Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed (131 page)
Read Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed Online
Authors: Noel Morimoto

. Web Server (IIS)
. Windows Deployment Services
. Windows Server Update Services
Within each role, a number of role services make up the role. The role services allow the
administrator to load only the specific services that are needed for a particular server
instance. In some cases, such as for the DHCP Server or DNS Server roles, the role and the
role service are one and the same. In other cases, the role will contain multiple services
that can be chosen. For example, the File Services role contains the following role services:
. File Server
. Distributed File System
. DFS Namespaces
. DFS Replication
. File Server Resource Manager
. Services for Network File System
. Windows Search Service
ptg
. Windows Server 2003 File Services
. Indexing Service
. BranchCache for Network Files
Adding a role and role services installs the binaries (that is, the code) that allow the
services to function. There is typically additional installation and configuration that
needs to be done after the roles are installed, such as for the Active Directory Domain
Services role.
Only loading the roles required for each server and, thus, only the appropriate binaries,
reduces the complexity, the attack surface, and the patch surface of the server. This results
in a more secure, less complex, and more efficient server—in short, resulting in fewer
headaches for the administrator who has to manage the server!
NOTE
The patch surface of a server is the code in the server that requires patches to be
applied. This can increase the need for patches and, thus, downtime, as well as
administrative overhead. If code is installed on a server, it needs to be patched even if
that particular code is not in use on a server. This is analogous to the attack surface
of the server.
A good example of this is the Web Server role. If a domain controller has the Web
Server role added, any patches that apply to the code base of the Web Server role
need to be installed. This is true even if the services are disabled or just not used.
Thus, the patch surface of the domain controller has been increased.
Managing Windows Server 2008 R2 Roles and Features
645
However, if the domain controller only has the roles (and, thus, the code) for the roles it
needs, the patches for other roles will not need to be applied to the domain controller.
Thus, the patch surface of the domain controller has been reduced.
Features in Windows Server 2008 R2
In addition to the roles and role services, Windows Server 2008 R2 also has the ability to
add features. Features are typically supporting components that are independent of the
server role, but might provide support for a role or role service. For example, a domain
controller is configured with the Active Directory Domain Services role. However, in some
organizations, the domain controller will also serve as a Windows Internet Naming Service
(WINS) server. WINS is a feature in Windows Server 2008 R2.
There are many different features in Windows Server 2008 R2, including the following:
. NET Framework 3.5.1 Features
. Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)
. BitLocker Drive Encryption
ptg
. BranchCache
. Connection Manager Administration Kit
. Desktop Experience
. DirectAccess Management Console
. Failover Clustering
. Group Policy Management
. Ink and Handwriting Services
. Internet Printing Client
. Internet Storage Name Server
. LPR Port Monitor
. Message Queuing
. Multipath I/O
20
. Network Load Balancing
. Peer Name Resolution Protocol
. Quality Windows Audio Video Experience
. Remote Assistance
646
CHAPTER 20
Windows Server 2008 R2 Management and Maintenance Practices
. Remote Differential Compression
. Remote Server Administration Tools
. RPC over HTTP Proxy
. Simple TCP/IP Services
. SMTP Server
. SNMP Services
. Storage Manager for SANs
. Subsystem for UNIX-Based Applications
. Telnet Client
. Telnet Server
. TFTP Client
. Windows Biometric Framework
. Windows Internal Database
. Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE)
ptg
. Windows Process Activation Service
. Windows Server Backup Features
. Windows Server Migration Tools
. Windows System Resource Manager
. Windows TIFF IFilter
. WinRM IIS Extension
. WINS Server
. Wireless LAN Service
. XPS Viewer
The features are installed with the Server Manager Add Features Wizard. To add a feature,
execute the following steps:
1. In the Initial Configuration Tasks Wizard or Server Manager, click the Add Features
link.
2. Select a feature or set of features.
3. Click Next to accept the selected features.
4. Click Install to install the selected features.
Server Manager
647
5. Click Close to exit the wizard.
6. Close the Server Manager window.
The feature will now be installed.
NOTE
Unlike previous versions of Windows, all the binaries for Windows Server 2008,
Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008 R2 are installed in the
C:\WINDOWS\WINSXS directory. All the components—that is, roles and features—are
stored in the WINSXS directory. This eliminates the need to use the original DVD instal-
lation media when adding roles or features.
However, the trade-off is that the WINSXS folder is more than 5GB, as it contains the
entirety of the operating system. In addition, it will grow over time as updates and ser-
vice packs are installed. For a physical machine, the additional disk space is not much
of an issue. However, for virtual machines, it means that there is an additional 5GB of
additional disk space that has to be allocated for each and every Windows server.
ptg
Server Manager is a new tool that provides a central location for managing all the roles
and features that Windows Server 2008 R2 provides. This console gives an administrator
access to the complete operational status, monitoring tools, and configuration tools for
the entire server in a convenient single console.
Server Manager enables the administrator to do the following:
. Add and remove roles and features from the server
. Monitor and manage the server
. Administer the roles and features on the server
In effect, Server Manager is a one-stop shop for all the administrator management and moni-
toring needs. The features of Server Manager are available via the Server Manager console.
Selecting the server name in the folder tree will show the Server Manager main window in
20
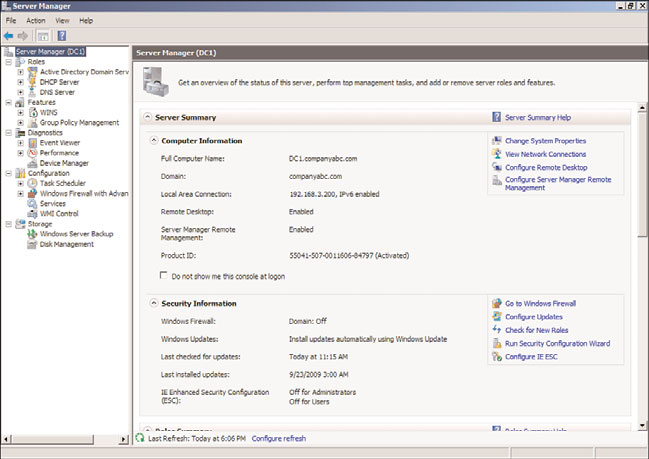
the Details pane. This consists of several section windows. The Server Summary window
(shown in Figure 20.2) shows computer information such as the computer name, network-
ing information, and if Remote Desktop is enabled. It also shows security information,
such as if Windows Firewall is enabled and the Windows Updates status. The window also
has active links that enable the administrator to launch wizards to change the configura-
tion or get help.
648
CHAPTER 20
Windows Server 2008 R2 Management and Maintenance Practices
FIGURE 20.2
Server Manager Server Summary window.
ptg
Server Manager launches automatically when the Initial Configuration Wizard is closed
and each time a user logs on to the server.
The next sections discuss the components and features of Server Manager.
Server Manager Roles and Features
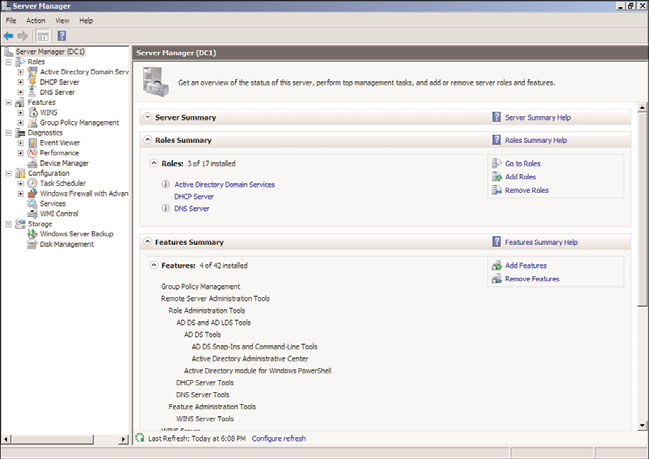
The Roles Summary and Feature Summary windows, shown in Figure 20.3, show which
roles and features are installed. In the Roles Summary window, the status of the roles can
be seen as well. As can be seen in the figure, the Active Directory Domain Services role
and the DNS Server role have information icons, indicating that there are informational
messages. If there were problems with the roles, these would change to warning or critical
icons. The summary windows also include links to add or remove roles and features, as
well as to access context-sensitive help.
Server Manager Roles Page
The Server Manager console has a folder tree dedicated to the roles of the server. Selecting
the Roles folder in the console tree shows a summary of the roles installed on the server,
as well as a summary page for each of the roles. The summary page for each role shows
the role status, such as the status of the system services and the events for the role.
However, selecting the folder for a specific role shows the Server Manager role-specific
page for that role. The role-specific pages are dedicated to the role and contain operational
information about the role. The following sections discuss the sections included in the
role-specific page.
Server Manager
649
FIGURE 20.3
Server Manager Roles and Features Summary windows.
ptg
Events Section
There is a problem with going to the full Event Viewer and seeing all the events for all
roles, services, and the operating system. There is usually so much information that it
ends up overloading the administrator, making it difficult to see real problems. The Events
section in the role-specific page addresses this by only presenting the role-specific events.
From the Events section, the administrator can see a summary of the events that pertain
to the role, review the details of the events, and filter the events as needed. The default
filter shows only events in the last 24 hours, but this can be adjusted via the Filter
Events control.
The full Event Viewer can also be launched from this section.
System Services Section
The System Services section lists the services that the role depends on and their status. It
also describes each service and includes control links to Stop, Start, Restart, and configure
Preferences.
20
The Preferences control enables the administrator to adjust the monitored services. For
example, if an administrator determines that the Windows Time service is essential to the
role of the Active Directory Domain Services server (that is, the domain controller), that
service can be monitored by checking it in the Preferences section.
Role Services Section
The Role Services section shows which of the role services that are available for the role
have been installed. There are also links to add or remove the role services.
650
CHAPTER 20
Windows Server 2008 R2 Management and Maintenance Practices
A nice feature of this section is that when a role service is selected, a brief description is
shown of what the role service is for. This includes a link to get more information on the
role service.
Advanced Tools Section
In the case of some roles, there will be an Advanced Tools section with a list of tools that
help support the role. This includes both command-line tools and MMC consoles with
brief explanations of their functions.
In the case of the Active Directory Domain Services role (which, by far, has the most
advanced tools of any role), there are 21 different tools in the section, including the
following:
