Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (123 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

S
a
O
2
is measured in any arterial sample (usually 93—98%)
S
v
O
2
(mixed venous O
2
) is measured in RA, RV or PA (assuming no shunt) (nl ~75%)

PULMONARY
CXR in heart failure
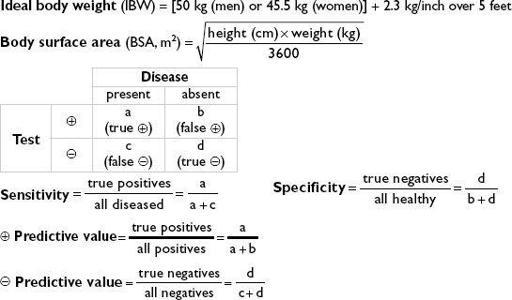
• ↑ cardiac silhouette (in systolic dysfxn, not in diastolic) • Pulmonary venous hypertension: cephalization of vessels (vessels size > bronchi in upper lobes), peribronchial cuffing (fluid around bronchi seen on end → small circles), Kerley B lines (horizontal 1—2-cm lines at bases), ↑ vascular pedicle width, loss of sharp vascular margins, pleural effusions (~75% bilateral) • Pulmonary edema: ranges from ground glass to consolidation; often dependent and central, sparing outer third (“bat wing” appearance)
Dead space
= lung units that are ventilated but not perfused
Intrapulmonary shunt
= lung units that are perfused but not ventilated
NEPHROLOGY
Anion gap
(AG) = Na − (Cl + HCO
3
) (normal = [alb] × 2.5; typically 12 ± 2 mEq)
Delta-delta
(ΔΔ) = [Δ AG (ie, calc. AG - expected) / Δ HCO
3
(ie, 24 - measured HCO
3
)]
Urine anion gap
(UAG) = (U
Na
+ U
K
) − U
Cl

HEMATOLOGY
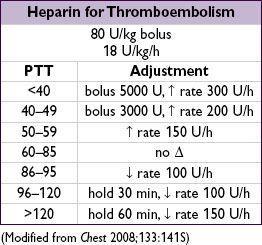
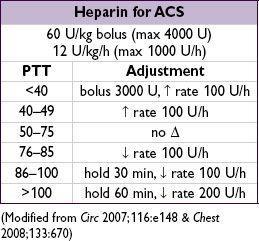
✓ PTT q6h after every Δ (t
1
⁄
2
of heparin ~90 min) and then qd or bid once PTT is therapeutic ✓ CBC qd (to ensure Hct and plt counts are stable)
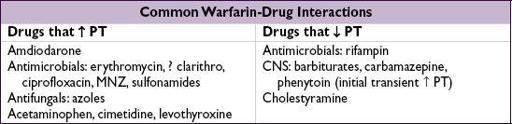
Warfarin-heparin overlap therapy
• Indications: when failure to anticoagulate carries ↑ risk of morbidity or mortality (eg, DVT/PE, intracardiac thrombus)
• Rationale: (1) Half-life of factor VII (3—6 h) is shorter than half-life of factor II (60—72 h);
∴warfarin can elevate PT
before achieving a true antithrombotic state
(2) Protein C also has half-life less than that of factor II;
∴theoretical concern of
hypercoagulable state
before antithrombotic state
• Method: (1) Therapeutic PTT is achieved using heparin
(2) Warfarin therapy is initiated
(3) Heparin continued until INR therapeutic for ≥2 d and ≥4—5 d of warfarin
(roughly corresponds to ~2 half-lives of factor II or a reduction to ~25%)
OTHER
NOTES
ABBREVIATIONS
| 5′-NT | 5′-nucleotidase |
| 6-MP | 6-mercaptopurine |
| AAA | abdominal aortic aneurysm |
| AAD | antiarrhythmic drug |
| Ab | antibody |
| ABE | acute bacterial endocarditis |
| ABG | arterial blood gas |
| abnl | abnormal |
| ABPA | allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis |
| abx | antibiotics |
| AC | assist control |
| ACE | angiotensin converting enzyme |
| ACEI | ACE inhibitor |
| ACI | anemia of chronic inflammation |
| ACL | anticardiolipin antibody |
| ACLS | advanced cardiac life support |
| ACS | acute coronary syndrome |
| ACTH | adrenocorticotrophic hormone |
| ACV | acyclovir |
| ADA | adenosine deaminase |
| ADH | antidiuretic hormone |
| ADL | activities of daily living |
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| AFB | acid-fast bacilli |
| AFL | atrial flutter |
| AFP | ɑ-fetoprotein |
| AFTP | ascites fluid total protein |
| AG | aminoglycoside |
anion gap | |
| Ag | antigen |
| AGN | acute glomerulonephritis |
| AI | aortic insufficiency |
| AIDS | acquired immunodefic. synd. |
| AIH | autoimmune hepatitis |
| AIHA | autoimmune hemolytic anemia |
| AIN | acute interstitial nephritis |
| AIP | acute interstitial pneumonia |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| ALF | acute liver failure |
| ALL | acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AMA | anti-mitochondrial antibody |
| AMI | anterior myocardial infarction |
| AML | acute myelogenous leukemia |
| amy | amylase |
| ANA | antinuclear antibody |
| ANCA | antineutrophilic cytoplasmic Ab |
| AoD | aortic dissection |
| AoV | aortic valve |
| APC | activated protein C |
| APL | acute promyelocytic leukemia |
| APLA | antiphospholipid Ab |
| APS | antiphospholipid Ab synd. |
| ARB | angiotensin receptor blocker |
| ARDS | acute resp distress synd. |
| ARV | antiretroviral |
| ARVC | arrhythmogenic RV CMP |
| AS | aortic stenosis |
| ASA | aspirin |
| ASD | atrial septal defect |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| asx | asymptomatic |
| AT | atrial tachycardia |
| ATII | angiotensin II |
| ATIII | antithrombin III |
| ATN | acute tubular necrosis |
| ATRA | all- |
| AV | atrioventricular |
| AVA | aortic valve area |
| AVB | atrioventricular block |
| AVNRT | AV nodal reentrant tachycardia |
| AVR | aortic valve replacement |
| AVRT | AV reciprocating tachycardia |
| a/w | associated with |
| AZA | azathioprine |
| Aϕ | alkaline phosphatase |
| b/c | because |
| BAL | bronchoalveolar lavage |
| βB | beta-blocker |
| BBB | bundle branch block |
| BCx | blood culture |
| BD | bile duct |
| BDZ | benzodiazepines |
| bili. | bilirubin |
| BIPAP | bilevel positive airway pressure |
| BIV | biventricular |
| BM | bone marrow |
bowel movement | |
| BMD | bone mineral density |
| BMI | body mass index |
| BMS | bare metal stent |
| BNP | B-type natriuretic peptide |
| BOOP | bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia |
| BP | blood pressure |
| BPH | benign prostatic hypertrophy |
| BRBPR | bright red blood per rectum |
| BS | breath sounds |
| BT | bleeding time |
| BUN | blood urea nitrogen |
| bx | biopsy |
| BYCE | buffered charcoal yeast extract |
| C ′ | complement |
| c/s | consult |
| c/w | compared with |
consistent with | |
| CABG | coronary artery bypass grafting |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CAH | congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
| CALLA | common ALL antigen |
| CAPD | chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis |
| CBC | complete blood count |
| CBD | common bile duct |
| CCB | calcium channel blocker |
| CCl 4 | carbon tetrachloride |
| CCP | cyclic citrullinated peptide |
| CCS | Canadian Cardiovascular Society |
| CCY | cholecystectomy |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
carotid endarterectomy | |
| ceph. | cephalosporin |
| CF | cystic fibrosis |
| Cftx | ceftriaxone |
| CFU | colony forming units |
| CHB | complete heart block |
| CHD | congenital heart disease |
| CHF | congestive heart failure |
| CI | cardiac index |
| CIAKI | contrast-induced AKI |
| CIDP | chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy |
| CJD | Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease |
| CK | creatine kinase |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CLL | chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| CMC | carpometacarpal (joint) |
| CML | chronic myelogenous leukemia |
| CMML | chronic myelomonocytic leukemia |
| CMP | cardiomyopathy |
| CMV | cytomegalovirus |
| CN | cranial nerve |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
cardiac output | |
| COP | cryptogenic organizing PNA |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulm dis. |
| COX | cyclo-oxygenase |
| CP | chest pain |
| CPAP | continuous positive airway pressure |
| CPP | cerebral perfusion pressure |
| CPPD | calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate |
| Cr | creatinine |
| CrAg | cryptococcal antigen |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| CrCl | creatinine clearance |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CRT | cardiac resynchronization therapy |
| CsA | cyclosporine A |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| CSM | carotid sinus massage |
| CT | computed tomogram |
| CTA | CT angiogram |
| CTD | connective tissue disease |
| CV | cardiovascular |
| CVA | cerebrovascular accident |
| CVD | cerebrovascular disease |
collagen vascular disease | |
| CVID | common variable immunodefic. |
| CVP | central venous pressure |
| CVVH | continuous veno-venous hemofiltration |
| CW | chest wall |
| cx | culture |
| CXR | chest radiograph |
| CYC | cyclophosphamide |
| d | day |
| D | death |
| ∆ MS | change in mental status |
| DA | dopamine |
| DAD | diffuse alveolar damage |
| DAH | diffuse alveolar hemorrhage |
| DAT | direct antiglobulin test |
| DBP | diastolic blood pressure |
| d/c | discharge |
discontinue | |
| DCIS | ductal carcinoma |
| DCMP | dilated cardiomyopathy |
| Ddx | differential diagnosis |
| DES | drug-eluting stent |
| DFA | direct fluorescent antigen detection |
| DI | diabetes insipidus |

