Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (91 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
4.76Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
•
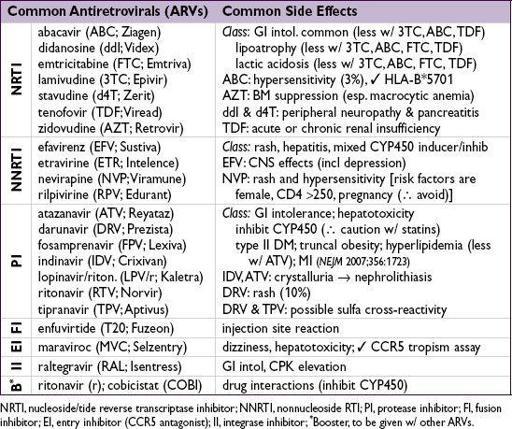
ARVs should be given in consultation w/ HIV specialist
(
JAMA
2010;304:321) • Counseling re: strict adherence to ARVs is essential; genotype prior to ART-initiation •
All
HIVPts should be considered for ARVs; strongly recommended initiate Rx for:
AIDS-defining illness
, pregnancy, HIV-assoc. nephropathy, HCV/HBV co-infxn
CD4 £500/mm
3
(
NEJM
2009;360:1815 & 2011;365:193; DHHS 2012;
http://aidsinfo.nih.gov
)
Consider if CD4 >500; depends on Rx toxicity, adherence, potential for transmission
• Regimens for treatment-naïve Pts (DHHS guidelines Mar 29, 2012;
http://aidsinfo.nih.gov
)
[NNRTI + 2 NRTI]
or
[PI (± low-dose ritonavir) + 2 NRTI] or [II + 2 NRTI]
• Initiation of ARVs may
transiently worsen
existing OIs for several wks due to immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS)
Approach to previously established HIVPt
•
H&P
(mucocutaneous, neurocognitive, OIs, malignancies, STDs); meds •
Review ARVs
(past and current); if any must be interrupted,
stop all
to ↓ risk of resistance • Failing regimen = unable to achieve undetectable viral load, ↑ viral load, ↓ CD4 count or clinical deterioration (with detectable viral load consider genotypic or phenotypic assay)
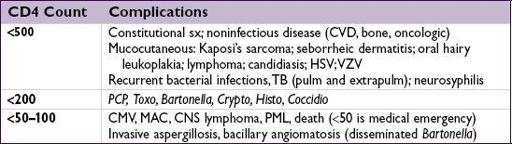
COMPLICATIONS OF HIV/AIDS
Fever
• Etiologies (
Infect Dis Clin North Am
2007;21:1013)
infxn (82–90%)
:
MAC
,
TB
,
CMV
,
early PCP
,
Histo
,
Crypto
,
Coccidio
,
Toxo
, endocarditis
noninfectious
:
lymphoma
,
drug reaction.
Non 1° HIV itself rarely (<5%) cause of fever.
• Workup: guided by CD4 count, s/s, epi, & exposures
CBC, chem, LFTs, BCx, CXR, UA, mycobact. & fungal cx, ✓ meds, ? ✓ chest & abd CT
CD4 <100–200 → serum crypto Ag, LP, urinary
Histo
Ag, CMV PCR or antigenemia
pulmonary s/s → CXR; ABG; sputum for bacterial cx, PCP, AFB; bronchoscopy
diarrhea → stool for fecal leuks, culture, O&P, AFB; endoscopy
abnormal LFTs → abd CT, liver bx (for pathology and culture)
cytopenias → BM bx (include aspirate for culture)
Cutaneous
• Seborrheic dermatitis; eosinophilic folliculitis;
warts
(HPV); HSV & VZV; MRSA skin & soft tissue infxns; scabies; candidiasis; eczema; prurigo nodularis; psoriasis; drug eruptions • Dermatophyte infx: prox subungual onychomycosis (at nail bed); pathognomonic for HIV
•
Molluscum contagiosum
(poxvirus): 2–5 mm pearly papules w/ central umbilication •
Kaposi’s sarcoma
(KSHV or HHV8): red-purple nonblanching nodular lesions •
Bacillary angiomatosis
(disseminated
Bartonella
): friable violaceous vascular papules
Ophthalmologic
•
CMV retinitis
(CD4 usu <50); Rx: gan-or valganciclovir, ganciclovir implant or cidofovir • HZV, VZV, syphilis (at any CD4 count) or
Toxo
: CD4 usually <100
Oral
•
Aphthous ulcers; KS; thrush
(oral candidiasis): curd-like patches typically w/ burning or pain;
oral hairy leukoplakia
: painless proliferation of papillae w/ adherent white coating usually on lateral tongue, caused by EBV but not precancerous
Endocrine/metabolic
•
Hypogonadism
; adrenal insufficiency (CMV, MAC, TB, HIV or med-related); wasting osteopenia/porosis (at all CD4 counts); fragility fractures •
Lipodystrophy
: central obesity, peripheral lipoatrophy, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia • Lactic acidosis: N/V, abd pain; ? mitochondrial toxicity of AZT, d4T, ddI, other NRTI
Cardiac
(
JACC
2013;61:511)
• Dilated CMP (10–20%); PHT; CVD (
NEJM
2003;348:702); pericarditis/effusion, VTE
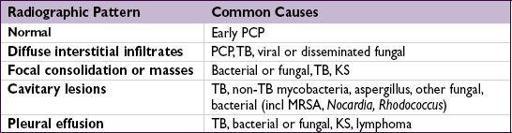
Pulmonary
•
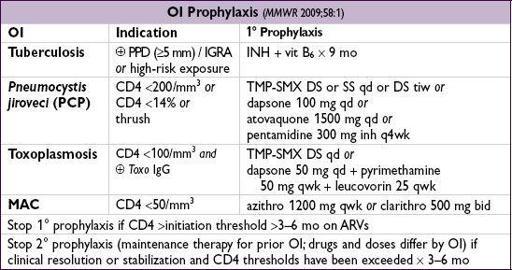
Pneumocystis jiroveci
(PCP) pneumonia (CD4 <200)
(
NEJM
1990;323:1444)
constitutional sx, fever, night sweats, dyspnea on exertion, nonproductive cough
CXR w/ interstitial pattern, ↓ P
a
O
2
, ↑ A-a ∇, ↑ LDH,PCP sputum stain,
β-glucan
Rx if P
a
O
2
>70:
TMP-SMX
15–20 mg of TMP/kg divided tid, avg dose = DS 2 tabs PO tid
Rx if P
a
O
2
<70 or A-a gradient >35:
prednisone
before abx (40 mg PO bid; ↓ after 5 d) Alternative Rx if sulfa-allergy or renal insufficiency
Other books
Naked, on the Edge by Elizabeth Massie
A Demon Does It Better by Linda Wisdom
Caging the Wolf (Snowdonia Wolves) by Sofia Grey
Love's Magic by Traci E. Hall
South by Southeast by Blair Underwood
The Kremlin Phoenix by Renneberg, Stephen
Whitechapel: The Final Stand of Sherlock Holmes by Bernard J. Schaffer
Vampire Girl 2: Midnight Star by Karpov Kinrade
Dragon Gold by Kate Forsyth
Storm Surge by Rhoades, J.D.