Breast Imaging: A Core Review (6 page)
Read Breast Imaging: A Core Review Online
Authors: Biren A. Shah,Sabala Mandava
Tags: #Medical, #Radiology; Radiotherapy & Nuclear Medicine, #Radiology & Nuclear Medicine

A. Dirt or dust on compression paddle
B. Ghost image
C. Readout failure
D. Dead pixels
E. Gridlines
50
What is the artifact present on the following mediolateral oblique (MLO) image? The second image denotes a part of the MLO view magnified.
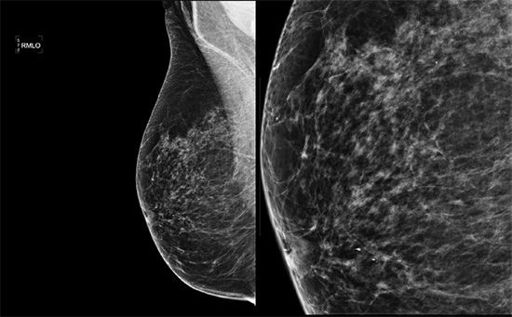
A. Motion
B. Gridlines
C. Deodorant
D. Filtration artifact
51
The universal amount of intravenous gadolinium used for contrast enhancement in breast MR imaging is:
A. 0.1 mmol/kg
B. 0.2 mmol/kg
C. 0.3 mmol/kg
D. 0.4 mmol/kg
E. 0.5 mmol/kg
52
In order to ensure the quality of the mammographic images, the posterior nipple line on MLO and CC projections should be within
A. 0.5 cm
B. 1.0 cm
C. 1.5 cm
D. 2.0 cm
E. It should be equal.
53a
Which one of the following artifacts is present on the T1-weighted non–fat-saturated localizer image?
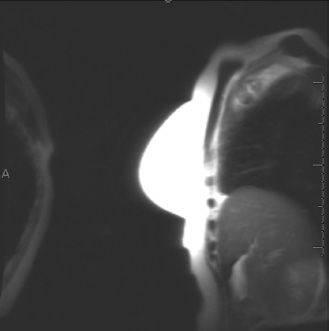
A. Chemical shift
B. Phase wrap/aliasing
C. Metallic susceptibility
D. Patient motion
53b
What can reduce phase wrap/aliasing artifact on breast MRI?
A. Enlarging the field of view
B. Reducing patient motion
C. Shimming the magnet frequently
D. Increasing the bandwidth
E. Check for a leak in the radiofrequency (RF) shield
54
Which feature of digital breast tomosynthesis allows it to decrease the effect of overlapping breast tissue?
A. Higher radiation dose than in mammography
B. Reconstruction of the projections into the mediolateral oblique (MLO) and craniocaudal (CC) views
C. Digital acquisition technique
D. Multiple exposures of the breast at different angles
E. Increased breast compression
55
The above mediolateral oblique (MLO) image taken during a screening mammogram examination demonstrates which type of digital mammogram artifact?
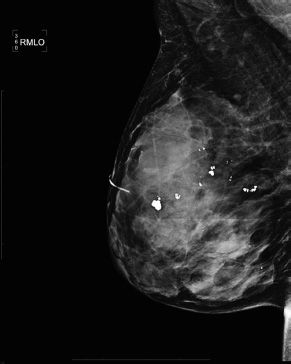
A. Detector interface line
B. Ghost image
C. Readout failure
D. Dead pixels
E. Gridlines
ANSWERS AND EXPLANATIONS
1
Answer C.
References:
www.fda.gov/cdrh/mammography
Ikeda D.
Breast Imaging: The Requisites
. 2nd ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Mosby; 2011:16.
2
A. Answer A.
BI-RADS 2—Dermal calcifications
B. Answer A.
BI-RADS 2—“Popcorn-like” calcification
C. Answer A.
BI-RADS 2—Secretory calcifications
D. Answer A.
BI-RADS 2—Round calcification
E. Answer A.
BI-RADS 2—Lucent center calcification (oil cyst)
F. Answer B.
BI-RADS 4—Linear branching calcifications
G. Answer B.
BI-RADS 4—Fine pleomorphic calcifications
H. Answer B.
BI-RADS 2—Milk of calcium
Reference: American College of Radiology (ACR). BI-RADS-Mammography.
The ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)
. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology; 2003:61–107.
3
Answer B.
Reference: Linver MN, Osuch JR, Brenner RJ, et al. The mammography audit: A Primer for the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA).
AJR Am J Roentgenol
1995;165:19–25.
4
Answer D.
Sensitivity is the probability of detecting a cancer when a cancer exists or the number of cancers diagnosed after being identified at mammography in a population within 1 year of the imaging examination, divided by all cancers present in that population in the same time period.
Sensitivity = TP/(TP + FN); TP = True positive; FN = False negative
References: American College of Radiology (ACR). BI-RADS—Mammography.
The ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)
. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology; 2003:231.
Linver MN, Osuch JR, Brenner RJ, et al. The mammography audit: A Primer for the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA).
AJR Am J Roentgenol
1995;165:19–25.
5
Answer C.
The appearance of the pectoral muscle is useful in assessing position on MLO views. The breast should be pulled up and out, the inframammary fold should be open on MLO views and neutral on craniocaudal views, and a small amount of the upper abdomen should be visible on MLO views.
Reference: Cardenosa G.
Breast Imaging Companion
. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2008:79–84.
6
Answer A.
A breast cancer diagnosed within a year of a negative screening mammogram is considered a false negative.
Reference: BI-RADS-Mammography.
The ACR Breast Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)
. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology.
Linver MN, Osuch JR, Brenner RJ, et al. The mammography audit: A Primer for the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA).
AJR Am J Roentgenol
1995;165:19–25.
7
Answer C.
Quality Control (QC) Test Schedule for Film-Screen Mammography
| TEST | PERFORMED |
| Darkroom cleanliness | Daily |
| Processor QC | Daily |
| Screen cleanliness | Weekly |
| Phantom images | Weekly |
| Viewbox cleanliness and viewing checklist | Quarterly |
| Repeat analysis | Quarterly |
| Fixer retention | Semiannually |
| Darkroom fog | Semiannually |
| Screen–film contact | Semiannually |
| Compression | Semiannually |
Other books
Piedras ensangrentadas by Donna Leon
Midnight on the Moon by Mary Pope Osborne
The Last Voice You Hear by Mick Herron
Goofy Foot by David Daniel
The Mammoth Book of Roman Whodunnits by Mike Ashley (ed)
Starbounders by Adam Jay Epstein
The Butterfly Forest (Mystery/Thriller) by Lowe, Tom
A Death in Valencia by Jason Webster
The Twelve Rooms of the Nile by Enid Shomer
All That He Wants by Olivia Thorne
