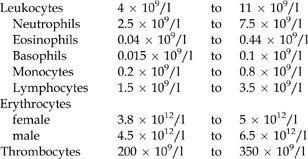Ross & Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness (215 page)
Read Ross & Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness Online
Authors: Anne Waugh,Allison Grant
Tags: #Medical, #Nursing, #General, #Anatomy

Conversion table for kPa/mmHg (for e.g. capillary pressures)
| 1 mmHg | = 0.13 kPa |
| 1 kPa | = 7.5 mmHg |
| 35 mmHg | = 4.7 kPa |
| 25 mmHg | = 3.3 kPa |
| 15 mmHg | = 2.0 kPa |
| 10 mmHg | = 1.3 kPa |
Hydrogen ion concentration (pH)
Neutral = 7 Acid = 0 to 7 Alkaline = 7 to 14
| Normal pH of some body fluids | |
|---|---|
| Blood | 7.35 to 7.45 |
| Saliva | 5.8 to 7.4 |
| Gastric juice | 1.5 to 3.5 |
| Bile | 6.0 to 8.5 |
| Urine | 4.5 to 8.0 |
Some normal plasma levels in adults
| Calcium | 2.12 to 2.62 mmol/l | (8.5 to 10.5 mg/100 ml) |
| Chloride | 97 to 106 mmol/l | (97 to 106 mEq/l) |
| Cholesterol | 3.6 to 6.7 mmol/l | (140 to 260 mg/100 ml) |
| Glucose | 3.5 to 8 mmol/l | (63 to 144 mg/100 ml) |
| Fasting glucose | 3.6 to 5.8 mmol/l | (65 to 105 mg/100 ml) |
| Potassium | 3.3 to 4.7 mmol/l | (3.3 to 4.7 mEq/l) |
| Sodium | 135 to 143 mmol/l | (135 to 143 mEq/l) |
| Urea | 2.5 to 6.6 mmol/l | (15 to 44 mg/100 ml) |
Arterial blood gases
| P O 2 | 12 to 15 kPa | (90 to 110 mmHg) |
| P CO 2 | 4.5 to 6 kPa | (34 to 46 mmHg) |
| Bicarbonate | 21 to 27.5 mmol/l | |
| H + ions | 36 to 44 nmol/l | (7.35 to 7.45 pH units) |
Blood pressure
Normal adult 120/80 mmHg.
Blood pressure above 140/90 is generally considered high.
Heart rate
| At rest | 60 to 80/min |
| Sinus bradycardia | <60/min |
| Sinus tachycardia | >100/min |
Respiration rate
At rest 15 to 18/min
| Tidal volume | 500 ml |
| Dead space | 150 ml |
| Alveolar ventilation | 15 (500 – 150) = 5.25 l/min |
Blood count
Diet
Vitamins. Daily requirements see
pages 272–274
.
| 1 kilocalorie (kcal) | = 4.182 kilojoules (kJ) |
| 1 kilojoule | = 0.24 kilocalories |
| Energy source | Energy released | Recommended proportion in diet |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate | 1 g = 17 kJ = 4 kcal | 55–75% |
| Protein | 1 g = 17 kJ = 4 kcal | 10–15% |
| Fat | 1 g = 38 kJ = 9 kcal | 15–30% |
Urine
| Specific gravity | 1.020 to 1.030 |
| Volume excreted | 1000 to 1500 ml/day |
Glucose is normally absent, but appears in urine when blood glucose levels exceed 9 mmol/l
Body temperatures
| Normal | 36.8°C: axillary |
| Hypothermia | ≤35°C: core temperature |
| Death when below | 25°C |
Cerebrospinal fluid pressure
Lying on the side 60–180 mm H
2
O
Intraocular pressure
1.3 to 2.6 kPa (10 to 20 mmHg)
Bibliography
Barker H.M.. Nutrition and dietetics for health care, 10th edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2002.
Bateman A.C., Carr N.. The flesh and bones of pathology. London: Mosby, 2008.
Boon N., Colledge M.R., Walker B.R.. Davidson's principles and practice of medicine, 20th edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2006.
Boron W.F., Boulpaep E.L.. Medical physiology, Updated edition. Oxford: Saunders, 2004.
Brashers V.L.. Clinical applications of pathophysiology: an evidence-based approach, 3rd edn. St Louis: Mosby, 2006.
British Nutrition Foundation The Eatwell Plate
http://www.nutrition.org.uk/home.asp?siteId=43§ionId=299&which=1
Online. Available: 21 January 2009
Campbell P.N., Smith A.D.. Biochemistry illustrated, 4th edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2000.
Carroll R.G.. Elsevier's integrated physiology. Edinburgh: Mosby, 2006.
Damjanov I.. Pathophysiology. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2008.
Department of Health. Dietary reference values of food energy and nutrients for the UK: COMA report. London: HMSO, 1991.
Friedman N.J., Kaiser P.K.. Essentials of ophthalmology. Edinburgh: Saunders, 2007.
Gaw A., Murphy M.J., Cowan R.A., et al. Clinical biochemistry, 4th edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2008.
Guyton A.C., Hall J.E.. Textbook of medical physiology, 11th edn. Edinburgh: Saunders, 2005.
Islam N., Strouthidis N., Keegan D., et al. Crash course: ophthalmology, dermatology, ENT. Edinburgh: Mosby, 2009.
Jafek B.W., Murrow B.W.. ENT secrets, 2nd edn. London: Mosby, 2001.
Kierszenbaum A.. Histology and cell biology: an introduction to pathology, 2nd edn. Edinburgh: Mosby, 2007.
King T.. Elsevier's integrated pathology. Edinburgh: Mosby, 2006.
Klug W.S., Cummings M.R.. Essentials of genetics, 4th edn. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2002.
Kumar P., Clark M.. Clinical medicine, 6th edn. Edinburgh: Saunders, 2005.
Kumar V., Abbas A.K., Fausto N., Mitchell R.. Robbins basic pathology, 8th edn. Edinburgh: Saunders, 2007.
Lim M.Y.. Crash course: metabolism and nutrition, 3rd edn. Edinburgh: Mosby, 2007.
Male D., Brostoff J., Roth D.B., et al. Immunology, 7th edn. Philadelphia: Mosby, 2006.
Martini F.H.. Fundamentals of anatomy and physiology, 7th edn. San Francisco: Pearson/Benjamin Cummings, 2006.
McCance K.L., Huether S.E.. Pathophysiology, the biologic basis for disease in adults and children, 5th edn. St Louis: Mosby, 2005.
Merck manual of diagnosis and therapy (2006) 18th edn, Merck Research Laboratories, New Jersey
Montague S.E., Watson R., Herbert R.. Physiology for nursing practice, 3rd edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2005.
Mueller R.F., Young I.D.. Emery's elements of medical genetics, 11th edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2002.
Russell P.J.. Genetics. San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings, 2002.
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) (2001) Hypertension in older people, publication 49
www.sign.ac.uk/pdf/sign49.pdf
Available: 24 May 2009
Standring S.. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice, 39th edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2005.
Telser A.G., Young J.K., Baldwin K.M.. Elsevier's integrated histology. Edinburgh: Mosby, 2007.
Thibodeau G.A., Patton K.T.. Anatomy and physiology, 6th edn. St Louis: Mosby, 2007.
Timbury M.C., McCartney A.C., Thakker B., et al. Notes on medical microbiology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2002.
Underwood J.C.E, editor. General and systematic pathology, 4th edn, Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2004.
Vander J.F., Gault J.A.. Ophthalmology secrets in color, 3rd edn. St Louis: Mosby, 2007.
World Health Organization Global database on body mass index
http://www.who.int/bmi/index.jsp?introPage=intro_3.html
Online. Available: 17 January 2009
Young B., Lowe J.S., Stevens A., et al. Wheater's functional histology: a text and colour atlas. Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, 2006.
Index
Page numbers in
bold
refer to main discussions of anato my and physiology. Those in
bold italics
diseases. Page numbers referring to anatomy and physiology are in ordinary type. Those referring to diseases are in
italics
. Page numbers followed by f refer to figures; those followed by t refer to tables, and those followed by b refer to boxes.
A
Abdominal cavity,
46–47
arterial supply,
100–102
contents,
46
f
,
47
,
47
f
lymph drainage,
131
regions,
47
f
venous return,
100–102
,
103
f
Abdominal wall
anterior,
415
,
416
f
muscles,
248
f
,
415–416
,
415
f
nerves,
164
posterior,
415
f
Abducent nerve (cranial nerve VI),
165
f
,
166
,
198
t
Abduction,
402
t
,
403
f
ABO blood group system,
60–61
,
61
f
,
433–434
Abscess,
361
,
369
appendix,
317
,
317f
deep-seated,
361
intra-abdominal,
317
,
317f
lung,
261
pelvic,
317
,
317f
subphrenic,
316
,
317
,
317f
subpleural,
261
superficial,
361
Absorption,
278
,
304
,
305
t