Ancient Iraq (65 page)

43
.
H. LENZEN
, ‘Ein Goldkranz aus Warka‘,
Sumer
, XIII (1957), pp. 205 – 6. On this tomb, the date of which has not been determined with certainty, cf.
UVB
, XV (1959), pp. 27 – 34; XVI (1960), pp. 23 – 9.
44
.
G. LE STRANGE
,
The Lands of the Eastern Caliphate
, 3rd ed., London, 1966, pp. 26 – 9.
Epilogue
I
.
W. W. TARN
,
La Civilisation Hellénistique
, Paris, 1936, pp. 219 – 37.
2
. A list of these words will be found in
H. W. F. SAGGS
,
The Greatness that was Babylon
, London, 1962, pp. 493 – 5. This book also contains other examples of our Mesopotamian heritage.
3
.
J. BOTTERO
, ‘L‘Assyriologie et notre histoire‘,
Dialogues d'Histoire Ancienne
, VII, Paris, 1981, p. 95.
4
. Numerous studies have been devoted to the relations between the Greek and Oriental civilizations. They include:
R. M. HAY-WOOD
,
Ancient Greece and the Near East
, London, 1965;
M. L. WEST
,
Early Greek Philosophy and the Orient
, London, 1971;
H. A. HOFFNER
(ed.),
Orient and Occident, (AOAT
, 22), Neukirchen-Vluyn, 1973; D.
KAGAN
,
Problems in Ancient History
, I,
The Ancient Near East and Greece
, New York, 1975.
5
.
E. PORADA
, ‘The cylinder seals found at Thebes in Beotia‘,
AfO
, XXVIII (1981 – 2), pp. 1 – 70;
J. A. BRINKMAN
, ‘The Western Asiatic seals found at Thebes in Greece’,
ibid
., pp. 73 – 7.
6
.
C. H. GORDON
,
Before the Bible
, London, 1962, pp. 9, 132.
7.
J. FILLIOZAT
, ‘Pronostic médicaux akkadiens, grecs et indiens’,
Journal Asiatique
, CCXL (1952), pp. 299 – 321;
M. SANDRAIL
,
Les Sources akkadiennes de la Pensée et de la Méthode hippocratiques
, Toulouse, 1953.
8
.
C. H. GORDON
, op. cit., pp. 49 – 97, 218 – 77.
R. GRAVES
,
The Greek Myths
, Harmondsworth, 1957, II, p. 89.
9
. See, for instance,
R. D. BARNETT
, ‘Ancient Oriental influences on archaic Greece‘, in
The Aegean and the Near East, Studies presented to H. Goldman
, New York, 1956, pp. 212 – 38;
R. A. JAIRAZBHOY
,
Oriental Influences in Western Art
, London, 1965.
10
.
M. ROSTOVTZEFF
,
The Social and Economic History of the Hellenistic World
, Oxford, 1941, I, p. 84.
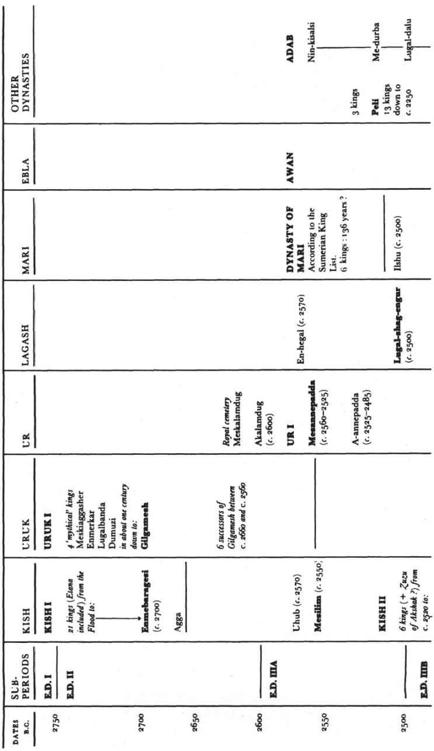
PERIOD | MESOPOTAMIA | TECHNICAL AND | |
DATES | NORTH | SOUTH | |
c | MIDDLE | Barda Balka | Neanderthal hunter-gatherers living in caves and rock shelters |
Shanidar D | |||
Hazar Merd | |||
35000 | |||
UPPER | Shanidar C | Homo sapiens sapiens. | |
25000 | |||
( | |||
12000 | |||
Shanidar B | |||
Zarzi. | |||
9000 | |||
MESOLITHIC | Shanidar B | Microlithic tools and weapons. Obsidian imported. Bone work. First clay figurines. First groups of dwellings. Beginnings of animal domestication | |
Zawi Chemi Shanidar | |||
8000 | Karim Shehir | ||
Mureybet | Bus Mordeh | ||
7000 | |||
NEOLITHIC | Jarmo | Ali Kosh | Progressive domestication of animals and edible plants. Villages. Invention of pottery. First baked bricks |
6000 | |||
CHALCOLITHIC | Umm Dabaghiuah | Use of copper. First mural paintings. Irrigation agriculture. First seals. First temples. Decorated luxury ware. Clay and alabaster figurines. Wide use of brick | |
HASSUNA | |||
5500 | | ||
| OUEILI | ||
5000 | ERIDU | ||
Choga Mami | |||
4500 | HAJJI MUHAMMAD | ||
NORTH UBAID | SOUTH UBAID | ||
4000 | Tepe Gawra | el-‘Ubaid, Ur | Temples and houses of increasing size and complexity |
3750 | and numerous other sites | and numerous other sites | Terracotta sickles and pestles |
URUK PERIOD | |||
Tepe Gawra | Urbanization. Potter's wheel. Swing-plough. Sail. Metal work (bronze, gold, silver). First cylinder-seals. Invention of writing | ||
Qalinj Agha, Grai | Uruk | ||
ANCIENT BRONZE | |||
Tell Brak | --------------------- | ||
3000 | NINEVEH V | JEMDAT NASR | |
Early Dynastic I | SUMERIAN CIVILIZATION | ||
2700 | City-states. Fortified towns. Development of writing | ||
Early Dynastic II | Administrative archives from Fara and Abu Salabikh | ||
HISTORIC | |||
2500 | Early Dynastic III |
c
. 2900 – 2384
B.C.
)
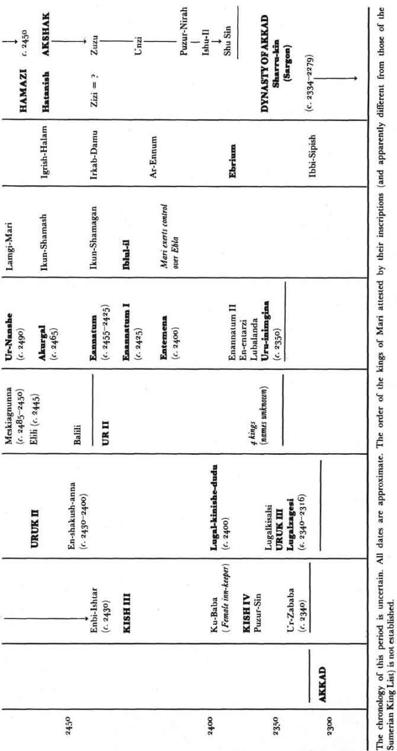
c
. 2334–2004
B.C.
)
| DATES B.C. | AKKAD/UR | URUK/ISIN | GUTI/LARSA | LAGASH | MARI |
| DYNASTY OF AKKAD | Lugalzagesi | ||||
| | |||||
| Sharru-kîn (Sargon) (2334–2279) | Sargon takes Mari and Ebla | ||||
| | |||||
| 2300 | Rimush (2278–2270) Manishtusu (2269–2255) | ||||
| | |||||
| 2250 | Narâm-Sîn (2254–2218) | Lugal-ushumgal (2230–2200) | Narâm-Sîn conquers Mari and destroys Ebla | ||
| | |||||
| 2200 | Shar-kalli-sharri (2217–2193) | DYNASTY OF GUTIUM 21 Guti Kings down to 2120 | SHAKKANAKKU Ididish Shu-Dagan Isma-Dagan (2199–2154) | ||
| | |||||
| Anarchy Shu-Turul (2168–2154) | URUK IV | The Guti invade Akkad and Sumer | ENSI OF LAGASH Ur-Baba (2155–2142) | Nur-Mêr Ishtup-Ilum | |
| 2150 | Ur-nigina (2153–2147) Ur-gigira (2146–2141) +3 kings | Gudea (2141–2122) Ur-Ningirsu (2121–2118) Pirig-me (2117–2115) Ur-gar (2114) Nam-mahazi (2113–2111) | Ishkun-Addu | ||
| UR III | URUK V Utu-hegal (2123–2113) | Tiriqan (x-2120) | Apil-Kin (2126–2091) | ||
| Ur-Nammu (2112–2095) | |||||
| 2100 | GOVERNORS OF LAGASH VASSALS OF UR | ||||
| Shulgi (2094–2047) | Ur-Ninsuna Ur-Ninkimara Lu-kirilaza | Iddin-Ilum Ilum-Ishtar Turam-Dagan (2071–2051) | |||
| | |||||
| 2050 | Amar-Sîn (2046–2038) Shu-Sîn (2037–2029) Ibbi-Sîn (2028–2004) | DYNASTY OF ISIN Ishbi-Erra (2017–1985) | DYNASTY OF LARSA Naplânum (2025–2005) | Ir-Nanna | Puzur-Ishtar (2050–2025) Hilal-Erra |
| | |||||
| 2000 | Fall of Ur (2004) | Emisum (2004–1977) | Lagash becomes independent (2023) | Hanun-Dagan (2016–2008) |
