Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (34 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
9.09Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
•
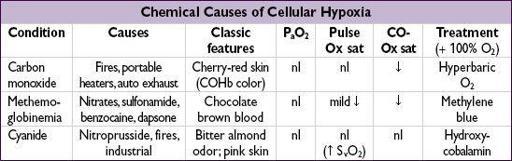
Cyanosis:
seen when >4 g/dL of reduced Hb in blood vessels of skin/mucous membranes central: ↓ S
a
O
2
(pulm disease, shunt); abnl Hb [metHb, sulfHb, COHb (not true cyanosis)] peripheral: ↓ blood flow → ↑ O
2
extraction (eg, ↓ CO, cold, arterial or venous obstruction)
CO binds to Hb more avidly than does O
2
. Pulse oximeter (Ox) misreads COHb as HbO
2
→ falsely nl sat. Oxidizing drugs Δ Hb (ferrous) to MetHb (ferric), which cannot carry O
2
. Pulse ox misreads MetHb as HbO
2
. Cyanide inhibits mitochondrial O
2
use → cellular hypoxia but pink skin and ↑
venous
O
2
sat.
MECHANICAL VENTILATION
Indications
• Improve gas exchange
↑ oxygenation
↑ alveolar ventilation and/or reverse acute respiratory acidosis
• Relieve respiratory distress
↓ work of breathing (can account for up to 50% of total oxygen consumption)
↓ respiratory muscle fatigue
• Apnea, airway protection, pulmonary toilet
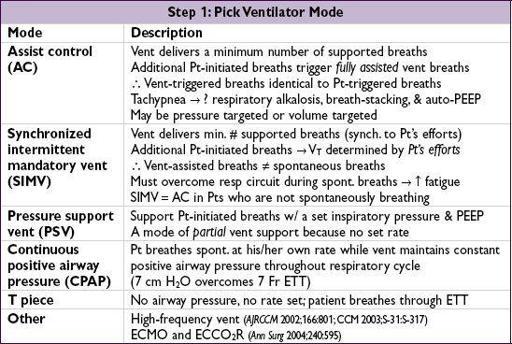
Choosing settings
(
NEJM
2001;344:1986)
1. Choose method (including potentially noninvasive ventilation, see later)
2. Pick ventilator mode, and (if appropriate) volume targeted or pressure targeted
3. Set or ✓ remaining variables (eg, F
i
O
2
, PEEP, I:E time, flow, airway pressures)
Tailoring the ventilator settings
• To improve oxygenation: options include ↑ F
i
O
2
, ↑ PEEP
First, ↑ F
i
O
2
. If >0.6 and oxygenation remains suboptimal, then try ↑ PEEP:
If ↑ P
a
O
2
/F
i
O
2
and
P
plat
stable, suggests recruitable lung (ie, atelectasis). Continue to ↑ PEEP until either can ↓ F
i
O
2
to <0.6 or P
plat
≥30 cm H
2
O. If PEEP 20 & F
i
O
2
1.0 and oxygenation remains suboptimal, consider rescue/expt strategies (see “ARDS”).
If ↑ PEEP yields no Δ
or
↓ P
a
O
2
/F
i
O
2
or
↑ P
a
CO
2
, suggests additional lung
not
recruitable and instead overdistending lung → ↑ shunt & dead space; ∴ ↓ PEEP
• To improve ventilation: ↑ V
T
or inspiratory pressure, ↑ RR (may need to ↓ I time). Nb, tolerate ↑ P
a
CO
2
(permissive hypercapnia) in ALI/ARDS (qv) as long as pH >7.15.
Acute ventilatory deterioration (usually ↑ PIP)
• Response to ↑ PIP: disconnect Pt from vent., bag, auscultate, suction, ✓ CXR & ABG
Figure 2-7 Approach to acute ventilatory deterioration
Weaning from the ventilator
(
NEJM
2012;367:2233)
• Perform daily assessment of readiness for spontaneous breathing trial (SBT)
• Clinical screening criteria: VS stable, minimal secretions, adequate cough, cause of respiratory failure or previously failed SBT reversed
• Vent parameters: P
a
O
2
/F
i
O
2
>200, PEEP ≤5, f/V
T
<105, V
E
<12 L/min, VC >10 mL/kg rapid shallow breathing index (f/V
T
) >105 predicts failure; NPV 0.95 (
NEJM
1991;324:1445)
Other books
Star Kitten by Purple Hazel
Marked Masters by Ritter Ames
The Gingerbread Dungeon by Elizabeth Thorne
Beary And Bright (Fire Bear Shifters 6) by Sloane Meyers
The Raven Chronicles Book 1 by Nicole Dixon
These Vicious Masks: A Swoon Novel by Zekas, Kelly, Shanker, Tarun
Tiempo de arena by Inma Chacón
A Passing Curse (2011) by C R Trolson
The Orphan and the Duke by Jillian Chantal
Bitten by Darkness by Marie E. Blossom