The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (727 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
3.81Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Elohim
(Heb., God(s)). A name for the God of the Jews. Its plural form may once have been literal—‘mighty ones’—but it became subsumed in the accumulating Jewish sense that if God is indeed
God
, then there can only be what God is: One, and not a plurality of gods.
God
, then there can only be what God is: One, and not a plurality of gods.
El
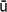 r
r
 (sacred Indian cave temples)
(sacred Indian cave temples)
:
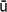 r
r (sacred Indian cave temples)
(sacred Indian cave temples):
Ema
(Jap.). Pictorial votive offerings.
Koema
(small ema) is a small flat wooden plaque, which may be rectangular, square, or pentagonal in shape, with a picture painted on its front surface.
 ema
ema
(large ema), which appeared after the 15th cent. is a work of art in many cases, painted by famous painters at the request of their rich patrons. Both
koema
and
 ema
ema
are offered to the
kami
of a shrine or to the deity of a temple for making wishes and for the fulfilment of the wishes.
The word
ema
(picture + horse) suggests its origin as a substitute for a live horse.
Koema
(small ema) is a small flat wooden plaque, which may be rectangular, square, or pentagonal in shape, with a picture painted on its front surface.
 ema
ema(large ema), which appeared after the 15th cent. is a work of art in many cases, painted by famous painters at the request of their rich patrons. Both
koema
and
 ema
emaare offered to the
kami
of a shrine or to the deity of a temple for making wishes and for the fulfilment of the wishes.
The word
ema
(picture + horse) suggests its origin as a substitute for a live horse.
Emaki
(Jap.). A picture scroll. A long scroll, viewed from right to left, contains a series of pictures, often with the text that illustrates a story.
Its motifs range from the secular to the religious.
Jigoku z
 shi
shi
(the Scroll of Hells), made in the 12th cent., is a religious emaki, in which the gruesome scenes of
hells
based on Genshin's
 j
j
 y
y
 sh
sh
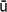 (The Essentials for Salvation) are vividly illustrated. Temples and shrines supplied legends and miracle stories, and as a result of the spread of Buddhism in the Kamakura period, the lives of exemplary people were added to its themes.
(The Essentials for Salvation) are vividly illustrated. Temples and shrines supplied legends and miracle stories, and as a result of the spread of Buddhism in the Kamakura period, the lives of exemplary people were added to its themes.
Its motifs range from the secular to the religious.
Jigoku z
 shi
shi(the Scroll of Hells), made in the 12th cent., is a religious emaki, in which the gruesome scenes of
hells
based on Genshin's
 j
j y
y sh
sh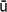 (The Essentials for Salvation) are vividly illustrated. Temples and shrines supplied legends and miracle stories, and as a result of the spread of Buddhism in the Kamakura period, the lives of exemplary people were added to its themes.
(The Essentials for Salvation) are vividly illustrated. Temples and shrines supplied legends and miracle stories, and as a result of the spread of Buddhism in the Kamakura period, the lives of exemplary people were added to its themes.Other books
Full Bloom by Jayne Ann Krentz
Empire of Avarice by Tony Roberts
Blood Ties by C.C. Humphreys
Annihilation (Star Force Series) by B. V. Larson
The Poison Master by Liz Williams
Stolen Sun (The Juliana Lucio Series) by L.C. DeCarlo
Predator by Richard Whittle
Eros Descending: Book 3 of Tales of the Velvet Comet by Mike Resnick
Immortal Desire by Tompkins, Denise
An Incidental Reckoning by Greg Walker


