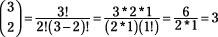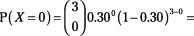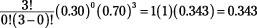Statistics Essentials For Dummies (10 page)

x
is the specified number of successes.
n
-
x
is the number of failures.
p
is the probability of success on any given trial.
1 -
p
is the probability of failure on any given trial. (
Note:
Some textbooks use the letter
q
to denote the probability of failure rather than 1 -
p
.)
These probabilities hold for any value of
X
between 0 (lowest number of possible successes in
n
trials) and
n
(highest number of possible successes).
The number of ways to arrange
x
successes among
n
trials is
called "
n
choose
x,
" and the notation is. For example,
means "3 choose 2" and stands for the number of ways to get 2 successes in 3 trials. In general, to calculate "
n
choose
x
,"
you use the formula
. The notation
n
! stands
for
n-factorial
, the number of ways to rearrange
n
items. To calculate
n
!, you multiply
n
(
n
- 1)(
n
- 2) . . . (2)( 1). For example 3! is 3(2)(1) = 6; 2! is 2(1) = 2; and 1! is 1. By convention, 0! equals 1. To calculate "3 choose 2," you do the following:
Suppose you cross three traffic lights on your way to work, and the probability of each of them being red is 0.30. (Assume the lights are independent.) You let
X
be the number of red lights you encounter and you want to find the probability distribution for
X
. You know
p
= probability of red light = 0.30; 1 -
p
= probability of a non-red light = 1 - 0.30 = 0.70; and the number of non-red lights is 3 -
X
. Using the formula, you obtain the probabilities for
X
= 0, 1, 2, and 3 red lights: