The Road to Ubar (10 page)
Authors: Nicholas Clapp

"Well, Bob..." Ron mused.
"Well, what?" Bob asked.
"Let's beat up on it," Ron said, a shade grimly.
"We could do an enhancement," Bob suggested, electronic gunslinger eyes narrowing. "Divide one band by another, that sort of thing..."
A dense computer-tech conversation ensued, which I only vaguely followed. Ron theorized that ancient tracksâhammered by the feet of thousands of camels over hundreds of yearsâwould be more compressed than those left by modern vehicles skittering over the terrain. Did this compression have a spectral signature?
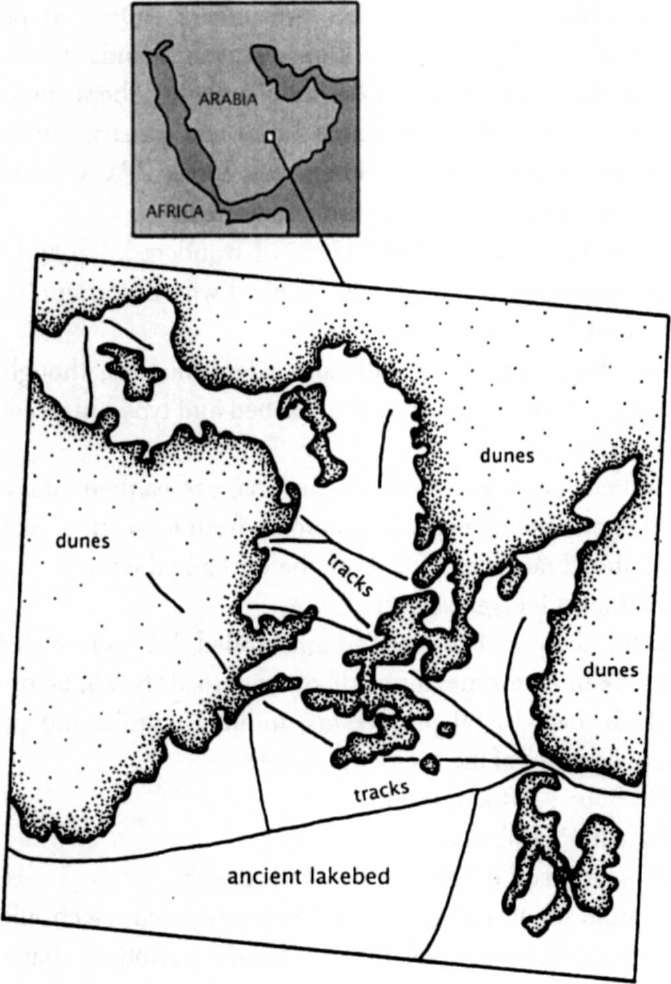
Detail of Landsat 5 image
"Hmm," Bob responded. He tentatively tapped his keyboard. "We could also hit up on the near-infrared, shift it to visible." Without waiting for a reply, Bob typed furiously. Then typed some more and rocked back in his chair.
"Hmm, we'll see."
The wall clock at the far end of the room read 3:52
P.M.
The image rescanned, now producing waves of color that were surreal, psychedelic. And a strange and curious thing happened. The tracks crisscrossing the image faded away, disappeared. All but one.

Landsat detail after image processing
"Well, look at that," said Bob. What remained on his monitor was a thin black line that arced up across the screen and led off into the dunes of the Rub' al-Khali.
We took turns, like little kids, following it with our fingers.
There it was, before our eyes and in far Arabia, the road to Ubar.
I
T DIDN'T TAKE LONG
to come up with an expedition scenario. On the ground we would locate and follow the thin black line that angled across JPL's Landsat image. Somewhere on or near it would be Ubarâthat is, if there ever was an Ubar.
In an enthusiastic letter, Father Jamme, the Jesuit epigrapher, gave us his blessing: "From JPL you have the revelation of an ancient road in the country of Ubar. Now you have a wonderful starting point which has to be discovered in place; it is an entirely new ball game. What a hope. Full speed ahead!"
Once JPL had made blow-ups of our satellite image, George Hedges framed one and sent it off to Ran Fiennes so that he could present it to Oman's Sultan Qaboos ibn Said, in the hope that he would eventually allow us to trek across his desert. Ran warned us, though, that we were not dealing with a land of quick responses.
Between us, Ron Blom and I spent hours scanning every millimeter of our full Landsat image and, tentatively, reconstructing the course of Oman's ancient Incense Road. It appeared that frankincense harvested in the mountains of Dhofar was first taken to two collection points, Hanun and Andhur, where there are known ruins. From Hanun and Andhur two separate routes went north across a gravel plain and converged at the well of Shisur.
1
From there a single route headed northwest and soon entered the dunes of the Rub' al-Khali. The telltale line on our Landsat image then shifted to the 325-degree alignment reported by Bertram Thomas. As the dunes became ever more massive, the line became fainter and fainter. Just short of where Thomas thought Ubar was to be found, it all but vanished.
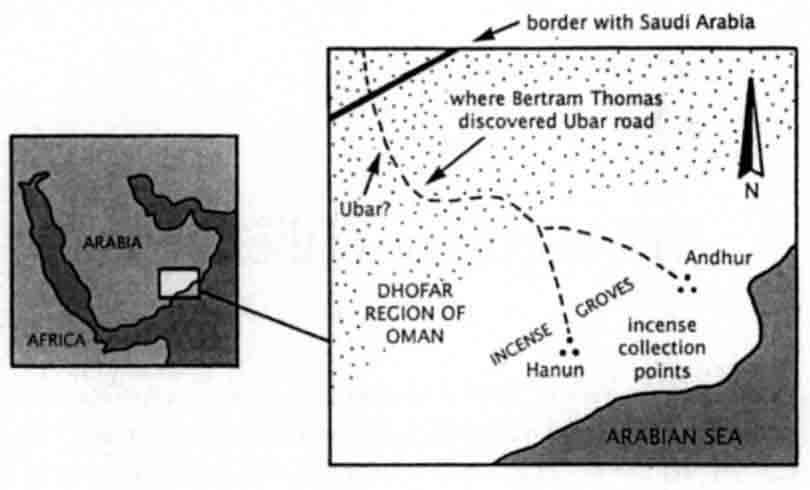
Incense caravan route through Oman
The road surely continued on, but we now could only approximate its route, for features generally have to be upward of thirty meters wide to show up on a Landsat image. For higher resolution, Ron suggested France's SPOT (Système Probatoire d'Observation de la Terre) satellite. Zeroing in on a smaller area and sacrificing color for black-and-white, it could image features less than ten meters across. Carefully, we plotted reference points for SPOT coverage so that as it arced over Arabia, the French satellite could align its lenses, prisms, and mirrors and further reveal the road to Ubar.
At about this time, we all agreed that we should recruit a trained, experienced archaeologist. It was one thing to look for Ubar, but if we found anything, any excavation would have to be directed by a professional. The obvious candidate for the job was Dr. Juris Zarins, who had recently completed a ten-year field survey of major archaeological sites in Saudi Arabia. Yet I hesitated to call him. His name conjured up the image of a long-bearded, stoop-shouldered academic, speaker of nine antique languages, who would say, dismissively, "Ubar! Ha! A fanciful myth, yes, but nothing more."
Zarins was currently teaching at Southwest Missouri State. When I finally phoned, I was surprised and delighted to find myself talking at great length with an immensely good-natured and enthusiastic individual. Within a week George Hedges and I were on a plane for Springfield, Missouri, to review the project.
It wasn't hard to break the ice with Juris Zarinsâsix foot four, mustache, but no long academic beard.
"Do you prefer to be called Juris or Juri?" George asked.
"Yes," he answered, deadpan, then broke into a broad smile and slapped us on our backs.
Juris/Juri had been born in Lithuania, raised in a German displaced persons camp, then had come to America with his family and settled in the Midwest. In high school he became a first-string basketball center, polished his English, and developed a lifelong fondness for terrible puns. And he took up the study of cuneiform.
"I guess the light struck early. I was interested in the origins of things, and even before college I got a summer job digging Lewis and Clark's fort. Guess what they gave me."
"The kitchen? Graveyard?" we ventured.
"The crapper. Personally excavated it."
With fellow farm kids, Juri served as a combat infantryman in Vietnam, then, on the GI Bill, earned a Ph.D. in archaeology from the University of Chicago. He was drawn to the Middle East and the evidence there of the origins of writing, cities, and civilization. Though he dearly loved his adopted Midwest, he thrived as well in the harsh, hostile deserts of the Mideast.
Within hours Juri was a member of our team. He thought Ubar could well be a real place. On the north side of the Rub' al-Khali, at the oasis of Jabrin, he had dug test pits that yielded bits of pottery from Mesopotamia. He knew that Mesopotamians had had trading colonies on the Arabian gulf coast, but what were they doing so far inland?
"It makes no sense," he mused, "unless, of course, there was an Ubar, and both sites functioned as stops for frankincense caravans." Heading north from Ubar, caravans could have followed a series of wells across the Rub' al-Khali to the oasis of Jabrin, then continued on their way to Mesopotamia. Zarins confirmed a larger vision of the Ubar road as a vital link in Arabia's incense trade (see map below).

Arabia's incense roads
By June of 1987 our now seven-member team had permission in the works, more space imagery on order, but still no moneyâso we had time to further research the myth of Ubar. Although I had more than twenty loose-leaf binders of notes, I didn't know that there would be another twenty-seven to go. The more I read, the more there was to read in English and (with the help of translators) German, French, and Arabicâincluding modern Arabic, medieval Arabic, and Epigraphic South Arabic (ESA), a long unspoken language known only in inscriptions from the time of Ubar.
What archaeologists really treasure at their sites is anything in writing. Scrawled graffiti will do; graven inscriptions are better. The South Arabians had left behind an abundance of both, and yet, Father Jamme had assured me, none made mention of Ubar or its People of 'Ad. But now, in an obscure volume, I happened across the story of the
Palinuris,
a British survey ship that in 1824 charted the coastline of southern Arabia. At 54°30'E, 20°15'N, the
Palinuris
dropped anchor in a protected natural harbor. From its white sand beach rose a spectacular black volcanic hill, which the local tribesmen called Husn al-Ghurab, the Fortress of the Crows. Ascending to its summit, the ship's first mate, Lieutenant Wellstead, discovered an imposing, finely carved inscription. He diligently copied it down, and sent it on to the Reverend Charles Foster, an English cleric who pronounced it to be an 'Adite inscription of "awful antiquity." Foster's translation revealed it to be an account of the golden age and ultimate grief of the People of 'Ad! It even mentioned the prophet Hud, Ubar's doomsayer, by name. In part the long inscription read:
And we hunted the game, by land, with ropes and reeds;
And we drew forth the fishes from the depths of the sea.
Kings reigned over us, far removed from baseness,
And vehement against the people of perfidy and fraud.
They sanctioned for us, from the religion of Hud, right laws,
And we believed in miracles, the resurrection,
And the resurrection of the dead by the breath of God.
Then came years barren and burnt up:
When one evil year had passed away, there came another to succeed it.
And we became as though we had never seen a glimpse of good.
They died: and neither foot nor hoof remained.
Thus fares it with him who renders not thanks to God:
His footsteps fail not to be blotted out from his dwelling.
2
What a wonderful poetic vision this was, except that it didn't quite make sense: early on in the inscription, its people "believed in the religion of Hud" and had kings "far removed from baseness," yet they later paid the price of "him who renders not thanks to God." And how could a people die offâ"neither foot nor hoof" remainingâthen pop back to elegize their own fate?
Ever hopeful, I sought Father Jamme's opinion, and by return mail received a freshly annotated translation. The inscription really did exist, he told me, but it had nothing to do with a lost golden age, the prophet Hud, or the promise of resurrection. The inscription was, in fact, the equivalent of the plaques that modern politicians delight in affixing to the walls of city halls and civic monuments. The inscription begins
not
with "And we hunted..." but with "
SMYF' 'SW'
[a proper name] and his sons
SRHB'L YKHL
and
M'DRKB Y'R
[two more proper names]..." It then listed a city council of some forty additional names, all taking credit for renovating the fortifications at the Fortress of the Crows around 525
A.D.
