Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (45 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
5.44Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Hepatitis B
(dsDNA; ~45% of acute viral hepatitis in U.S.;
Lancet
2009;373:582)
• Transmission: blood (IVDU, transfusion), sexual, perinatal
• Incubation: 6 wk–6 mo (mean 12–14 wk)
• Acute infxn: 70% subclinical, 30% jaundice, <1% fulminant hepatitis (up to 60% mortality) • Chronic infxn: <5% (adult-acquired; higher if immunosupp), >90% (perinatally acquired); ~40% chronic carriers → cirrhosis; ↑ risk of cirrhosis if HCV, HDV or HIV coinfection • Hepatocellular carcinoma (w/ or w/o concurrent cirrhosis); ↑ risk w/ perinatal transmission & ↑’d HBV DNA. Screen chronic carriers w/ AFP & U/S vs. MRI q6mo.
• Extrahepatic syndromes: PAN (<1%), MPGN, arthritis, dermatitis, PMR
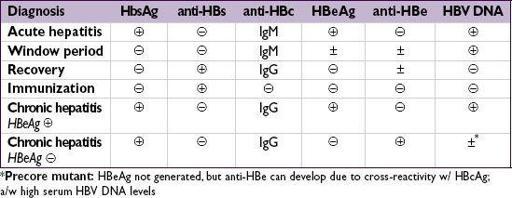
• Serologic and virologic tests
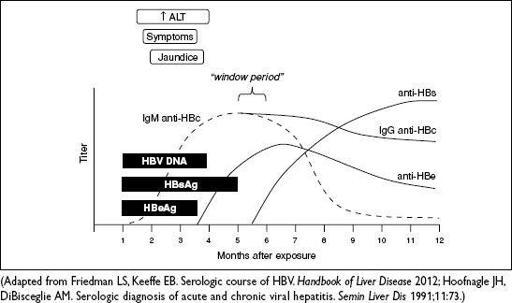
HBsAg: appears before sx; used to screen blood donors; persists >6 mo = chronic HBV
HBeAg: evidence of viral replication and ↑ infectivity
IgM anti-HBc: first Ab to appear; indicates acute infection window period = HBsAg become, anti-HBs not yet
, anti-HBc only clue to infection
IgG anti-HBc: indicates previous (HBsAg) or ongoing (HBsAg
) HBV infection
anti-HBe: indicates waning viral replication, ↓ infectivity
anti-HBs: indicates resolution of acute disease & immunity (sole marker after vac)
HBV DNA: presence in serum correlates w/ active viral replication in liver
Figure 3-7
Serologic course of acute HBV infection with resolution
• Treatment for acute HBV: supportive; hospitalize for Δ MS or ↑ INR (liver transplant ctr) • Treatment for chronic HBV if: (1) HBeAgw/ DNA >20,000 IU/mL & elevated ALT; (2) HBeAg
w/ DNA >2000 IU/mL & elevated ALT or liver bx demonstrates stage ≥2 fibrosis (
NEJM
2008;359:1486;
Hep
2009;50:661;
Clin Gas Hep
2011;9:285) • 1st line is nucleo(s/t)ide analogues:
entecavir
or
tenofovir
; well tolerated & low resistance (1% for entecavir at 5 y in Rx-naïve Pts); at 5 y HBeAg seroconversion is 30–40% & loss of HBsAg is 5–10% (
Gastro
2012;142:1360;
Lancet
2013;381:468) •
PEG IFN
ɑ-2a: best rate of HBeAg seroconversion at 1 y (27%), low tolerability limits use • Goal: if HBeAg→ HBeAg
, anti-HBe
; if HBeAg
or seroconversion or Asian Pt → indefinite tx or until HBsAg clears (if ever) • If undergo liver transplant: HBIG + nucleo(s/t)ide analogue effective in preventing reinfection • HIV/HBV
coinfection
: Rx w/ 2 drugs active against both HBV & HIV (
NEJM
2007;356:1445) • If inactive carrier scheduled to receive immunosuppression/chemotherapy → Rx
Other books
CounterPoint by Daniel Rafferty
Lord of the Abyss & Desert Warrior by Nalini Singh
The Barrow by Mark Smylie
Wayfaring Stranger: A Novel by James Lee Burke
The Perfect Crime by Roger Forsdyke
The Shadow by Kelly Green
Tagged & Ashed (The Sterling Shore Series #2) by Owens, C.M.
A Bone to Pick by Gina McMurchy-Barber
The Legacy by Shirley Jump