The Better Angels of Our Nature: Why Violence Has Declined (57 page)
Read The Better Angels of Our Nature: Why Violence Has Declined Online
Authors: Steven Pinker
Tags: #Sociology, #Psychology, #Science, #Amazon.com, #21st Century, #Crime, #Anthropology, #Social History, #Retail, #Criminology

BOOK: The Better Angels of Our Nature: Why Violence Has Declined
3.6Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
The point of this chapter is that these zeroes—the Long Peace—are a result of one of those psychological retunings that take place now and again over the course of history and cause violence to decline. In this case it is a change within the mainstream of the developed world (and increasingly, the rest of the world) in the shared cognitive categorization of war. For most of human history, influential people who craved power, prestige, or vengeance could count on their political network to ratify those cravings and to turn off their sympathies for the victims of an effort to satisfy them. They believed, in other words, in the legitimacy of war. Though the psychological components of war have not gone away—dominance, vengeance, callousness, tribalism, groupthink, self-deception—since the late 1940s they have been disaggregated in Europe and other developed countries in a way that has driven down the frequency of war.
Some people downplay these stunning developments by pointing out that wars still take place in the developing world, so perhaps violence has only been displaced, not reduced. In the following chapter we will examine armed conflict in the rest of the world, but for now it’s worth noting that the objection makes little sense. There is no Law of Conservation of Violence, no hydraulic system in which a compression of violence in one part of the world forces it to bulge out somewhere else. Tribal, civil, private, slave-raiding, imperial, and colonial wars have inflamed the territories of the developing world for millennia. A world in which war continues in some of the poorer countries is still better than a world in which it takes place in both the rich
and
the poor countries, especially given the incalculably greater damage that rich, powerful countries can wreak.
and
the poor countries, especially given the incalculably greater damage that rich, powerful countries can wreak.
A long peace, to be sure, is not a perpetual peace. No one with a statistical appreciation of history could possibly say that a war between great powers, developed countries, or European states will never happen again. But probabilities can change over spans of time that matter to us. The house odds on the iron dice can decline; the power-law line can sink or tilt. And in much of the world, that appears to have happened.
The same statistical consciousness, though, alerts us to alternative possibilities. Perhaps the odds haven’t changed at all, and we’re overinterpreting a random run of peaceful years in the same way that we are liable to overinterpret a random cluster of wars or atrocities. Perhaps the pressure for war has been building and the system will blow at any moment.
But probably not. The statistics of deadly quarrels show that war is not a pendulum, a pressure cooker, or a hurtling mass, but a memoryless game of dice, perhaps one with changing odds. And the history of many nations affirms that a peace among them can last indefinitely. As Mueller puts it, if war fever were cyclical, “one would expect the Swiss, Danes, Swedes, Dutch, and Spaniards to be positively
roaring
for a fight by now.”
150
Nor are Canadians and Americans losing sleep about an overdue invasion across the world’s longest undefended border.
roaring
for a fight by now.”
150
Nor are Canadians and Americans losing sleep about an overdue invasion across the world’s longest undefended border.
What about the possibility of a run of good luck? Also unlikely. The postwar years are by far the longest period of peace among great powers since they came into being five hundred years ago.
151
The stretch of peace among European states is also the longest in its bellicose history. Just about any statistical test can confirm that the zeroes and near zeroes of the Long Peace are extremely improbable, given the rates of war in the preceding centuries. Taking the frequency of wars between great powers from 1495 to 1945 as a baseline, the chance that there would be a sixty-five-year stretch with only a single great power war (the marginal case of the Korean War) is one in a thousand.
152
Even if we take 1815 as our starting point, which biases the test against us by letting the peaceful post-Napoleonic 19th century dominate the base rate, we find that the probability that the postwar era would have at most four wars involving a great power is less than 0.004, and the probability that it would have at most one war between European states (the Soviet invasion of Hungary in 1956) is 0.0008.
153
151
The stretch of peace among European states is also the longest in its bellicose history. Just about any statistical test can confirm that the zeroes and near zeroes of the Long Peace are extremely improbable, given the rates of war in the preceding centuries. Taking the frequency of wars between great powers from 1495 to 1945 as a baseline, the chance that there would be a sixty-five-year stretch with only a single great power war (the marginal case of the Korean War) is one in a thousand.
152
Even if we take 1815 as our starting point, which biases the test against us by letting the peaceful post-Napoleonic 19th century dominate the base rate, we find that the probability that the postwar era would have at most four wars involving a great power is less than 0.004, and the probability that it would have at most one war between European states (the Soviet invasion of Hungary in 1956) is 0.0008.
153
The calculation of probabilities, to be sure, critically depends on how one defines the events. Odds are very different when you estimate them in full knowledge of what happened (a post hoc comparison, also known as “data snooping”) and when you lay down your prediction beforehand (a planned or a priori comparison). Recall that the chance that two people in a room of fifty-seven will share a birthday is ninety-nine out of a hundred. In that case we are specifying the exact day only after we identify the pair of people. The chance that someone will share
my
birthday is less than one in seven; in that case we specify the day beforehand. A stock scammer can exploit the distinction by sending out newsletters with every possible prediction about the trajectory of the market. Several months later the fraction of recipients that got the lucky matching run will think he is a genius. A skeptic of the Long Peace could claim that anyone making a big deal of a long run of nonwars at the end of that very run is just as guilty of data snooping.
my
birthday is less than one in seven; in that case we specify the day beforehand. A stock scammer can exploit the distinction by sending out newsletters with every possible prediction about the trajectory of the market. Several months later the fraction of recipients that got the lucky matching run will think he is a genius. A skeptic of the Long Peace could claim that anyone making a big deal of a long run of nonwars at the end of that very run is just as guilty of data snooping.
But in fact there is a paper trail of scholars who, more than two decades ago, noticed that the war-free years were piling up and attributed it to a new mindset that they expected to last. Today we can say that their a priori predictions have been confirmed. The story can be told in titles and dates: Werner Levi’s
The Coming End of War
(1981), John Gaddis’s “The Long Peace: Elements of Stability in the Postwar International System” (1986), Kalevi Holsti’s “The Horsemen of the Apocalypse: At the Gate, Detoured, or Retreating?” (1986), Evan Luard’s
The Blunted Sword: The Erosion of Military Power in Modern World Politics
(1988), John Mueller’s
Retreat from Doomsday: The Obsolescence of Major War
(1989), Francis Fukuyama’s “The End of History?” (1989), James Lee Ray’s “The Abolition of Slavery and the End of International War” (1989), and Carl Kaysen’s “Is War Obsolete?” (1990).
154
In 1988 the political scientist Robert Jervis captured the phenomenon they were all noticing:
The Coming End of War
(1981), John Gaddis’s “The Long Peace: Elements of Stability in the Postwar International System” (1986), Kalevi Holsti’s “The Horsemen of the Apocalypse: At the Gate, Detoured, or Retreating?” (1986), Evan Luard’s
The Blunted Sword: The Erosion of Military Power in Modern World Politics
(1988), John Mueller’s
Retreat from Doomsday: The Obsolescence of Major War
(1989), Francis Fukuyama’s “The End of History?” (1989), James Lee Ray’s “The Abolition of Slavery and the End of International War” (1989), and Carl Kaysen’s “Is War Obsolete?” (1990).
154
In 1988 the political scientist Robert Jervis captured the phenomenon they were all noticing:
The most striking characteristic of the postwar period is just that—it can be called “postwar” because the major powers have not fought each other since 1945. Such a lengthy period of peace among the most powerful states is unprecedented.
155
These scholars were confident that they were not being fooled by a lucky run but were putting their finger on an underlying shift that supported predictions about the future. In early 1990, Kaysen added a last-minute postscript to his review of Mueller’s 1989 book in which he wrote:
It is clear that a profound transformation of the international structure in Europe—and the whole world—is underway. In the past, such changes have regularly been consummated by war. The argument presented in this essay supports the prediction that this time the changes can take place without war (although not necessarily without domestic violence in the states concerned). So far—mid-January—so good. The author and his readers will be eagerly and anxiously testing the prediction each day.
156
Precocious assessments of the obsolescence of interstate war are especially poignant when they come from military historians. These are the scholars who have spent their lives immersed in the annals of warfare and should be most jaded about the possibility that this time it’s different. In his magnum opus
A History of Warfare
, John Keegan (the military historian who is so habitually called “distinguished” that one could be forgiven for thinking it is part of his name) wrote in 1993:
A History of Warfare
, John Keegan (the military historian who is so habitually called “distinguished” that one could be forgiven for thinking it is part of his name) wrote in 1993:
War, it seems to me, after a lifetime of reading about the subject, mingling with men of war, visiting the sites of war and observing its effects, may well be ceasing to commend itself to human beings as a desirable or productive, let alone rational, means of reconciling their discontents.
157
The equally distinguished Michael Howard had already written, in 1991:
[It has become] quite possible that war in the sense of major, organized armed conflict between highly developed societies may not recur, and that a stable framework for international order will become firmly established.
158
And the no-less-distinguished Evan Luard, our guide to six centuries of war, had written still earlier, in 1986:
Most startling of all has been the change that has come about in Europe, where there has been a virtual cessation of international warfare.... Given the scale and frequency of war during the preceding centuries in Europe, this is a change of spectacular proportions: perhaps the single most striking discontinuity that the history of warfare has anywhere provided.
159
More than two decades later, none of them would have a reason to change his assessment. In his 2006 book
War in Human Civilization,
a military history that is more sweeping than its predecessors and salted with the Hobbesian realism of evolutionary psychology, Azar Gat wrote:
THE LONG PEACE: ATTITUDES AND EVENTSWar in Human Civilization,
a military history that is more sweeping than its predecessors and salted with the Hobbesian realism of evolutionary psychology, Azar Gat wrote:
Among affluent liberal democracies . . . a true
state
of peace appears to have developed, based on genuine mutual confidence that war between them is practically eliminated even as an option. Nothing like this had ever existed in history.
160
The italics in Gat’s “true
state
of peace” highlight not just the datum that the number of wars between developed states happens to be zero but a change in the countries’ mindsets. The ways that developed countries conceptualize and prepare for war have undergone sweeping changes.
state
of peace” highlight not just the datum that the number of wars between developed states happens to be zero but a change in the countries’ mindsets. The ways that developed countries conceptualize and prepare for war have undergone sweeping changes.
A major feeder of the increasing deadliness of war since 1500 (see figure 5–16) has been conscription, the stocking of national armies with a renewable supply of bodies. By the time of the Napoleonic Wars, most European countries had some form of a draft. Conscientious objection was barely a concept, and recruitment methods were far less polite than the telegram dreaded by young American men in the 1960s that began: “Greetings.” The idiom
pressed into service
comes from the institution of press gangs, groups of goons paid by the government to snatch men from the streets and force them into the army or navy. (The Continental Navy during the American Revolutionary War was almost entirely rounded up by press gangs.)
161
Compulsory military service could consume a substantial portion of a man’s life—as much as twenty-five years for a serf in 19th-century Russia.
pressed into service
comes from the institution of press gangs, groups of goons paid by the government to snatch men from the streets and force them into the army or navy. (The Continental Navy during the American Revolutionary War was almost entirely rounded up by press gangs.)
161
Compulsory military service could consume a substantial portion of a man’s life—as much as twenty-five years for a serf in 19th-century Russia.
Military conscription represents the application of force squared: people are coerced into servitude, and the servitude exposes them to high odds of being maimed or killed. Other than at times of existential threat, the extent of conscription is a barometer of a country’s willingness to sanction the use of force. In the decades after World War II, the world saw a steady reduction in the length of compulsory military service. The United States, Canada, and most European countries have eliminated conscription outright, and in the others it functions more as a citizenship-building exercise than as a training ground for warriors.
162
Payne has compiled statistics on the length of military conscription between 1970 and 2000 in forty-eight long-established nations, which I have updated for 2010 in figure 5–19. They show that conscription was in decline even before the end of the Cold War in the late 1980s. Only 19 percent of these countries did without conscription in 1970. The proportion rose to 35 percent in 2000 and to 50 percent in 2010, and it will soon exceed 50 percent because at least two other countries (Poland and Serbia) plan to abolish the draft in the early 2010s.
163
162
Payne has compiled statistics on the length of military conscription between 1970 and 2000 in forty-eight long-established nations, which I have updated for 2010 in figure 5–19. They show that conscription was in decline even before the end of the Cold War in the late 1980s. Only 19 percent of these countries did without conscription in 1970. The proportion rose to 35 percent in 2000 and to 50 percent in 2010, and it will soon exceed 50 percent because at least two other countries (Poland and Serbia) plan to abolish the draft in the early 2010s.
163
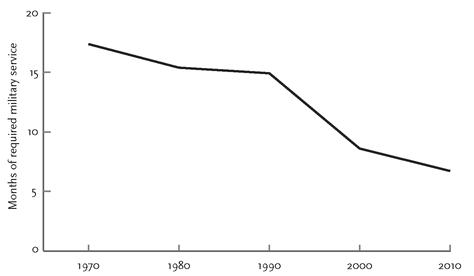
FIGURE 5–19.
Length of military conscription, 48 major long-established nations, 1970–2010
Length of military conscription, 48 major long-established nations, 1970–2010
Sources:
Graph for 1970–2000 from Payne, 2004, p. 74, based on data from the International Institute for Strategic Studies (London),
The Military Balance
, various editions. Data for 2010 from the 2010 edition of
The Military Balance
(International Institute for Strategic Studies, 2010), supplemented when incomplete from
The World Factbook
, Central Intelligence Agency, 2010.
Graph for 1970–2000 from Payne, 2004, p. 74, based on data from the International Institute for Strategic Studies (London),
The Military Balance
, various editions. Data for 2010 from the 2010 edition of
The Military Balance
(International Institute for Strategic Studies, 2010), supplemented when incomplete from
The World Factbook
, Central Intelligence Agency, 2010.
Other books
Anchor Line by Dawne Walters
Jack the Ripper: The Hand of a Woman by kindels
The Illusion of Conscious Will by Daniel M. Wegner
One Mile Under by Gross, Andrew
The Heartbreaker Series: Books 1-3 by Grace,Evan
Leena’s Dream by Marissa Dobson
Naughty or Nice by Harmon, Kari Lee
Believe by Lauren Dane
Slime by Halkin, John
