The Other Slavery (50 page)
Authors: Andrés Reséndez

Appendix 2
Slaving Licenses in the Caribbean, 1509–1522
43
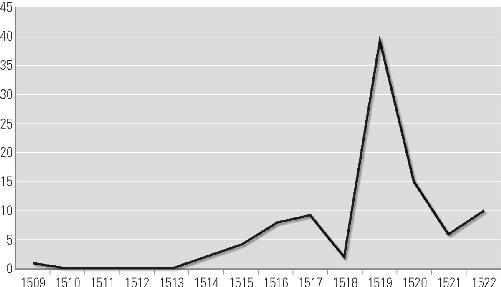
Appendix 3
Average Price of Indian Slaves by Gender and Age in the Caribbean, 1521–1535
44
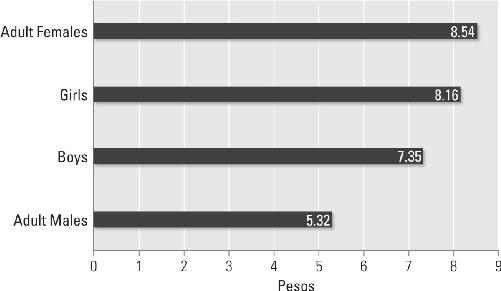
Appendix 4
Production of Mexican Silver and U.S. Gold, 1520–1900
45
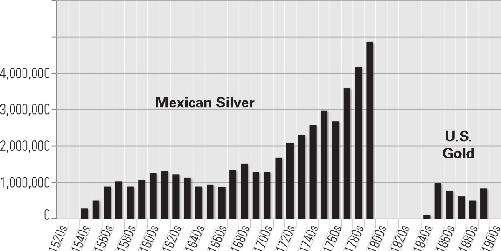
Appendix 5
Indians from New Mexico Listed in Baptismal Records from Parral, 1634–1700
46
| | Apaches | Apaches from New Mexico | Indians from New Mexico | Quiviras | Total |
| 1634–1639 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 11 |
| 1640–1644 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1645–1648 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 7 |
| 1649–1655 | 9 | 4 | 8 | 0 | 21 |
| 1656–1660 | 14 | 1 | 34 | 0 | 49 |
| 1661–1665 | 20 | 0 | 8 | 1 | 29 |
| 1665–1670 | 4 | 2 | 95 | 1 | 102 |
| 1671–1675 | 45 | 0 | 22 | 2 | 69 |
| 1676–1680 | 100 | 1 | 15 | 5 | 121 |
| 1681–1685 | 54 | 0 | 10 | 2 | 66 |
| 1686–1691 | 18 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 20 |
| 1695–1700 | 21 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 22 |
Appendix 6
Indian Slaves in Mexico and North America, 1492–1900 (in thousands)
47
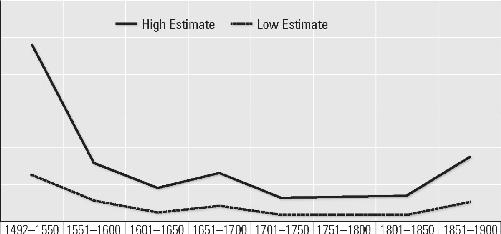
Appendix 7
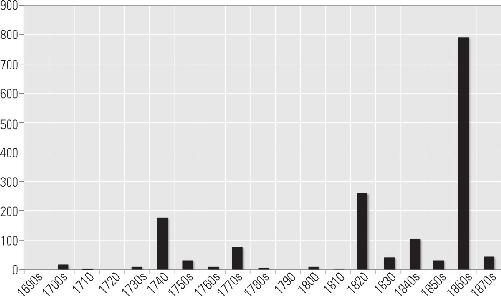
Navajo Baptisms in New Mexico, 1690–1880
48
Notes
INTRODUCTION
1. For country-by-country estimates of people in bondage today, see the Global Slavery Index, Walk Free Foundation,
http://www.globalslaveryindex.org/findings/#rankings
.
2. Colonial Americans in places such as New England, Virginia, and the Carolinas had Indian slaves in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. But the institution was subsequently eclipsed by African slavery. By the middle of the nineteenth century, the memory of these earlier Indian slaves had been sufficiently erased that many easterners experienced the phenomenon of Indian slavery in the West as a novelty. (See
chapter 10
.) For a sampling of the new scholarship that is excavating the old Indian slavery in the East, see Alan Gallay,
The Indian Slave Trade: The Rise of the English Empire in the American South, 1670–1717
(New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2002); Alan Gallay, ed.,
Indian Slavery in Colonial America
(Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2009); Christina Snyder,
Slavery in Indian Country: The Changing Face of Captivity in Early America
(Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2010); Barbara Krauthamer,
Black Slaves, Indian Masters: Slavery, Emancipation, and Citizenship in the Native American South
(Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2013); Brett Rushforth,
Bonds of Alliance: Indigenous and Atlantic Slaveries in New France
(Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2012); and Robbie Ethridge and Sheri M. Shuck-Hall, eds.,
Mapping the Mississippian Shatter Zone: The Colonial Indian Slave Trade and Regional Instability in the American South
(Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2009).
3. The quotes from the commander are from John B. Montgomery, “A Proclamation to the Inhabitants of the Northern District of California,”
California Star,
March 6, 1847, available online in the California Digital Newspaper Collection,
http://cdnc.ucr .edu/cgi-bin/cdnc
. The proclamation was issued on September 15, 1846. On the impact of the Indian Act of 1850, see Michael F. Magliari, “Free Soil, Unfree Labor: Cave Johnson Couts and the Binding of Indian Workers in California, 1850–1867,”
Pacific Historical Review
73:3 (2004), 349–389; Sherburne F. Cook,
The Conflict Between the California Indian and White Civilization
(Berkeley: University of California Press, 1976), 314–315; Robert F. Heizer, “Indian Servitude in California,” in Wilcomb E. Washburn, ed.,
Handbook of North American Indians: History of Indian-White Relations,
vol. 4 (Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1988), 414–417;
Stacey L. Smith,
Freedom’s Frontier: California and the Struggle over Unfree Labor, Emancipation, and Reconstruction
(Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2013), passim; and Benjamin Madley, “‘Unholy Traffic in Human Blood and Souls’: System of California Indian Servitude Under U.S. Rule,”
Pacific Historical Review
83:4 (November 2014), 626–667.
4. The quotes are from James S. Calhoun, Indian agent, to Orlando Brown, Commissioner of Indian Affairs, Santa Fe, March 15, 1850, in
The Official Correspondence of James S. Calhoun While Indian Agent at Santa Fe and Superintendent of Indian Affairs in New Mexico,
ed. Annie Heloise Abel (Washington, DC: Government Printing Office, 1915), 162; and report of James S. Calhoun, Santa Fe, March 31, 1850, in
Annual Report of the Commissioner of Indian Affairs to the Department of the Interior
(Washington, DC: Office of the Commissioner of Indian Affairs, 1850), 105. “Sear and yellow leaf,” a quote from
Macbeth,
refers to the autumn of one’s life.
