Read The Success and Failure of Picasso Online
Authors: John Berger
Tags: #Biography & Autobiography, #Artists; Architects; Photographers
The Success and Failure of Picasso (31 page)

114
Picasso. Couple with Masks. 24 January 1954
On the next day, the 25th of January, 1954, Picasso, all his imagination now roused, dismisses the monkey and pursues the logic of his fantasy further. As the masks are swapped, they can also be transformed. He wears the mask of the young girl representing her almost as she is. She wears his mask, but instead of representing him as an obscene old man, it has become the mask of a virile young god. And so they play a charade (a charade that is played in many hotel bedrooms every night). Yet at the same time the prodigy in Picasso, the
duende
that possesses him, insists upon his telling the truth. He draws himself playing the charade so earnestly that he looks absurd. And he draws her kneeling indulgently so as to be on his level, playing as with a child to keep him happy.
115
Picasso. Old Man and Young Woman with Masks. 25 January 1954
116
Picasso. Girl, Clown, Mask, and Monkey. 25 January 1954
Finally, one of the last drawings of the series shows the vanity of any attempt at escape from the absurdity of the situation. The mask – a symbol now for all that imagination can construct and subjectivity enjoy – is shown to the triumphant monkey. The monkey gazes at it blankly. The mask is held by a sad clown, whose own face is made up as though it too were a mask. But the monkey sits on its haunches beside the legs of the young woman, ready at any moment to jump into her lap and there be welcome.
Thus far one might consider this series of drawings as a very poignant and bitter lament for lost youth, and a protest against the savage sexual deprivation of old age. I think often, as I look at them, of Yeats. (Somehow, in a way that I have not yet fully understood, many connexions suggest themselves between Picasso and Yeats: the paintings of the one frequently evoke the poems of the other.)
‘Because I am mad about women
I am mad about the hills,’
Said that wild old wicked man
Who travels where God wills.
‘Not to die on the straw at home,
Those hands to close these eyes,
That is all I ask, my dear,
From the old man in the skies.
Daybreak and a candle-end
‘Kind are all your words, my dear,
Do not the rest withhold.
Who can know the year, my dear,
When an old man’s blood grows cold?
I have what no young man can have
Because he loves too much.
Words I have that can pierce the heart,
But what can he do but touch?’
Daybreak and a candle-end
But Picasso’s confession is even more comprehensive and more tragic. For, apart from the directly sexual theme, there is another, parallel to it, but with different implications. Throughout the whole series of drawings Picasso turns from one to the other, as though they were different aspects of the same reality. The second theme is that of the artist and his model.
117
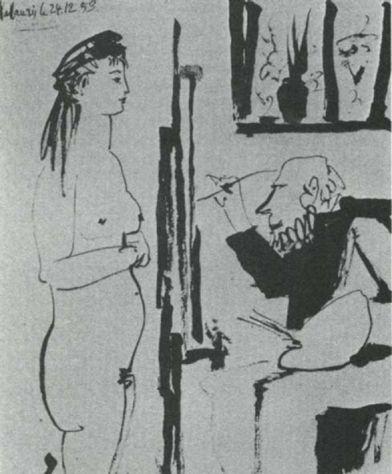
Picasso. Painter and Model. 24 December 1953
The model is the same young woman – in so far as she too is sex, nature, life. And the painter, though sometimes he is depicted as old and sometimes young, sometimes thin and sometimes fat, is the same man in so far as he is absurd and helpless. The complaint is different. It is no longer that an old man’s desires are obscene and absurd despite himself: it is that to
paint
in front of such a young woman, to put marks on canvas and to peer at her proportions, instead of making love to her, is also absurd, and absurd in such a dry, pedantic way that it too becomes obscene.
118
Picasso. Painter and Model. 25 December 1953
Thus the role of the young woman remains very similar. Her youth, her beauty, her natural appetites, her tenderness and all that makes her desirable are there to mock all men who cannot or will not take her on her own terms: and those terms are both as perfect and as ruthless as nature. For her, old age is a debility and a hindrance, an act of imagination is a transitory game, art is an incomprehensible – at best harmless – way of passing the time. Her true companion is the monkey. Finally she chooses him instead of the man, or at least in proxy for the man who is eternally incapacitated.
119
Picasso. Woman, Apple, Monkey, Man. 26 January 1954
Perhaps the bitterest drawing of the whole series is that in which the monkey pretends to paint, and where, for the first time, the young woman, instead of looking indifferent whilst being painted, responds to him and smiles. The degree to which that response mocks us is shown by Picasso in the pun that he has drawn between her breast and his muzzle. Many have called this witty. It is witty, but it is a wit born out of much suffering.
120
Picasso. Woman and Monkey Painting. 10 January 1954
In his old man’s confession, Picasso confesses to despair. It is not the social despair of Goya; it is a despair confined and belonging to his own life. The drawings are like a retrospective exhibition of that life. The despair is to some extent qualified by the fact that he can express it. But it remains.
It is the despair of the idealized ‘noble savage’ who, alone, abstracted from history and insulated from any social reality, is forced back and back until finally he is left with all his imagination unaccounted for by the pure nature which he must worship. The monkey who was once his companion in freedom, a dumb critic of society by the side of a more articulate one, becomes in the end his rival and humiliator. His gifts become his absurdity. Nor is it that he simply considers his own work a failure. It is the very idea of art which is attacked – attacked by Nature, with which now as an old man, without a unique people and so without any true followers, he has been left utterly alone. He himself now believes in this attack and actually sides with Nature against art because civilization, as he has found it, has given him only one thing: acclaim.
The gifts of an imaginative artist are often the outriders of the gifts of his period. Frequently the new abilities and attitudes become recognizable in art and are given a name before their existence in life has been appreciated. This is why a love of art which accompanies a fear or rejection of life is so inadequate. It is also why ideally there should always be a road open to art even for those to whom the medium, the talent, the activity involved mean nothing. Art is the nearest to an oracle that our position as modern scientific men can allow us.