he was taken to the town's Beverley Gate and there hanged in chains.
5
One female-line granddaughter of Sir Robert Constable and his wife, Catherine Manners, was Margaret Babthorpe. Margaret married Sir Henry Cholmley of Whitby, Yorkshire, and she bore him three sons and seven daughters.
6
The third amongst these daughters was Barbara Cholmley. This child, who was probably born in about 1580, may have been named in honour of her grandmother, Barbara Constable.
F
AMILY
T
REE
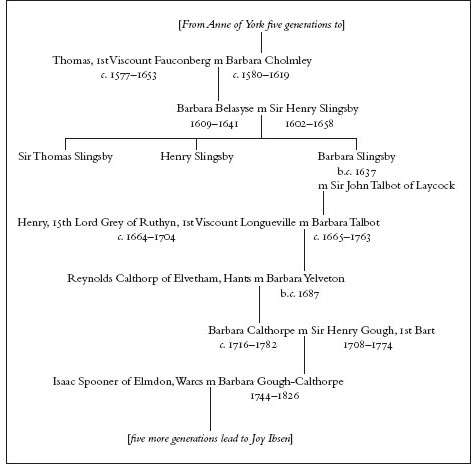
5: The line of Barbaras.
When Barabara Constable had been born, in about 1525, practically everyone in England had been Catholic. The Reformation had as yet scarcely touched the land. Subsequently, however, there had been many changes, culminating in Queen Elizabeth I's establishment of the Anglican Church, which she perceived as an
aurea mediocritas.
Not all of her subjects found Elizabeth's middle way acceptable, however, and there was dissent from both Catholics and Puritans. In Yorkshire, many remained Catholics. Among them was the family of Barbara Cholmley. Thus the little girl was brought up in the old religion.
In about 1600, Barbara married Thomas Belasyse of Newborough, Yorkshire, the only son and heir of Henry Belasyse, MP for Thirsk, who was to be created a baronet in 1611. As a family, the Belasyses were not, at that time, Catholics. However, the death of Elizabeth I, and the accession of James I and his Catholic consort, Anne of Denmark, was thought at first to offer hope of renewed tolerance to Catholics, and in due course Thomas Belasyse converted to Catholicism, though he has been described as a âchurch papist'.
7
He succeeded his father as the second baronet in 1624, and in 1627 he was created first Baron Fauconberg by the new king Charles I. Conspicuously loyal to Charles as the situation in England became ever more polarised and threatening, in 1643 Thomas was elevated to the rank of Viscount Fauconberg. He outlived his king, and died in 1653, in an England then ruled by Oliver Cromwell. Barbara Cholmley, however, witnessed little of this drama. She had died in January 1619 (before her husband had even succeeded to his baronetcy) having born Thomas at least two sons and two daughters.
Although the line of her elder son would inherit the title of viscount, and that of her younger son the title of baron, it is Barbara Cholmley's daughters who concern us here. It was her elder daughter, Barbara Belasyse, who maintained the female line of Richard III's mitochondrial DNA, which survives to the present day. On 7 July 1631, at the age of about 22, Barbara Belasyse married Henry Slingsby, the second son (and, since his elder brother's death in 1617, the heir) of Sir Henry Slingsby of Scriven, Yorkshire. The young Henry Slingsby was a graduate of Queens' College Cambridge, and sometime MP for Knaresborough. He succeeded to his father's estates in 1634 and was created a baronet in 1638.
Unlike her mother, Barbara Belasyse lived long enough to profit from her husband's new rank, and she became a lady. Sir Henry Slingsby's religious beliefs are somewhat difficult to disentangle. He is said to have much disliked the views of the Scottish Covenanters, and in general he appeared to be a practising Anglican of somewhat Arminian tendancy, favouring reverence in worship, while nevertheless expressing disapproval of âbowing and adoring towards the altar' and other ânew ceremonies.'
8
At the same time, however, he opposed the clerical policies of Archbishop Laud, to the extent that he supported the exclusion of the bishops from the House of Lords. Henry Slingsby certainly married the daughter of a Catholic. Indeed, it is virtually certain that Barbara Belasyse was herself a Catholic. Moreover, although he showed no overt sign of it during his lifetime (professing himself an Anglican) Sir Henry, also, is reported to have been a Catholic, at least at the time of his death. Subsequently, Henry and Barbara's eldest son, Sir Thomas Slingsby, was a strong supporter of Charles II's overtly Catholic younger brother, the Duke of York (the future King James II), standing by him through the Exclusion crisis.
As for Sir Henry Slingsby's own politics, he was outspokenly Royalist, stating in Parliament that to refuse to pay the king ship money was tantamount to an act of rebellion. This was a point of view to which many of his fellow MPs took very vehement exception. When the Civil War started, Slingsby left London to join Charles I at York. He commanded a regiment of foot, and fought for the king at Marston Moor and at Naseby. His property was confiscated by Parliament (though relatives purchased it, to hold it in trust for his children). Barbara, his wife, was not, however, forced to endure the discomforts of this confiscation, having died in 1641.
After the execution of the king in January 1649, Sir Henry Slingsby remained in contact with the Royalist underground, and delivered a secret letter from the future Charles II to Lady Fairfax (who was a connection of his late wife's family â Barbara Belasyse (Slingsby's) paternal grandmother having been a Fairfax). Eventually, and perhaps inevitably, Sir Henry was arrested and tried at Westminster for treason against the new state. On 8 June 1658 he was beheaded on Tower Hill. His descendant, Joy Brown (Ibsen), once commented to me that she found it intriguing to have âan ancestor, Sir Henry Slingsby, beheaded on Tower Hill in 1658 “for his loyalty”. â What an interesting age.'
9
Barbara Belasyse (Slingsby)'s daughter, Barbara Slingsby, married Sir John Talbot of Lacock, Wiltshire, thus becoming Lady Talbot. Their family home, Laycock Abbey, had originally been an Augustinian nunnery founded in the thirteenth century. John Talbot belonged to a cadet line of the descendants of the great John Talbot.
As we have seen, Barbara's family was Catholic. The main line of the Talbots of Shrewsbury also adhered to the old religion, but some cadet Talbot lines (including that which leads to the present Earl of Shrewsbury) adopted Anglicanism. The religion of Barbara Belasyse's husband is, therefore, uncertain. It is possible that he was an Anglican. Indeed, it seems to be at about this period that the family line which we are tracing finally parted company with the old religion. John Talbot and Barbara Belasyse produced two daughters: Anne and Barbara Talbot. Anne, the elder daughter, married Sir John Ivory, MP, of Wexford. As for Barbara Talbot, on 11 July 1689, at the church of St Martin-in-the-Fields, she married Henry Yelverton, Lord Grey. Henry's title carried with it the priviledge of carrying the golden spurs at coronations, and Henry had done so in 1685, at the coronation of James II.
However, Henry Yelverton deserted the Stuart king in 1688, giving his support to James' son-in-law and elder daughter, William and Mary. Henry went on to carry the spurs at the coronation of the new, Protestant sovereigns, and in 1690 the new king, William III, gave the recently married Lord Grey the title of Viscount Longueville. The new viscount once again carried the spurs at the coronation of Queen Anne, and he served as gentleman of the bedchamber to her husband, Prince George of Denmark, until his early death, in 1704. His widow (who had borne her husband two sons and one daughter) long outlived him, dying in 1763, at the age of well over 90.
The will of the Right Honourable Barbara, Viscountess Longueville, dated 13 July 1759 and proved on 5 February 1763, is preserved in the National Archives.
10
The dowager viscountess desired to be buried beside her husband privately and without fuss. Twelve men were to attend her corpse and there was to be a coach provided for her women servants. The sum of 20s was to be paid to the minister of every village through which her body passed on its last journey, for distribution to the local poor. The bulk of her estate was divided between her surviving younger son, the Hon. Henry Yelverton, and her grandson, the second Earl of Sussex (her elder son having predecessed her). The date of death of her daughter, Barbara Yelverton (Calthorpe), is not known, but it seems virtually certain that she too had predeceased her mother, since nothing is left to her in the will. To her daughter's daughter, Lady Gough (
née
Barbara Calthorpe), however, the old lady left the sum of £100, âand also my little japan cabinet in my chamber and my red and buff damask bed and the two leaf screen which was my daughter Yelverton's'.
11
There were various bequests to servants, and in particular âmy poor servant Elizabeth Cramp' was to have £10, together with all the viscountess' clothing (except her morning dress and the underwear which went with it). Elizabeth Cramp was also to have âthe chest of drawers in her bed chamber, a wainscot cupboard, and all the useful things in the closet by my chamber (except plate), together with my books of devotion'. As for her porcelain, her pictures and the rest of her chests and cabinets, they were to be held in trust for the young earl of Sussex by Lady Gough's husband, Sir Henry Gough, Bart. The will was signed âB. Longueville', and was witnessed by D. Wright, by the picturesquely named John Lickorish, and by Thomas Harris.
It was Viscountess Longueville's only daughter, Barbara Yelverton, who carried on the mtDNA line of Richard III, marrying (as his second wife) Reynolds Calthorpe. The latter had acquired his seat of Elvetham from his first wife (and first cousin), the only daughter and heiress of Sir Robert Reynolds.
12
The daughter of Barbara Yelverton and Reynolds Calthorpe was Barbara Calthorpe who, as we have just seen, inherited a laquered cabinet, a damask bed and a screen from her grandmother under the terms of the latter's will. Unbeknown to her, Barbara Calthorpe had also inherited old Lady Longueville's mitochondrial DNA.
Barbara Calthorpe married Sir Henry Gough of Edgbaston, first baronet, and Barbara Gough-Calthorpe, the elder of their two daughters, was born in 1744. Barbara Gough-Calthorpe must have known her great grandmother, Lady Longueville, for she was already 19 years of age when that elderly aristocrat (then rapidly approaching her century) died at Brandon in Warwickshire.
Barbara Gough-Calthorpe came from a hybrid background. Her father, Sir Henry Gough, was a wealthy merchant while her mother was the daughter of a county family with estates in Norfolk and Suffolk. Barbara's maternal inheritance, of course, comprised more than status, for the mtDNA which her mother had inherited from Viscountess Longueville was the mtDNA of Catherine de Roët, of Cecily Neville and of Richard III. This genetic inheritance was transmitted by Lady Gough to her two daughters: Barbara Gough-Calthorpe and her younger sister, Charlotte.
Barbara Gough-Calthorpe married, according to the lights of the time, somewhat beneath her. Her husband, Isaac Spooner, was rich, but he was an ironmaster, merchant and banker from nearby Birmingham, with a pedigree which was unremarkable. His family fortune was a recent phenomenon. It had been founded by his father, Abraham, and was then extended by Isaac himself. By contrast Barbara's younger sister, Charlotte Gough-Calthorpe (1747â83) enjoyed greater marital success, acquiring as a husband a baronetted MP who conferred upon his fortunate spouse the title of Lady Palmer.
When she married Isaac Spooner in 1770, Charlotte's elder sister, Barbara, acquired no special matrimonial handle to her name. Nevertheless, Mr and Mrs Spooner ranked among the leading citizens of Birmingham. They lived at nearby Elmdon Hall, and enjoyed the luxury of a second house in fashionable Bath, though the society which surrounded them there was evidently regarded as less than brilliant, since one visitor uncharitably described their Bath house as âthe very temple of dullness'.
Barbara and Isaac Spooner had a large family. The majority of their ten children were boys. Curiously, one of these was given the name âRichard'; a name which was in Barbara's family, for she also had a brother called Richard. Is it possible that those who named these boys had some inkling of their family connection with Richard III? Probably not. In any case, the boys were a genetic dead end. However, there were girls in the family too, and these were capable of passing on into the future the inherited DNA of Catherine de Roët and Richard III.
